Resources:
Links:
http://sourcemaking.com/design_patterns
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/design_pattern/index.htm
Book: Head First Design Pattern
Defines a one-to-many dependency between objects so that when one
object changes state, all its dependents are notified
and updated automaticaly.
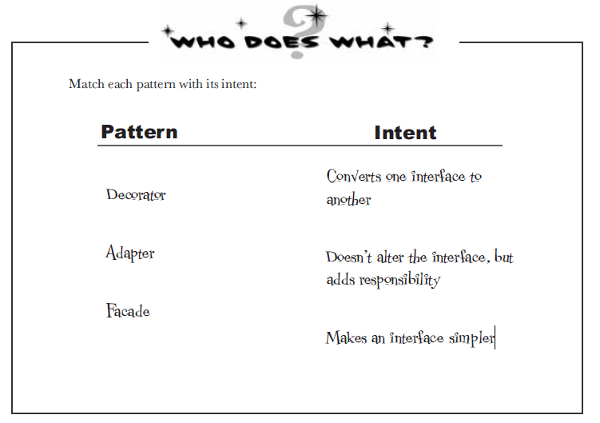
Attaches additional responsibilities to an
object dynamically. Decorators provide a flexible alternative to
subclassing for extending functionality.
- Provide an interface for creating families of related or dependent objects
without specifying their concrete classes. - A hierarchy that encapsulates: many possible "platforms", and
the construction of a suite of "products". - The new operator considered harmful.
- Define an interface for creating an object, but let subclasses
decide which class to instantiate. Factory Method lets a class defer
instantiation to subclasses. - Defining a "virtual" constructor.
- The new operator considered harmful.
- Ensure a class has only one instance,
and provide a global point of access to it. - Encapsulated "just-in-time initialization"
or "initialization on first use".
- Encapsulate a request as an object, thereby letting you
parameterize clients with different requests, queue or log
requests, and support undoable operations. - Promote "invocation of a method on an object" to full object status
- An object-oriented callback
- Convert the interface of a class into another interface clients expect.
Adapter lets classes work together that couldn't otherwise because of
incompatible interfaces. - Wrap an existing class with a new interface.
- Impedance match an old component to a new system
- Provide a unified interface to a set of interfaces in a subsystem. Facade defines a higher-level interface that makes the subsystem easier to use.
- Wrap a complicated subsystem with a simpler interface.
In Template pattern, an abstract class exposes defined way(s)/template(s)
to execute its methods. Its subclasses can override the method implementation
as per need but the invocation is to be in the same way as defined by an
abstract class.
Base class declares algorithm 'placeholders', and derived classes
implement the placeholders.
This pattern comes under behavior pattern category.
- Provide a way to access the elements of an aggregate object sequentially without exposing
its underlying representation.
- Compose objects into tree structures to represent whole-part hierarchies. Composite lets clients treat
individual objects and compositions of objects uniformly. - Recursive composition
- "Directories contain entries, each of which could be a directory."
1-to-many "has a" up the "is a" hierarchy
- Allow an object to alter its behavior when its internal state
- changes. The object will appear to change its class.
- An object-oriented state machine
wrapper + polymorphic wrappee + collaboration
- Define the skeleton of an algorithm in an operation, deferring some steps to
client subclasses. Template Method lets subclasses redefine certain steps of an
algorithm without changing the algorithm's structure. - Base class declares algorithm 'placeholders', and derived classes implement the
placeholders.
- Provide a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it.
- Use an extra level of indirection to support distributed, controlled, or intelligent access.
- Add a wrapper and delegation to protect the real component from undue complexity.