VisualDL is a deep learning visualization tool that can help design deep learning jobs. It includes features such as scalar, parameter distribution, model structure and image visualization. Currently it is being developed at a high pace. New features will be continuously added.
At present, most DNN frameworks use Python as their primary language. VisualDL supports Python by nature. Users can get plentiful visualization results by simply add a few lines of Python code into their model before training.
Besides Python SDK, VisualDL was writen in C++ on the low level. It also provides C++ SDK that can be integrated into other platforms.
VisualDL now provides 4 components:
- graph
- scalar
- image
- histogram
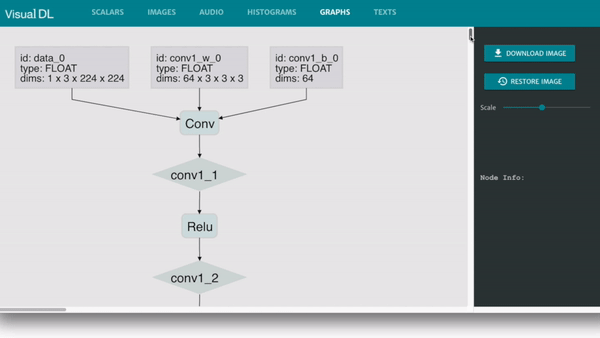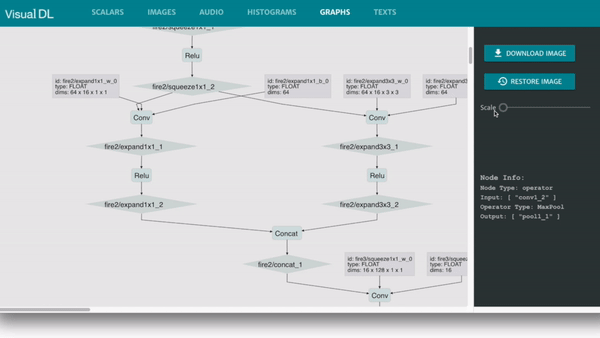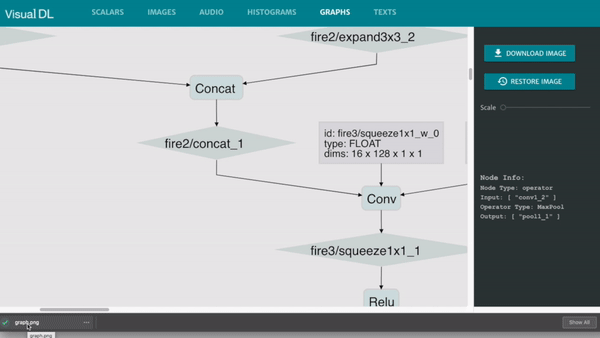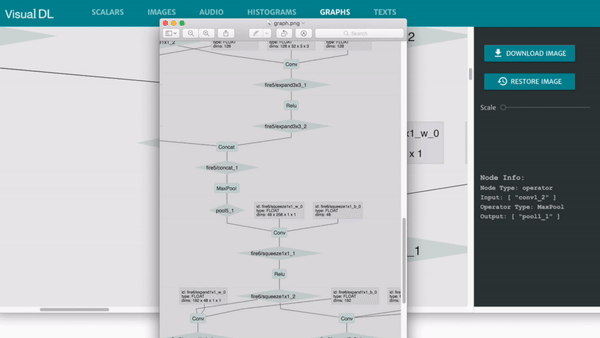
Graph is compatible with ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange), Cooperated with Python SDK, VisualDL can be compatible with most major DNN frameworks, including PaddlePaddle, PyTorch and MXNet.
Scalar can be used to show the trends of error during training.
Image can be used to visualize any tensor or intermediate generated image.
Histogram can be used to visualize parameter distribution and trends for any tensor.
To give the VisualDL a quick test, please use the following commands.
# Install the VisualDL. Preferably under a virtual environment or anaconda.
pip install --upgrade visualdl
# run a demo, vdl_create_scratch_log will create logs for testing.
vdl_create_scratch_log
visualdl --logdir=scratch_log --port=8080
# visit http://127.0.0.1:8080
If you run into issues in above steps, it could be error caused by environmental issues by different python or pip versions. Following installation methods might fix the issues.
Virtualenv creates isolated Python environment that prevents interfering by other Python programs on the same machine and make sure Python and pip are located properly.
On macOS, install pip and virtualenv by:
sudo easy_install pip
pip install --upgrade virtualenv
On Linux, install pip and virtualenv by:
sudo apt-get install python3-pip python3-dev python-virtualenv
Then create a Virtualenv environment by one of following command:
virtualenv ~/vdl # for Python2.7
virtualenv -p python3 ~/vdl for Python 3.x
~/vdl will be your Virtualenv directory, you may choose to install anywhere.
Activate your Virtualenv environment by:
source ~/vdl/bin/activate
Now you should be able to install VisualDL and run our demo:
pip install --upgrade visualdl
# run a demo, vdl_create_scratch_log will create logs for testing.
vdl_create_scratch_log
visualDL --logdir=scratch_log --port=8080
# visit http://127.0.0.1:8080
If you still have issues installing VisualDL from Virtualenv, try following installation method.
Anaconda is a python distribution, with installation and package management tools. Also it is an environment manager, which provides the facility to create different python environments, each with their own settings.
Follow the instructions on the Anaconda download site to download and install Anaconda. Download Python 3.6 version command-Line installer.
Create a conda environment named vdl or anything you want by:
conda create -n vdl pip python=2.7 # or python=3.3, etc.
Activate the conda environment by:
source activate vdl
Now you should be able to install VisualDL and run our demo:
pip install --upgrade visualdl
# run a demo, vdl_create_scratch_log will create logs for testing.
vdl_create_scratch_log
visualDL --logdir=scratch_log --port=8080
# visit http://127.0.0.1:8080
If you still have issues installing VisualDL, try installing from sources as in following section.
#Preferably under a virtualenv or anaconda.
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/VisualDL.git
cd VisualDL
python setup.py bdist_wheel
pip install --upgrade dist/visualdl-*.whl
If there are still issues regarding the pip install, you can still start Visual DL by starting the dev server
here
VisualDL provides both Python SDK and C++ SDK in order to fit more use cases.
VisualDL now supports both Python 2 and Python 3. Below is an example of creating a simple Scalar component and inserting data from different timestamps:
import random
from visualdl import LogWriter
logdir = "./tmp"
logger = LogWriter(logdir, sync_cycle=10000)
# mark the components with 'train' label.
with logger.mode("train"):
# create a scalar component called 'scalars/scalar0'
scalar0 = logger.scalar("scalars/scalar0")
# add some records during DL model running.
for step in range(100):
scalar0.add_record(step, random.random())Here is the C++ SDK identical to the Python SDK example above:
#include <cstdlib>
#include <string>
#include "visualdl/logic/sdk.h"
namespace vs = visualdl;
namespace cp = visualdl::components;
int main() {
const std::string dir = "./tmp";
vs::LogWriter logger(dir, 10000);
logger.SetMode("train");
auto tablet = logger.AddTablet("scalars/scalar0");
cp::Scalar<float> scalar0(tablet);
for (int step = 0; step < 1000; step++) {
float v = (float)std::rand() / RAND_MAX;
scalar0.AddRecord(step, v);
}
return 0;
}After some logs have been generated during training, users can launch Visual DL application to see real-time data visualization by:
visualDL --logdir <some log dir>
visualDL also supports following optional parameters:
--hostset IP--portset port--model_pbspecify ONNX format for model file to view graph
VisualDL is initially created by PaddlePaddle and ECharts. We welcome everyone to use, comment and contribute to Visual DL :)