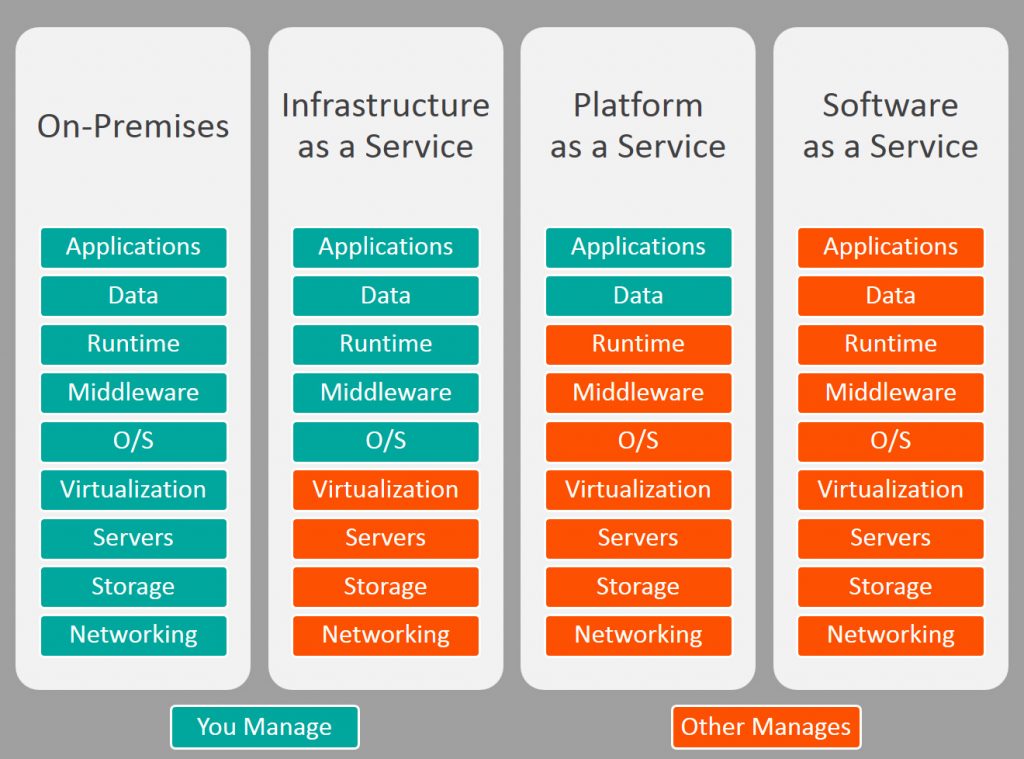
If your brain starts to explode while thinking about the whole lot of AWS tools, here's some help
We'll try to shed some light into all the tools by classifying them into some categories (like IaaS, hybrid IaaS/PaaS, PaaS & Configuration Management) and also trying to separate them from each other.
Just "usual" VMs
EC2 instances use Amazon Machine Images (AMI) as there base images.
These images could be found inside the EC2 instance creation wizard:
or with the help of the AWS CLI and the command aws ec2 describe-images (see the docs).
Specific images - like Ubuntu 18.04 - could be found through the AWS Marketplace or specific AMI finder pages like the ubuntu Amazon EC2 AMI Locator.
There are multiple AMI instance types (see https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/instance-store-vs-ebs/) - especially
- instance store : is directly attached and should be used for temporary data only, instance store volumes is not persistent through instance stops
- EBS: In Amazon Elastic Block Store data will retain longer - EBS volumes preserve their data through instance stops and terminations, backup is easy with EBS snapshot
VPS (Virtual Private Server) like DigitalOcean / 1&1 (see https://www.heise.de/select/ix/2017/5/1492861894740647)
Subset of EC2, much simpler (512 MiB Lightsail Instance == t2.nano EC2, see https://stackoverflow.com/a/40932906/4964553)
Databases
Based on Docker-Containers - could be a good choice for mature projects & mid-term
Like Beanstalk, but with much more control for scaling, size/number of nodes (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/29586384/4964553), auto-scaling etc.
Could use EC2 Container Registry (ECR) / AWS CLI
CLI example:
aws ecs describe-clustersLike ECS, but Kubernetes based (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/eks/latest/userguide/what-is-eks.html)
EKS manages the Kubernetes management infrastructure for you - distributed to different AWS availability zones (https://www.heise.de/developer/meldung/Amazon-EKS-Elastic-Container-Service-fuer-Kubernetes-jetzt-verfuegbar-4069657.html)
CloudWatch and CloudTrail for logging/monitoring AWS workloads
Amazon EKS passed the Cloud Native Computing Foundation conformance test to become a certified hosted platform, which means that all the plugins and extensions that work with upstream Kubernetes will work as is in EKS (https://thenewstack.io/how-amazon-eks-brings-best-of-kubernetes-and-amazon-web-services/)
PaaS! More for project kickoffs
AWS Elastic Beanstalk == Pivotal CloudFoundry == Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (see https://www.dev-insider.de/grundlagen-und-zweck-von-aws-elastic-beanstalk-a-654399/)
Blue prints for usual apps
based on EC2, Route53 etc. --> but compared to CloudFoundry et.al. you can access EC2 instances beneath via SSH
manages all details of capacity provisioning, loadbalancing, autoscaling and monitoring
GUI, CLI, IDE plugins
Could use EC2 Container Registry (ECR) / AWS CLI
Dockerrun.aws.json:
{
"AWSEBDockerrunVersion": "1",
"Image": {
"Name": "janedoe/image",
"Update": "true"
},
"Ports": [
{
"ContainerPort": "1234"
}
],
"Volumes": [
{
"HostDirectory": "/var/app/mydb",
"ContainerDirectory": "/etc/mysql"
}
],
"Logging": "/var/log/nginx"
}CLI example
eb runPaaS for Containers
Managed Service, NO server access + NO responsibility for updating, patching etc., intended not for 24/7 running services
removes any need of Docker host management (https://www.reddit.com/r/aws/comments/7mjs6x/elastic_beanstalk_vs_ecs_fargate/)
relatively expensive compared to ECS (with Fargate is .25 vCPU and 512 MB memory. The 30 day price for 1 container would be $13.68. A t2.micro offers 1 vCPU and 1GB of ram for $8.35.)
Part of Docker EE
onpremise download "Docker Universal Control Plane (UCP)"
In the Cloud use cloud.docker.com
Connect all Nodes running Docker, Cloud or on-Premise in one Browser-Dashboard (also AWS resources)
Ansible can be used to define, deploy, and manage a wide variety of AWS services (see https://www.ansible.com/integrations/cloud/amazon-web-services)
Out of the box, Ansible has nearly 100 modules supporting AWS capabilities, including:
AMI Management Autoscaling Groups CloudFormation CloudTrail CloudWatch DynamoDB ElastiCache Elastic Block Store (EBS) Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2) Elastic IPs (EIP) Elastic Load Balancers (ELB) Identity Access Manager (IAM) Kinesis Lambda Relational Database Service Route53 Security Groups Security Token Service Simple Storage Service (S3) Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Ansible AWS Guide: https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/scenario_guides/guide_aws.html
Ansible modules provide an easier to use interface than CloudFormation in many examples, without defining a complex JSON document. This is recommended for most users.
example
# demo_setup.yml
- hosts: localhost
connection: local
gather_facts: False
tasks:
- name: Provision a set of instances
ec2:
key_name: my_key
aws_access_key: "{{ec2_access_key}}"
aws_secret_key: "{{ec2_secret_key}}"
group: test
instance_type: t2.micro
image: "{{ ami_id }}"
wait: true
exact_count: 5
count_tag:
Name: Demo
instance_tags:
Name: Demo
register: ec2AWS managed configuration management service, based on Chef (https://www.dev-insider.de/aws-opsworks-stacks-und-opsworks-for-chef-automate-a-663363/)
2 varieties (https://www.dev-insider.de/aws-opsworks-stacks-und-opsworks-for-chef-automate-a-663363/):
- AWS OpsWorks for Chef Automate (costs (Enterprise Chef), as like AWS OpsWorks Puppet Enterprise (see https://www.dev-insider.de/chef-server-fuers-konfigurationsmanagement-aufsetzen-a-775500/))
- AWS OpsWorks Stacks
alternative to Jenkins / GitLab (see https://aws.amazon.com/codepipeline/) - but bound to AWS
AMI baseconfig --> bootstrapping / boot up maybe needs a lot of time (Patches usw.) --> user defined AMIs could be a good way
VPCs, Security-Groups, Network-ACLs, Router, LBs ...
https://aws.amazon.com/certification/certified-solutions-architect-associate/
https://dev.to/totalcloudio/ecs-vs-eks-vs-fargate-the-good-the-bad-the-ugly-58he
https://grahamlyons.com/article/everything-you-need-to-know-about-networking-on-aws
https://aws.amazon.com/solutions/ (AWS Solutions are technical reference implementations built and vetted by AWS Architects and AWS Partners, designed to help customers solve the common problems faced by their peers around the world. AWS Solutions are built to be operationally effective, performant, reliable, secure, cost effective, and be Well-Architected.)