- Big O Notation
- Array
- Linked List
- Prefix Sum
- Frequency array
- Insertion Sort Algorithm
- Bubble Sort Algorithm
- Binary Search
- Selection Sort
- dynamic Programming
- Binary Search Tree
- Heap Data Structure
- Hash Table Data Structure
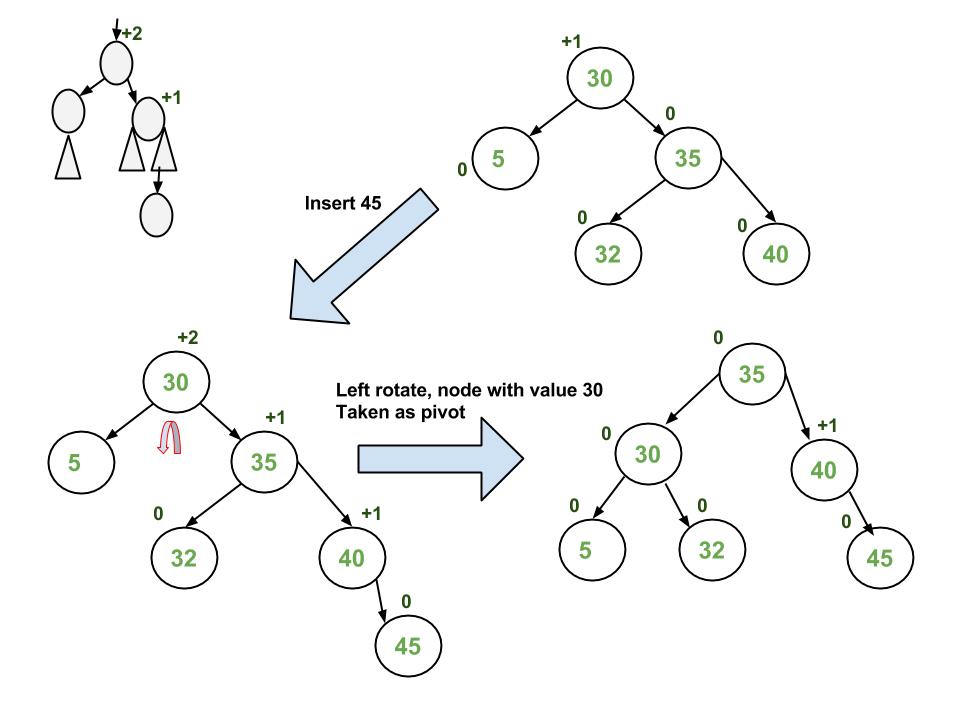
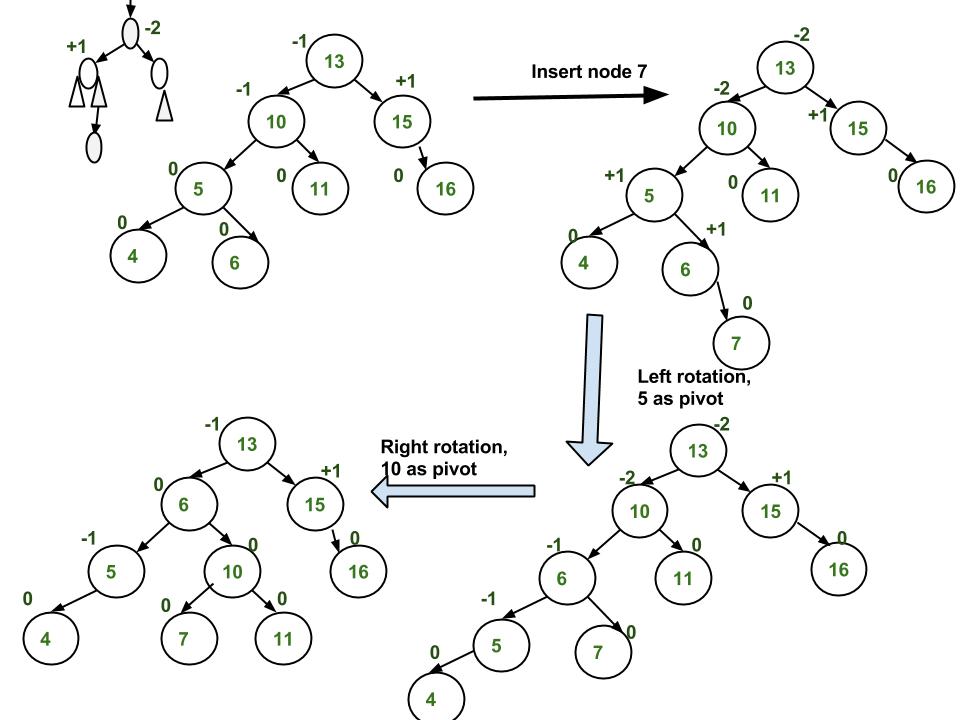
- AVL Tree
- Bitwise operations
- Breadth First Search (BFS)
Big O notation is special notation that tells you how fast an algorithm is.
This covers the space and time Big-O complexities of common algorithms used in Computer Science.
An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations.Array is a container which can hold a fix number of items
and these items should be of the same type. Most of the data structures make use of arrays to implement their algorithms.
Following are the important terms to understand the concept of Array.
Element − Each item stored in an array is called an element.
Index − Each location of an element in an array has a numerical index, which is used to identify the element.
Advantages of Array :
1-Arrays are easy to use as many algorithms like searching and sorting techniques, finding maximum and minimum values, reversing can be easily implemented using arrays.
2-The time complexity to access any element of an array is O(1), i.e, it takes a constant amount of time to access an element.
3-Arrays use indexes to identify their elements. These indexes starting from ‘zero’ and ending at ‘length of array – 1’ can be used to access all elements of an array.
4-Along with simple arrays, we also have 2- dimensional arrays, which are used to store elements of a matrix of any dimensions.
5-Since arrays store elements in contiguous memory locations, no extra memory is allocated outside this contiguous block, which prevents wastage of memory.
6-Being one of the most basic data structures, arrays can be used to implement other data structures like linked lists, stacks, queues, graphs, trees, etc.
7-Reading element time complexity is O(1) by access the element by it's index .
Disadvantages of Array:
1-The size of an array is fixed. Once the memory is allocated to an array, it cannot be increased or decreased. This prevents us from storing extra data in case we want to.
These arrays of fixed size are called static arrays.
2-A single array cannot store values of different data types, i.e, an array is homogenous in nature.
3-The deletion and insertion operations in arrays are very difficult to implement as they store data in contiguous memory locations. To overcome this problem, linked lists are implemented which provide random access of elements.
4-insertion element in array time complexity is O(n) ,because you have to shift all the rest of the elements down. And if there’s no space, you might have to copy everything to a new location .
5-Deletions element in array time complexity is O(n) ,because everything needs to be moved up when you delete an element.
For More information about Array Data Structure Visit this website
With linked lists, your items can be anywhere in memory.
Each item stores the address of the next item in the list. A bunch of
random memory addresses are linked together.
It’s like a treasure hunt. You go to the first address, and it says, “The next
item can be found at address 123.” So you go to address 123, and it says,
“The next item can be found at address 847,” and so on. Adding an item
to a linked list is easy: you stick it anywhere in memory and store the
address with the previous item.
With linked lists, you never have to move your items. You also avoid
another problem. Let’s say you go to a popular movie with five of your
friends. The six of you are trying to find a place to sit, but the theater
is packed. There aren’t six seats together. Well, sometimes this happens
with arrays. Let’s say you’re trying to find 10,000 slots for an array. Your
memory has 10,000 slots, but it doesn’t have 10,000 slots together. You
can’t get space for your array! A linked list is like saying, “Let’s split up
and watch the movie.” If there’s space in memory, you have space for your linked list.
Advantages of Linked List:
1-The linked list is a dynamic data structure.
2-You can also decrease and increase the linked list at run-time. That is, you can allocate and deallocate memory at run-time itself.
3-In this, you can easily do insertion and deletion functions. That is, you can easily insert and delete the node.
4-Memory is well utilized in the linked list. Because in it, we do not have to allocate memory in advance.
5-Its access time is very fast, and it can be accessed at a certain time without memory overhead.
6-You can easily implement linear data structures using the linked list like a stack, queue.
4-insertion element in Linked List time complexity is O(1) ,because it’s as easy as changing what the previous element points to.
5-Deletions element in array time complexity is O(1) ,because it’s as easy as changing what the previous element points to.
Disadvantages of Linked List:
1-The linked list requires more memory to store the elements than an array, because each node of the linked list points a pointer, due to which it requires more memory.
2-It is very difficult to traverse the nodes in a linked list. In this, we cannot access randomly to any one node. (As we do in the array by index.) For example: –
If we want to traverse a node in an n position, then we have to traverse all the nodes that come before n, which will spoil a lot of our time.
3-Reverse traversing in a linked list is very difficult, because it requires more memory for the pointer.
Application of Linked List :
The linked list is a primitive data structure, which is used in various types of applications.
1-It is used to maintain directory names.
2-The linked list can perform arithmetic operations in the long integer.
3-Polynomials can be manipulated by storing constant in the node of the linked list.
4-We can also use it to next and previous images in the image viewer.
5-With the help of the linked list, we can move songs back and forth in the music player.
6-The linked list is also used for undo in word and Photoshop applications.
7-All the running applications in the computer are stored in the circular linked list, and the operating system provides them with a fixed time slot.
8-It can also be used to implement hash tables.
Here Implementation of Linked List
Given an array arr[] of size n, its prefix sum array is another array prefixSum[] of the same size, such that the value of prefixSum[i] is arr[0] + arr[1] + arr[2] … arr[i].
Examples :
Input : arr[] = {10, 20, 10, 5, 15}
Output : prefixSum[] = {10, 30, 40, 45, 60}
Explanation : While traversing the array, update
the element by adding it with its previous element.
prefixSum[0] = 10,
prefixSum[1] = prefixSum[0] + arr[1] = 30,
prefixSum[2] = prefixSum[1] + arr[2] = 40 and so on.
Example :
// prefix sum arrayclass
static void fillPrefixSum(int[] arr, int n,
int[] prefixSum)
{
prefixSum[0] = arr[0];
// Adding present element
// with previous element
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1] + arr[i];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 10, 4, 16, 20 };
int n = arr.Length;
int[] prefixSum = new int[n];
fillPrefixSum(arr, n, prefixSum);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(prefixSum[i] + " ");
Console.Write("");
}
The usage of frequency arrays has its limitations. Remember that you need an array whose size is equal to the value of the largest integer in the original array. Which means that you can't use a frequency array if the values in the original array can be up to 10^9 for example.
You can use a frequency array to sort an array in O(M) time, where M is the value of the largest integer in the array. Which could be much more efficient than merge sort (which runs in O(NlogN)) in cases where the array size is large but the values inside the array are bounded with a small number.
Example :
Given an array which may contain duplicates, print all elements and their frequencies.
Input : arr[] = {10, 20, 20, 10, 10, 20, 5, 20}
Output : 10--> 3
20--> 4
5--> 1
static void countFreq(int []arr, int n)
{
Dictionary<int, int> mp = new Dictionary<int,int>();
// Traverse through array elements and
// count frequencies
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (mp.ContainsKey(arr[i]))
{
var val = mp[arr[i]];
mp.Remove(arr[i]);
mp.Add(arr[i], val + 1);
}
else
{
mp.Add(arr[i], 1);
}
}
// Traverse through map and print frequencies
foreach(KeyValuePair<int, int> entry in mp)
{
Console.WriteLine(entry.Key + " " + entry.Value);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []arr = {10, 20, 20, 10, 10, 20, 5, 20};
int n = arr.Length;
countFreq(arr, n);
}
Time Complexity : O(n)
Auxiliary Space : O(n)
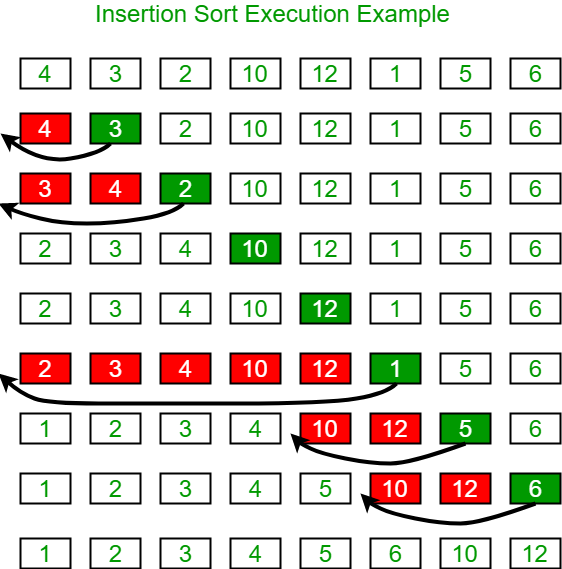
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works similar to the way you sort playing cards in your hands. The array is virtually split into a sorted and an unsorted part. Values from the unsorted part are picked and placed at the correct position in the sorted part.
Algorithm
To sort an array of size n in ascending order:
1: Iterate from arr[1] to arr[n] over the array.
2: Compare the current element (key) to its predecessor.
3: If the key element is smaller than its predecessor, compare it to the elements before. Move the greater elements one position up to make space for the swapped element.
Example:
Another Example:
12, 11, 13, 5, 6
Let us loop for i = 1 (second element of the array) to 4 (last element of the array)
i = 1. Since 11 is smaller than 12, move 12 and insert 11 before 12
11, 12, 13, 5, 6
i = 2. 13 will remain at its position as all elements in A[0..I-1] are smaller than 13
11, 12, 13, 5, 6
i = 3. 5 will move to the beginning and all other elements from 11 to 13 will move one position ahead of their current position.
5, 11, 12, 13, 6
i = 4. 6 will move to position after 5, and elements from 11 to 13 will move one position ahead of their current position.
5, 6, 11, 12, 13
void InsertionSort(int[] arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
// Move elements of arr[0..i-1],
// that are greater than key,
// to one position ahead of
// their current position
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j = j - 1;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
Best Case : : Complexity: O(n) if array is sorted .
Average Case : Complexity: O(n^2)
Worst Case : Complexity: O(n^2)
Bubble Sort is the simplest sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in wrong order.
Example:
First Pass:
( 5 1 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 5 4 2 8 ), Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps since 5 > 1.
( 1 5 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 5 2 8 ), Swap since 5 > 4
( 1 4 5 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Swap since 5 > 2
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Now, since these elements are already in order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
Second Pass:
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 )
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 ), Swap since 4 > 2
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
Now, the array is already sorted, but our algorithm does not know if it is completed. The algorithm needs one whole pass without any swap to know it is sorted.v
Third Pass:
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
static void bubbleSort(int []arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++)
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
// swap temp and arr[i]
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
Best Case : : Complexity: O(n) if we put condition if first iteration didn't swap any element array is sorted .
Average Case : Complexity: O(n^2)
Worst Case : Complexity: O(n^2)
Given a sorted array arr[] of n elements, write a function to search a given element x in arr[].
A simple approach is to do a linear search. The time complexity of the above algorithm is O(n). Another approach to perform the same task is using Binary Search.
Binary Search: Search a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half. Begin with an interval covering the whole array. If the value of the search key is less than the item in the middle of the interval, narrow the interval to the lower half. Otherwise, narrow it to the upper half. Repeatedly check until the value is found or the interval is empty.
public static int BinarySearch(int[]arr,int l,int r,int x)
{
int mid;
while (r>=l)
{
mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
else if (arr[mid] > x)
r = mid- 1;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
// We reach here when element is not present
return -1;
}
Time Complexity: O(log n)
note : we usually used Binary Search for Optimization Problems such as find large index in array , Minimaize max(sumblock[j]) ... etc
we solve it in 3 step :
1-Define your search space (make array that contain input)
2-Design function that check that a solution satisfies the constraint ===> Can()
3-Binary search over search space
The selection sort algorithm sorts an array by repeatedly finding the minimum element (considering ascending order) from unsorted part and putting it at the beginning. The algorithm maintains two subarrays in a given array.
Following example explains the above steps:
arr[] = 64 25 12 22 11
// Find the minimum element in arr[0...4]
// and place it at beginning
11 25 12 22 64
// Find the minimum element in arr[1...4]
// and place it at beginning of arr[1...4]
11 12 25 22 64
// Find the minimum element in arr[2...4]
// and place it at beginning of arr[2...4]
11 12 22 25 64
// Find the minimum element in arr[3...4]
// and place it at beginning of arr[3...4]
11 12 22 25 64
static void sort(int []arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
// One by one move boundary of unsorted subarray
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// Find the minimum element in unsorted array
int min_idx = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
// Swap the found minimum element with the first
// element
int temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
Time Complexity: O(n^2)
if some problem instance can be seen as piece of other problems instance ,we can store our work along the way to avoid doing same work twice .
Dynamic Programming (DP):
When we solve a recursive problem that its sub-problems overlaps, hence calling sub-problems
More than once and repeating its calculation in nature that typically makes the order exponentials!
When the original space is small enough to be memorized, then saving these sub-problems
makes order small too, as sub-problems calculated once.
General Rules:
1- Recursive Function
2- Sub-calls Overlap
3- Small Search Space, so putting in memory is doable
Do we need to apply DP for merge sort? NEVER, a call will never be repeated! like most of D & C problems.
Dynamic Programming most typical cases: Minimization, Maximization and Counting. But could have adhock usages.
In fact, above code is not called DP, it is call Memoization (NOT Memorization).<br/
It is a technique when we have a recurive function and save calls)
DP is to build bottom up according to recurrence while Memoization is top-down
Here some exercises of dp problems : [Link](https://github.com/mahmoud-khaled1/DataStructures-Algorithms/tree/master/Data%20Structures%20%26%26%20Algorithms%20implementation/DP/DP%20basics)
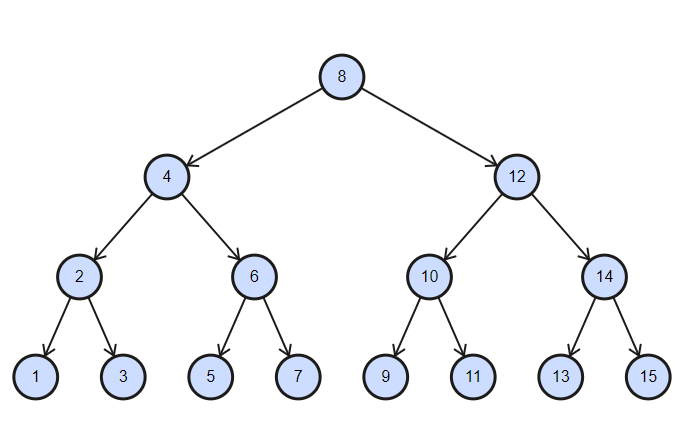
The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys lesser than the node’s key.
The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
The left and right subtree each must also be a binary search tree.
1-Searching become very efficient in a binary search tree since, we get a hint at each step, about which sub-tree contains the desired element.
2-The binary search tree is considered as efficient data structure in compare to arrays and linked lists. In searching process,
it removes half sub-tree at every step. Searching for an element in a binary search tree takes o(log2n) time. In worst case, the time it takes to search an element is 0(n).
3-It also speed up the insertion and deletion operations as compare to that in array and linked list.
Here Link of Implementation of Binary Search Tree :Implementation
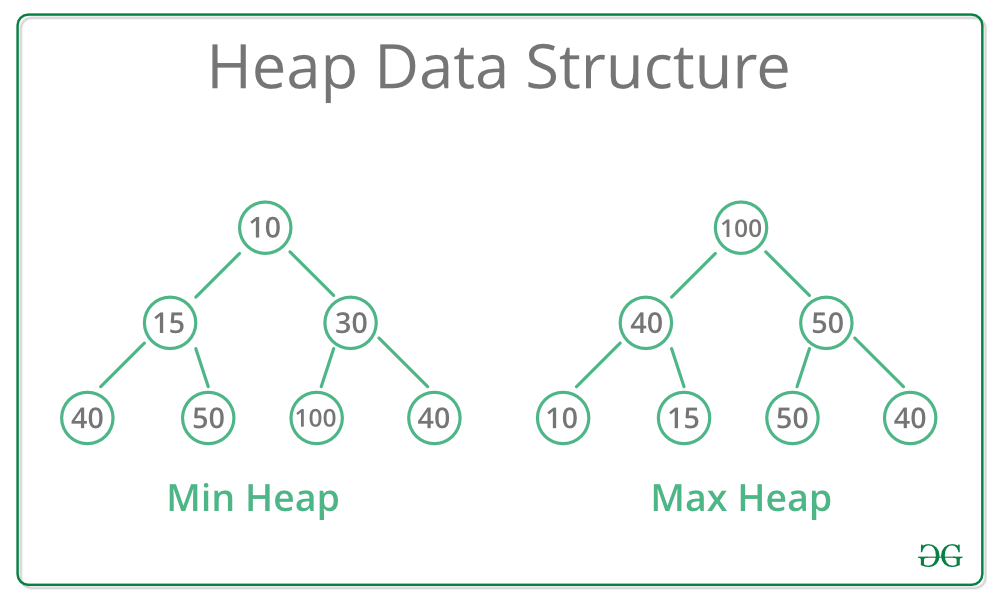
A Heap is a special Tree-based data structure in which the tree is a complete binary tree. A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which all the levels except the last level, leaf node should be completely filled, and all the nodes should be left-justified.
Generally, Heaps can be of two types:
Max-Heap: In a Max-Heap the key present at the root node must be greatest among the keys present at all of it’s children. The same property must be recursively true for all sub-trees in that Binary Tree.
Min-Heap: In a Min-Heap the key present at the root node must be minimum among the keys present at all of it’s children. The same property must be recursively true for all sub-trees in that Binary Tree.
The heap is one maximally efficient implementation of an abstract data type called a priority queue, and in fact, priority queues are often referred to as "heaps", regardless of how they may be implemented. In a heap, the highest (or lowest) priority element is always stored at the root. However, a heap is not a sorted structure; it can be regarded as being partially ordered. A heap is a useful data structure when it is necessary to repeatedly remove the object with the highest (or lowest) priority.
if we map the heap data structure to array such as priority queue , we can travels to the heap level by level and insert element to array ,after mapping this heap to array we can
get parent and children of any element by using this equation , if we need find childrens of specific element in array we can use this equation (2i+1 , 2i+2)
if we need find parent of specific element in array we can use this equation (i/2-1)
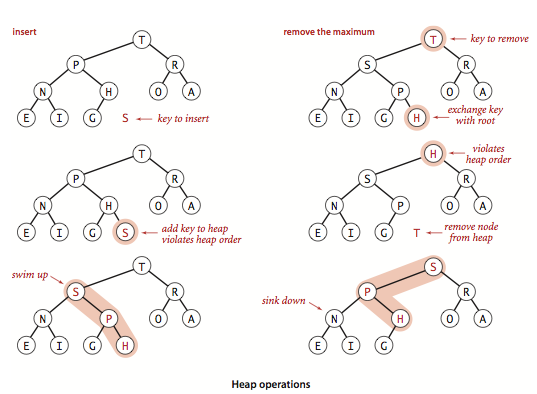
Here Some Operation in heap such as insert element and remove element
A heap can be implemented in 2 ways
Tree Node Implementation with pointers
Heap as Array Implementation
Applications –
Some Applications of Heap are :
Heapsort sorting algorithm
Graph algorithms like – Prim’s minimal-spanning-tree algorithm and Dijkstra’s shortest-path algorithm.
A priority queue can be implemented with a heap or a variety of other methods.
Min Heap Implementation as sorting Array Implementation
Here tutorial of Heaps/Priority Queues :tutorial
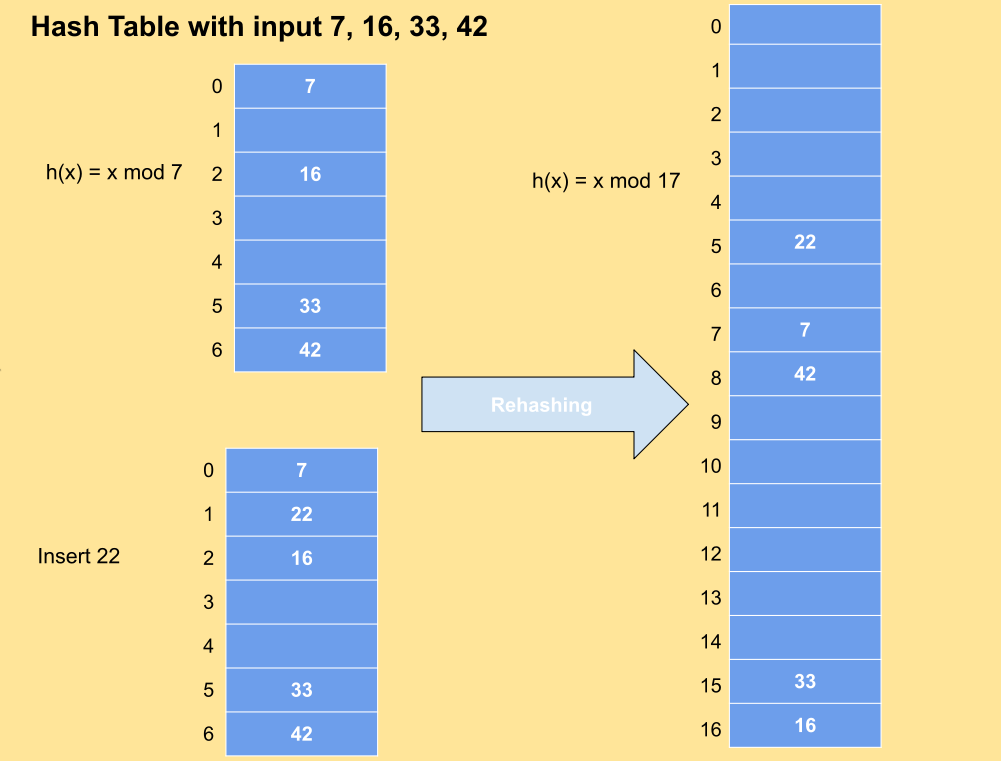
Hash tables are used everywhere. This section will show you a few use cases :-
1-Using hash tables for lookups ,Your phone has a handy phonebook built in.
Each name has a phone number associated with it.
2-Hash tables are used for lookups on a much larger scale. For example,
suppose you go to a website like http://adit.io. Your computer has to
translate adit.io to an IP address.
Wow, mapping a web address to an IP address? Sounds like a perfect
use case for hash tables! This process is called DNS resolution. Hash
tables are one way to provide this functionality
Disadvantages
Hash collisions are practically unavoidable. when hashing a random subset of a large set of possible keys.
Hash tables become quite inefficient when there are many collisions.
Hash table does not allow null values, like hash map.
Here Implementation of Hash Table With C# : Implementation
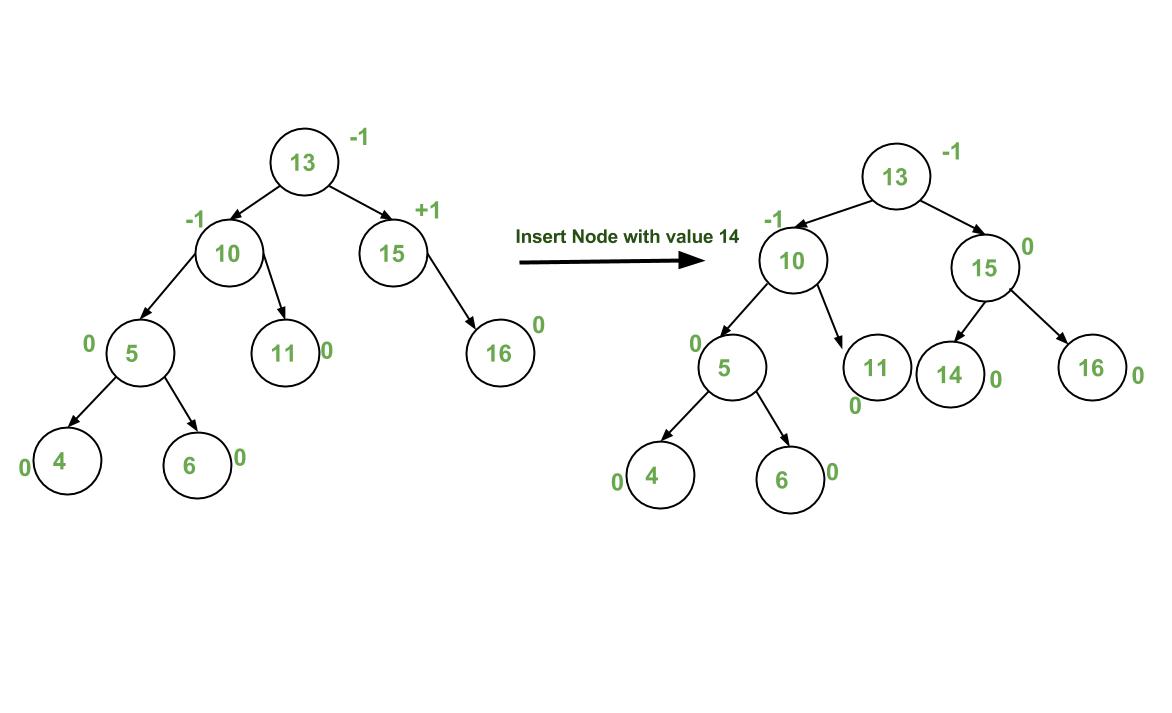
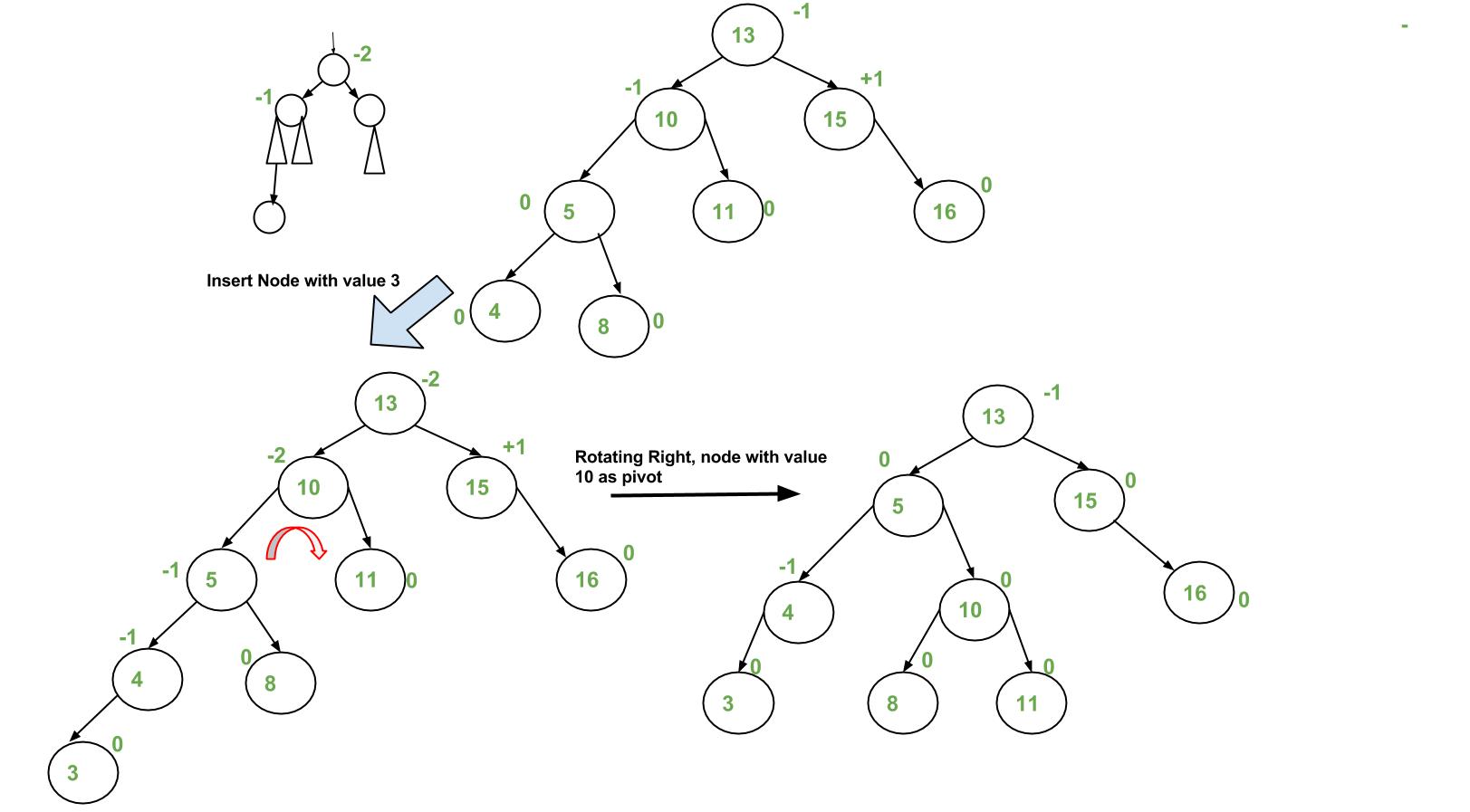
Here Implementation of AVL Tree With C# : Implementation
For More Explanation and Examples Visit : Basics of Bit Manipulation
Complexity
The time complexity of BFS is O(V + E), where V is the number of nodes and E is the number of edges.
For more information about BFS Visit:
Here implementation of BFS problem in Grokking algorithm book implementaion