Pepesan a.k.a Penjawab Pesan (Message Responder) is a simple and reliable JavaScript library to create a chat bot for WhatsApp, support for message pattern, routing, controller, and middleware similar to common REST API development framework such as Laravel.
- @whiskeysockets for the awesome WhatsApp socket library Baileys
> npm i --save pepesanor directly install from the repository to get the latest beta version
> npm i --save github:mqad21/pepesanconst Pepesan = require("pepesan");
const router = require("./router");
(async () => {
const pepesan = Pepesan.init(router)
await pepesan.connect()
})()You can add some configurations in second parameter.
const Pepesan = require("pepesan");
const router = require("./router");
(async () => {
const config = {
browserName: 'My first chat bot',
sessionPath: './example/session',
allowedNumbers: ['6281234567890', '6289876543210'],
db: {
path: './example/data.sqlite',
username: 'mqad21',
password: '4dm!n'
}
}
const pepesan = Pepesan.init(router, config)
await pepesan.connect()
})()Router is an instance of Router class. Here you define some rules for bot replies.
const { Router, Response } = require("pepesan")
const BotController = require("./BotController")
const router = new Router()
/**
* If user send "ping",
* bot will reply "pong".
*/
router.keyword("ping", () => {
return "pong"
})
/**
* If user send "ping 3 times",
* method pingManyTimes in BotController will be called
* and "3" will be passed as parameter.
*/
router.keyword("ping {n} times", [BotController, 'pingManyTimes'])
/**
* If user send "get my number"
* and the state is equal to "loggedIn",
* method getMyNumber in BotController will be called.
*/
router.state("loggedIn").group(() => {
router.keyword("get my number", [BotController, 'getMyNumber'])
})
/**
* If user send "buy"
* or user click a button with value "buy"
* and AuthMiddleware function return true,
* method buy in BotController will be called.
*/
router.middleware(AuthMiddleware).group(() => {
router.keyword("buy", [BotController, 'buy'])
router.button("buy", [BotController, 'buy'])
})
module.exports = routerController is a class that extends Controller class.
const { Controller, Response } = require("pepesan")
module.exports = class BotController extends Controller {
/**
* Bot will reply "pong" n times.
*/
pingManyTimes(request, n) {
return Array(Number(n)).fill("pong") // ["pong", "pong", ..., "pong"] n times
}
/**
* Bot will reply "Wait for a while..."
* then bot will reply an image
* after it has been received from server.
*/
async pingWithImage() {
await this.reply(Response.text.fromString("Wait for a while..."))
const image = await getImageFromServer()
return Response.image.fromBuffer(image)
}
/**
* Bot will reply user WhatsApp number.
*/
getMyNumber(request) {
return request.number
}
/**
* Bot will reply button "yes" and "cancel"
* with "Are you sure?" text.
*/
buy() {
const buttons = ["yes", "cancel"]
return Response.button.fromArrayOfString(buttons, "Are you sure?")
}
}Middleware is an async/sync function that return Boolean or Response.
const { Response } = require("pepesan")
module.exports = (request, next) => {
/**
* If user number is not equal to "6281234567890",
* bot will reply "You are not allowed"
* else bot will execute the routes below it.
*/
if (request.number !== "6281234567890") {
return "You are not allowed"
}
return next()
}{
printQRInTerminal: boolean // default: true
sessionPath: string, // default: "./session"
browserName: string, // default: "Pepesan"
allowedNumbers: string[],
blockedNumbers: string[],
onOpen: (state: Partial<ConnectionState>) => void
onClose: (state: Partial<ConnectionState>) => void
onReconnect: (state: Partial<ConnectionState>) => void
onQR: (state: Partial<ConnectionState>) => void,
onMessage: (message: WAMessage) => Promise<void>,
db: {
name: string,
user: string,
pass: string,
path: string // default: "data.sqlite"
}
}printQRInTerminal: indicates whether or not the QR code should be print in terminal.sessionPath: folder path to save session files.
e.g. "/mysession"browserName: name that display in the device list of your WhatsApp app.allowedNumbers: list of number you allowed for using bot. Let innullorundefinedif you want to allow all numbers.
e.g. ["6281234567890", "6289876543210"]blockedNumbers: list of number you blocked for using bot. Let innullorundefinedif you want to allow all numbers.
e.g. ["6281234567890", "6289876543210"]onOpen: a callback function when WhatsApp connection opened.onClose: a callback function when WhatsApp connection closed.onClose: a callback function when WhatsApp connection needs to reconnect.onQR: a callback function when WhatsApp QR code received.onMessage: a callback function when a new message received.db: configurations for your SQLite database.name: Database name.user: Database username.pass: Database password.path: Path to your ".sqlite" file.
e.g. "/data.sqlite"'
Keyword route handles user's message, media caption, or button response text that match the route pattern.
router.keyword("hello", ...) // only match to "hello" text.
router.keyword("hello*", ...) // match to all texts start with "hello".
router.keyword("(hello|hi)", ...) // only match to "hello" or "hi" text.
router.keyword("hello {name}", ...) // match to "hello muhammad", "hello qadri", etc.State route handles user's state that match with the route pattern.
router.state("idle", ...) // only match to "idle" state.
router.state("idle*", ...) // match to all states start with "idle".
router.state("(idle|active)", ...) // only match to "idle" or "active" state.
router.state("active {time}", ...) // match to "active today", "active tonight", etc.Middleware route handles all user's message if only middleware function return true.
router.middleware(AuthMiddleware, ...) // if AuthMiddleware return true, the callback will be called.
router.middleware([AuthMiddleware, param1, param2, ...], ...) // Middleware also can receive parameters.Button route handles text or value of button clicked by user that match with the route pattern.
router.button("buy", ...) // only match to "buy" button text or value.
router.button("buy*", ...) // match to all button values or texts that start with "buy".
router.button("(buy|cancel)", ...) // only match to "buy" or "cancel" button text or value.
router.button("buy {product}", ...) // match to "buy iphone", "buy macbook", etc.Route can also be grouped if the callback or the second parameter is not set.
router.middleware([AuthMiddleware, 'change settings']).group(() => {
// Code block below is only executed if AuthMiddleware function returns true.
router.keyword("Change payment to (cash|transfer)", [PaymentController, 'changePayment'])
router.button("Change profile", [ProfileController, 'changeProfile'])
})
router.state("loggedIn").group(() => {
// Code block below is only executed if user state equals to "loggedIn".
router.keyword("View my balance", [BalanceController, 'viewBalance'])
router.button("View my profile", [ProfileController, 'viewProfile'])
})-
Controller method can be an async/sync function.
-
The first parameter is
Requestobject and the rest is route parameter. -
The return value is the response message of bot. It can be
stringorResponseobject. -
If you want the bot respond more than one message, you can make the return value as
Array.Example:
introduction(request, firstName, lastName) { return `Hello ${firstName} ${lastName}` } pingTwoTimes(request) { return ["Ping 1", "Ping 2"] } async downloadYoutube(request) { const url = request.text const youtube = await download(url) return [ Response.video.fromBuffer(youtube.video), youtube.title ] }
-
The
replymethod is used to reply to the user's message. -
The parameter can be
string,Response,Array of string,Array of Response, orArray of Response or string.Example:
async convertToMp3(request) { await this.reply("Please wait...") await this.reply(Response.image.fromURL("...")) const url = request.text const mp3 = await toMp3(url) return Response.audio.fromBuffer(mp3) }
-
The
sendmethod is used to send message to the another user. -
The first parameter is recipient WhatsApp number.
-
The second parameter can be
string,Response,Array of string,Array of Response, orArray of Response or string.Example:
async sendConfirm(request) { const message = request.text await this.send("6289876543210", [ message, Response.image.fromURL("...") ]) return "Confirmed" }
-
The
getMediamethod is used to get any media sent by user. -
The return of this method is
Promise<Buffer>Example:
async uploadReceipt(request) { const receipt = await this.getMedia() await this.send("6289876543210", Response.image.fromBuffer(receipt)) return "Uploaded" }
-
The
setStatemethod is used to set current user state. -
The parameter is state
string.Example:
async login(request) { const key = request.text const isAllowed = await checkKey(key) if (isAllowed) { await this.setState("loggedIn") return "You are logged in" } return "Invalid key" }
-
The
deleteStatemethod is used to delete the current user state.Example:
async logout(request) { await this.deleteState() return "Logged out" }
Request is an object that contains information from the user's message.
Example:
{
id: '3EB00744EB342283C522', // Message ID
key: ..., // Message key object
text: "Hello", // Message text or caption
button: ..., // { text: "Button text", value: "Button value or ID" }
jid: "6281234567890@s.whatsapp.net", // User's JID
number: "6281234567890", // User's WhatsApp number
name: "Muhammad Qadri", // User's name
state: "MyState", // Current user's state
stateObject: ..., // User's state object
type: ..., // 'image' | 'video' | 'document' | 'sticker'
message: ..., // Message object
document: ..., // Document message object
image: ..., // Video message object
sticker: ..., // Sticker message object
contact: ..., // Contact message object
route: ... // Current route object
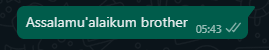
}Response.text.fromString("Assalamu'alaikum brother")Response.image.fromBuffer(imageBuffer, "caption")
Response.image.fromURL("https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/6b/WhatsApp.svg/2044px-WhatsApp.svg.png", "caption")Response.video.fromBuffer(videoBuffer, "caption")
Response.video.fromStream(videoStream, "caption")
Response.video.fromURL("http://techslides.com/demos/sample-videos/small.mp4", "caption")Response.audio.fromBuffer(webpBuffer)
Response.audio.fromURL("https://download.quranicaudio.com/quran/wadee_hammadi_al-yamani/001.mp3")Response.sticker.fromBuffer(webpBuffer)
Response.sticker.fromURL("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mqad21/pepesan-assets/main/sticker.webp")Response.button.fromArrayOfString(["yes", "cancel"], "Content", "Footer")
Response.button.fromArrayOfObject([{text: "yes", value: "1"}, {text:"no", value: "0"}], "Content", "Footer")-
Middleware is an async/sync function that return
BooleanorResponsevalue -
The first parameter is
Requestobject. -
The second parameter is
nextfunction. -
The rest is route parameter.
Example:
(request, next, action) => { if (request.number !== "6281234567890") { let errorMessage = "You are not allowed" if (action) errorMessage += ` to ${action}` return errorMessage } return next() }
Access to WASocket object anywhere after initiate the Pepesan class.
Access to Database object anywhere after initiate the Pepesan class.