- Author: Lakshmanan Meiyappan
- Email: lmeiya2@uic.edu
This project uses AWS Lambda to implement gRPC based request using Protobuf, built with Scala and sbt.
- Scala 2.13.4
- SBT 1.5.2
- slf4j-api 2.0.0
- typesafe config 1.4.1
- aws-lambda-java-core 1.2.1
- aws-lambda-java-events 3.10.0
- scalapb-runtime-grpc
- AWS Lambda is a Serverless Application Model (SaaS) that allows you to run serverless code on AWS.
- gRPC is a framework for building high-performance, distributed, and fault-tolerant applications.
- Protobuf is a language for encoding and decoding data structures.
- Scala is a general-purpose programming language that is class-based, object-oriented, and strong-typed.
gRPC requires a server and a client. The server is the one that receives the request and sends the response. So, we need a gRPC server to be active. But implementing in AWS Lambda is not possible. gRPC Server implementation is not possible for various reasons -
- It defeats the purpose of AWS Lambda of serverless computing
- We do not control the ports in AWS Lambda
- AWS Lambda is billed based on the number of requests, execution time and memory consumed. So, even if we find a workaround to implement gRPC server in AWS Lambda, it will result in high execution costs.
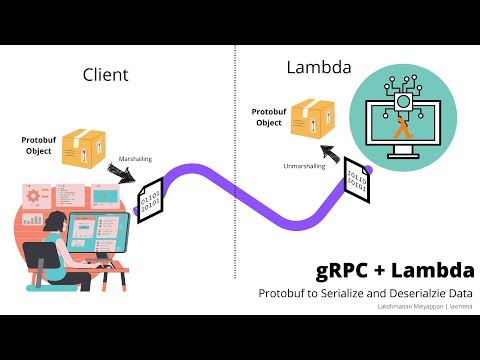
So, we need to find a workaround to make the language independent distributed computing work. To accomplish that, we make use of Protobuf - to get language independent representation of data structures.
We then transfer this Protobuf objects to the AWS Lambda function through HTTP as encoded data. In the Lambda, we receive the encoded data and decode it to the Protobuf object. We then make use of the data to compute the result and return the result back to the client in similar manner.
Here is the higher level workflow of the project:
- Protobuf object from client is encoded, and sent in the body of the HTTP request
- Lambda function receives the encoded data and decodes it to the Protobuf object
- Lambda function uses the Protobuf object to compute the result
- Lambda function encodes the result and sends it back to the client
- Client receives the encoded result and decodes it to the Protobuf object
- Client uses the Protobuf object to get the result
Note: All Lambda Functions are written in Python.
Lambda functions source code is in the LambdaCode directory.
Please refer this article, on how to bundle the Lambda functions with dependencies, as AWS Lambda does not have gRPC packages available by default.
Find the Lambda Functions here:
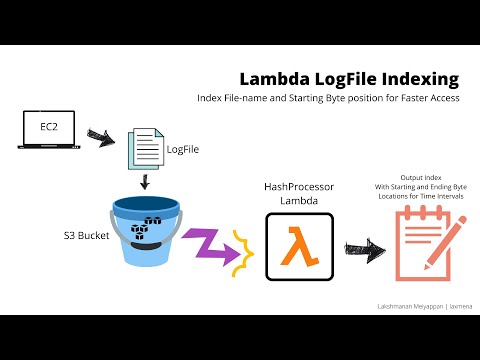
LogProcessor program in EC2 machine generates Log files, and stores them in S3 bucket. We have a second Lambda that is triggered when there is a new file added to the S3 bucket. It reads the file and indexes the log file. It creates key-value pairs of the TimeStamp(HH:MM:SS) and the value as (LogFileName, startByte, endByte), and stores them in a pickle file.
This significantly speeds up the lookup time for the future requests
Steps:
- Client triggers API Gateway to send the request to the Lambda function.
- Lambda function receives the request and decodes the Protobuf object.
- Lambda function uses the Protobuf object to compute the result.
- Lambda function looks up the Date TimeStamp in the pickle file and gets the LogFileName, startByte and endByte.
- If the Date TimeStamp is found in the pickle file, it reads the LogFile from S3 and returns the result - True (as protobuf object).
- If the Date TimeStamp is not found in the pickle file, it returns False (as protobuf object).
Please find the Documentation of this Project hosted in Github pages here: Documentation
Demo and Walk-through Video:
gRPC Protobuf + AWS Lambda for LogQuery Processing | Part 1
How Lambda Functions work | Part 2
git clone https://github.com/laxmena/AWS-Lambda-with-gRPC.git
cd AWS-Lambda-with-gRPC-Restsbt clean compile
sbt test
sbt "run YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS window"- First argument is the Date in the format YYYY-MM-DD
- Second argument is the time in the format HH:MM:SS
- Third argument is the window, integer value in seconds. (Which is just placeholder for this gRPC implementation.)
This is a sample output after running the following command:
sbt "run 2021-11-05 22:19:23 1"Output:
[info] running com.laxmena.LambdaClient 2021-11-05 22:19:23 1
17:22:04.223 [run-main-0] INFO java.lang.Class - LambdaClient started
17:22:04.582 [run-main-0] INFO java.lang.Class - date: 2021-11-05, time: 22:19:23, window: 1
17:22:04.618 [run-main-0] INFO java.lang.Class - Loaded Config
17:22:04.621 [run-main-0] INFO java.lang.Class - Loaded Grpc Config
17:22:04.625 [run-main-0] INFO java.lang.Class - Starting AWS Protobuf Client
17:22:09.955 [run-main-0] INFO java.lang.Class - req: HttpResponse([B@50166a01,200,TreeMap(Apigw-Requestid -> Vector(IWg5OiP9oAMEMWA=), Connection -> Vector(keep-alive), Content-Length -> Vector(2), Content-Type -> Vector(text/plai
n; charset=utf-8), Date -> Vector(Fri, 05 Nov 2021 22:22:25 GMT), Status -> Vector(HTTP/1.1 200 OK)))
17:22:09.976 [run-main-0] INFO java.lang.Class - LogQueryResponse: LogQueryResponse(true,UnknownFieldSet(Map()))
17:22:09.978 [run-main-0] INFO java.lang.Class - LogQueryResponse is available
- https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/api-management/understanding-grpc-openapi-and-rest-and-when-to-use-them
- https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/rest-is-the-new-soap-97ff6c09896d/
- https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/opensource/the-versatility-of-grpc-an-open-source-high-performance-rpc-framework/
- https://youtu.be/MgQDeKwTnDQ
- https://www.youtube.com/c/amazonwebservices/videos
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/47764448/how-to-test-grpc-apis
- https://www.scala-sbt.org/1.x/docs/Installing-sbt-on-Linux.html
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/python-package.html
- https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-install-python-packages-for-aws-lambda-layer-74e193c76a91