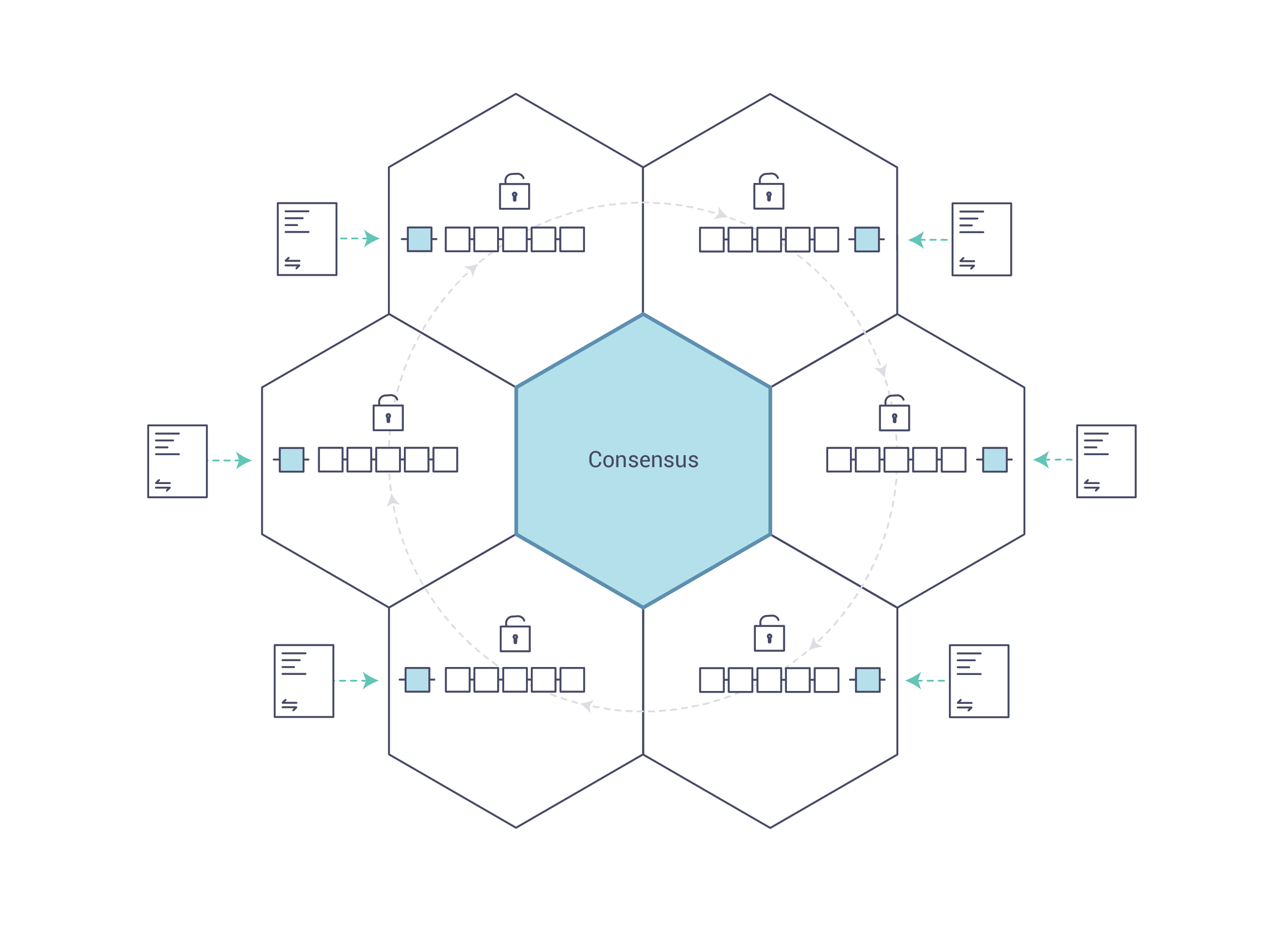
Source: chainhero.io/2017/07/tutorial-build-blockchain-app
This tutorial will introduce you to the Hyperledger Fabric Go SDK and allows you to build a simple application using the blockchain principle.
This tutorial uses Hyperledger Fabric version 1.0.0-rc1
First part This is the first part of this tutorial. The basics SDK features will be shown, but the second part is scheduled to demonstrate a more complex application.
This tutorial won’t explain in detail how Hyperledger Fabric works. I will just give some tips to understand the general behavior of the framework. If you want to get a full explanation of the tool, go to the official documentation there is a lot of work there that explains what kind of blockchain, Hyperledger Fabric is.
This tutorial has been made on Ubuntu 16.04 but the Hyperledger Fabric framework is compatible with Mac OS X, Windows and other Linux distributions.
We will use the Go language to design a first application, because the Hyperledger Fabric has been built also in Go and the Fabric SDK Go is really simple to use. In addition, the chaincode (smart contract) can be written in Go too. So the full-stack will be only in Go! There are other SDK if you want to, like for NodeJS, Java or Python.
Hyperledger Fabric uses Docker to easily deploy a blockchain network. In addition, in the v1.0, some component (peers) also deploys docker containers to separate data (channel). So make sure that the platform supports this kind of virtualization.
Hyperledger Fabric is a platform for distributed ledger solutions underpinned by a modular architecture delivering high degrees of confidentiality, resiliency, flexibility and scalability. It is designed to support pluggable implementations of different components and accommodate the complexity and intricacies that exist across the economic ecosystem.
See the full explaination from the official documentation, in the introduction part: Hyperledger Fabric Blockchain
This tutorial was made on Ubuntu 16.04, but there is some help for make the installation in Windows, Mac OS X and other Linux distributions.
The required version for docker is 1.12 or greater, this version is already available in the package manager on Ubuntu. Just install it with this command line:
sudo apt install docker.io
In addition, we need docker-compose 1.8+ to manage multiple containers at once. You can also use your package manager that hold the right version:
sudo apt install docker-compose
Now we need to manage the current user to avoid using root access when we will use docker. To do so, we need to add the current user to the docker group:
sudo groupadd docker
sudo gpasswd -a ${USER} docker
sudo service docker restart
In order to apply these changes, you need to logout/login and then check versions with:
docker --version
docker-compose version
Dowload and install the latest Docker.dmg package for Mac OS X available on the Docker website. This will install docker-compose as well.
See links below:
See instructions from the Docker website: docker.com/docker-for-windows
Hyperledger Fabric requires a Go version 1.7.x or more and we have only Go version 1.6.x in package manager. So this time we need to use the official installation method. You can follow instructions from golang.org or use these generics commands that will install Golang 1.8.3 and prepare your environment (generate your GOPATH) for Ubuntu:
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/golang/go1.8.3.linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.8.3.linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
rm go1.8.3.linux-amd64.tar.gz && \
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin' | sudo tee -a /etc/profile && \
echo 'export GOPATH=$HOME/go' | tee -a $HOME/.bashrc && \
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:$GOROOT/bin:$GOPATH/bin' | tee -a $HOME/.bashrc && \
mkdir -p $HOME/go/{src,pkg,bin}
To make sure that the installation works, you can logout/login (again) and run:
go version
Now we can install the main framework: Hyperledger Fabric. We will fix the commit level to the v1.0.0-rc1 because the Fabric SDK Go is compatible with it. All the code is available in a mirror on github, just check out (and optionally build binaries):
mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/hyperledger && \
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/hyperledger && \
git clone https://github.com/hyperledger/fabric.git && \
cd fabric && \
git checkout v1.0.0-rc1
Same for the Hyperledger Fabric CA part:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/hyperledger && \
git clone https://github.com/hyperledger/fabric-ca.git && \
cd fabric-ca && \
git checkout v1.0.0-rc1
We won’t use directly the framework, but this is useful to have the framework locally in your GOPATH to compile your app.
Finally, we install the Hyperledger Fabric SDK Go that will allow us to easily communicate with the Fabric framework. To avoid versions issues, we directly checkout a specific commit that works with the following tutorial.
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/hyperledger && \
git clone https://github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go.git && \
cd fabric-sdk-go && \
git checkout 85fa3101eb4694d464003c3a900672d632f17833
Then we will use the golang built in functions in order to install packages:
go get github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/pkg/fabric-client && \
go get github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/pkg/fabric-ca-client
If you get the following error:
../fabric-sdk-go/vendor/github.com/miekg/pkcs11/pkcs11.go:29:18: fatal error: ltdl.h: No such file or directory
You need to install the package libltdl-dev and re-execute previous command (go get ...):
sudo apt install libltdl-dev
Then you can go inside the new fabric-sdk-go directory in your GOPATH and we will install dependencies and check out if all is ok:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go && make
The installation can take a while (depending on your network connection), but in the end you should see Integration tests passed. During this process, a virtual network has been built and some tests have been made in order to check if your system is ready. Now we can work with our first application.
In order to make a blockchain network, we will use docker to build virtual computers that will handle different roles. In this tutorial we will stay as simple as possible. Hyperledger Fabric needs a lot of certificates to ensure encryption during the whole end to end process (SSL, TSL, authentification...). Fortunately, the Fabric SDK Go provides them. In order to use them, we simply use the network deployed by the testing part of the SDK.
Make a new directory in the src folder of your GOPATH, we name it heroes-service:
mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service
Now, we can copy the environment of the Fabric SDK Go placed in the test folder:
cp -r $GOPATH/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/test/fixtures ./
We can clean up a little bit to make it more simple. We remove the default chaincode, as we will make our own chaincode later. We also remove some files used by the test script of the SDK:
rm -rf fixtures/{config,src,.env,latest-env.sh}
In order to make it work, we have to edit the docker-compose.yaml file, which is the configuration file for docker-compose command. It tells which containers needs to be created/started and with the right configuration for each. Take your favorite text editor and copy/paste content from this repository:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
vi fixtures/docker-compose.yaml
see fixtures/docker-compose.yaml
Now if we use docker-compose, we will setup two Fabric Certificate Authorities with one peer for each. Peers will have all roles: ledger, endorser and commiter. In addition, an orderer is also created with the solo ordering algorithm (no consensus is made).
In order to check if the network works, we will use docker-compose to start or stop all containers at the same time. Go inside the fixtures folder, and run:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/fixtures && \
docker-compose up
You will see a lot of logs with different colors (for your information, red isn't equal to errors).
Open a new terminal and run:
docker ps
You will see : two peers, the orderer and two CA containers. You have successfully made a new network ready to use with the SDK. To stop the network go back to the previous terminal, press Ctrl+C and wait that all containers are stopped. If you want to explore more deepper, check out the official documentation about this: Building Your First Network
Tips: when the network is stopped, all containers used remain accessible. This is very useful to check logs for example. You can see them with
docker ps -a. In order to clean up these containers, you need to delete them withdocker rm $(docker ps -aq)or if you have used adocker-composefile, go where this file is and rundocker-compose down.
Tips: you can run the
docker-composecommand in background to keep the prompt. To do so, use the parameter-d, like this:docker-compose up -d. To stop containers, run in the same folder where thedocker-compose.yamlis, the command:docker-compose stop(ordocker-compose downto clean up after all containers are stopped).
As we removed the config folder, we need to make a new config file. We will put in it everything that the Fabric SDK Go and our custom parameters for our app needs to work. The config file will contain all our custom parameters and everything else the Fabric SDK Go needs for our app to work. For the moment, we will only try to make the Fabric SDK Go work with the default chaincode:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
vi config.yaml
client:
peers:
# peer0
- host: "localhost"
port: 7051
eventHost: "localhost"
eventPort: 7053
primary: true
tls:
# Certificate location absolute path
certificate: "$GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/fixtures/channel/crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/cacerts/org1.example.com-cert.pem"
serverHostOverride: "peer0.org1.example.com"
tls:
enabled: true
security:
enabled: true
hashAlgorithm: "SHA2"
level: 256
tcert:
batch:
size: 200
orderer:
host: "localhost"
port: 7050
tls:
# Certificate location absolute path
certificate: "$GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/fixtures/channel/crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/cacerts/example.com-cert.pem"
serverHostOverride: "orderer.example.com"
logging:
level: info
fabricCA:
tlsEnabled: true
id: "Org1MSP"
name: "ca-org1"
homeDir: "/tmp/"
mspDir: "msp"
serverURL: "https://localhost:7054"
certfiles :
- "$GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/fixtures/tls/fabricca/ca/ca_root.pem"
client:
keyfile: "$GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/fixtures/tls/fabricca/client/client_client1-key.pem"
certfile: "$GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/fixtures/tls/fabricca/client/client_client1.pem"
cryptoconfig:
path: "$GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/fixtures/channel/crypto-config"
The full configuration file is available here: config.yaml
We add a new folder named blockchain that will contain the whole interface that communicate with the network. We will see the Fabric SDK Go only in this folder.
mkdir $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/blockchain
Now, we add a new go file named setup.go :
vi $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/blockchain/setup.go
package blockchain
import (
api "github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/api"
fsgConfig "github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/pkg/config"
bccspFactory "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/bccsp/factory"
fcutil "github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/pkg/util"
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/pkg/fabric-client/events"
"fmt"
)
// FabricSetup implementation
type FabricSetup struct {
Client api.FabricClient
Channel api.Channel
EventHub api.EventHub
Initialized bool
ChannelId string
ChannelConfig string
}
// Initialize reads the configuration file and sets up the client, chain and event hub
func Initialize() (*FabricSetup, error) {
// Add parameters for the initialization
setup := FabricSetup{
// Channel parameters
ChannelId: "mychannel",
ChannelConfig: "fixtures/channel/mychannel.tx",
}
// Initialize the configuration
// This will read the config.yaml, in order to tell to
// the SDK all options and how contact a peer
configImpl, err := fsgConfig.InitConfig("config.yaml")
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Initialize the config failed: %v", err)
}
// Initialize blockchain cryptographic service provider (BCCSP)
// This tool manages certificates and keys
err = bccspFactory.InitFactories(configImpl.GetCSPConfig())
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed getting ephemeral software-based BCCSP [%s]", err)
}
// This will make a user access (here the admin) to interact with the network
// To do so, it will contact the Fabric CA to check if the user has access
// and give it to him (enrollment)
client, err := fcutil.GetClient("admin", "adminpw", "/tmp/enroll_user", configImpl)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Create client failed: %v", err)
}
setup.Client = client
// Make a new instance of channel pre-configured with the info we have provided,
// but for now we can't use this channel because we need to create and
// make some peer join it
channel, err := fcutil.GetChannel(setup.Client, setup.ChannelId)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Create channel (%s) failed: %v", setup.ChannelId, err)
}
setup.Channel = channel
// Get an orderer user that will validate a proposed order
// The authentication will be made with local certificates
ordererUser, err := fcutil.GetPreEnrolledUser(
client,
"ordererOrganizations/example.com/users/Admin@example.com/keystore",
"ordererOrganizations/example.com/users/Admin@example.com/signcerts",
"ordererAdmin",
)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Unable to get the orderer user failed: %v", err)
}
// Get an organisation user (admin) that will be used to sign the proposal
// The authentication will be made with local certificates
orgUser, err := fcutil.GetPreEnrolledUser(
client,
"peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/users/Admin@org1.example.com/keystore",
"peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/users/Admin@org1.example.com/signcerts",
"peerorg1Admin",
)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Unable to get the organisation user failed: %v", err)
}
// Initialize the channel "mychannel" based on the genesis block by
// 1. locating in fixtures/channel/mychannel.tx and
// 2. joining the peer given in the configuration file to this channel
if err := fcutil.CreateAndJoinChannel(client, ordererUser, orgUser, channel, setup.ChannelConfig); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("CreateAndJoinChannel return error: %v", err)
}
// Give the organisation user to the client for next proposal
client.SetUserContext(orgUser)
// Setup Event Hub
// This will allow us to listen for some event from the chaincode
// and act on it. We won't use it for now.
eventHub, err := getEventHub(client)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if err := eventHub.Connect(); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed eventHub.Connect() [%s]", err)
}
setup.EventHub = eventHub
// Tell that the initialization is done
setup.Initialized = true
return &setup, nil
}
// getEventHub initialize the event hub
func getEventHub(client api.FabricClient) (api.EventHub, error) {
eventHub, err := events.NewEventHub(client)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Error creating new event hub: %v", err)
}
foundEventHub := false
peerConfig, err := client.GetConfig().GetPeersConfig()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Error reading peer config: %v", err)
}
for _, p := range peerConfig {
if p.EventHost != "" && p.EventPort != 0 {
fmt.Printf("EventHub connect to peer (%s:%d)\n", p.EventHost, p.EventPort)
eventHub.SetPeerAddr(fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", p.EventHost, p.EventPort),
p.TLS.Certificate, p.TLS.ServerHostOverride)
foundEventHub = true
break
}
}
if !foundEventHub {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("No EventHub configuration found")
}
return eventHub, nil
}
The file is available here: blockchain/setup.go
At this stage, we only initialised a client that will communicate to a peer, a CA and an orderer. We also made a new channel and connected this peer to this channel. See the comments in the code for more information.
To make sure that the client managed to initialise all his components, we will make a simple test with the network launched. In order to do this, we need to build the go code. Since we we haven't any main file we have to add one:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
vi main.go
package main
import (
"github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/blockchain"
"fmt"
"os"
"runtime"
"path/filepath"
)
// Fix empty GOPATH with golang 1.8 (see https://github.com/golang/go/blob/1363eeba6589fca217e155c829b2a7c00bc32a92/src/go/build/build.go#L260-L277)
func defaultGOPATH() string {
env := "HOME"
if runtime.GOOS == "windows" {
env = "USERPROFILE"
} else if runtime.GOOS == "plan9" {
env = "home"
}
if home := os.Getenv(env); home != "" {
def := filepath.Join(home, "go")
if filepath.Clean(def) == filepath.Clean(runtime.GOROOT()) {
// Don't set the default GOPATH to GOROOT,
// as that will trigger warnings from the go tool.
return ""
}
return def
}
return ""
}
func main() {
// Setup correctly the GOPATH in the environment
if goPath := os.Getenv("GOPATH"); goPath == "" {
os.Setenv("GOPATH", defaultGOPATH())
}
// Initialize the Fabric SDK
_, err := blockchain.Initialize()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Unable to initialize the Fabric SDK: %v", err)
}
}
The file is available here: main.go
As you can see, we fixed the GOPATH of the environment if it's not set. We will need this feature in order to compile the chaincode (we will see this in the next step).
The last thing to do before starting the compilation is to use a vendor directory. In our GOPATH we have Fabric, Fabric CA, Fabric SDK Go and maybe other projects. When we will try to compile our app, there may be some conflicts (like multiple definitions of BCCSP). We will handle this by using a tool like govendor to flatten these dependencies. Just install it and import external dependencies inside the vendor directory like this:
go get -u github.com/kardianos/govendor && \
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
govendor init && govendor add +external
Now we can make the compilation:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
go build
After some time, a new binary named heroes-service will appear at the root of the project. Try to start the binary like this:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
./heroes-service
At this point, it won't work because there is no network deployed that the SDK can talk with. Start the network and launch the app again:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/fixtures && \
docker-compose up -d && \
cd .. && \
./heroes-service
Great! We initialised the SDK with our local network. In the next step, we will interact with a chaincode.
The Fabric SDK generates some files, like certificates and/or temporally files. Shutting down the network won't fully clean up your environment and when you will need to start it again, these files will be reused to avoid building process. For development you can keep them to test quickly but for a real test, you need to clean up all and start from the beginning.
How clean up my environment ?
- Shut down your network:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/fixtures && docker-compose down - Remove MSP folder (defined in the config file, in the
fabricCAsection):rm -rf /tmp/msp - Remove enrolment files (defined when we initialise the SDK, in the setup file, when we get the client):
rm -rf /tmp/enroll_user - Remove some docker containers and docker images not generated by the
docker-composecommand:docker rm -f -v `docker ps -a --no-trunc | grep "heroes-service" | cut -d ' ' -f 1` 2>/dev/nullanddocker rmi `docker images --no-trunc | grep "heroes-service" | cut -d ' ' -f 1` 2>/dev/null
How to be more efficient ?
We can automatise all these tasks in one single step. Also the build and start process can be automated. To do so, we will create a Makefile. First, ensure that you have the tool:
make --version
If make is not installed do (Ubuntu):
sudo apt install make
Then create a file named Makefile at the root of the project with this content:
.PHONY: all dev clean build env-up env-down run
all: clean build env-up run
dev: build run
##### BUILD
build:
@echo "Build ..."
@govendor sync
@go build
@echo "Build done"
##### ENV
env-up:
@echo "Start environnement ..."
@cd fixtures && docker-compose up --force-recreate -d
@echo "Sleep 15 seconds in order to let the environment setup correctly"
@sleep 15
@echo "Environnement up"
env-down:
@echo "Stop environnement ..."
@cd fixtures && docker-compose down
@echo "Environnement down"
##### RUN
run:
@echo "Start app ..."
@./heroes-service
##### CLEAN
clean: env-down
@echo "Clean up ..."
@rm -rf /tmp/enroll_user /tmp/msp heroes-service
@docker rm -f -v `docker ps -a --no-trunc | grep "heroes-service" | cut -d ' ' -f 1` 2>/dev/null || true
@docker rmi `docker images --no-trunc | grep "heroes-service" | cut -d ' ' -f 1` 2>/dev/null || true
@echo "Clean up done"
The file is available here: Makefile
Now with the task all:
- the whole environment will be cleaned up,
- then our go program will be compiled,
- after which the network will be deployed and
- finally the app will be up and running.
To use it, go in the root of the project and use the make command:
- Task
all:makeormake all - Task
build:make build - Task
env-up:make env-up - ...
We are almost there to use the blockchain system. But for now we haven't set up any chaincode (smart contract) yet that will handle queries from our application. First, let's create a new directory named chaincode and add a new file named main.go:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
mkdir chaincode && \
vi chaincode/main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim"
pb "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/peer"
)
// HeroesServiceChaincode implementation of Chaincode
type HeroesServiceChaincode struct {
}
// Init of the chaincode
// This function is called only one when the chaincode is instantiated.
// So the goal is to prepare the ledger to handle future requests.
func (t *HeroesServiceChaincode) Init(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
fmt.Println("########### HeroesServiceChaincode Init ###########")
// Get the function and arguments from the request
function, _ := stub.GetFunctionAndParameters()
// Check if the request is the init function
if function != "init" {
return shim.Error("Unknown function call")
}
// Put in the ledger the key/value hello/world
err := stub.PutState("hello", []byte("world"))
if err != nil {
return shim.Error(err.Error())
}
// Return a successful message
return shim.Success(nil)
}
// Invoke
// All future requests named invoke will arrive here.
func (t *HeroesServiceChaincode) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
fmt.Println("########### HeroesServiceChaincode Invoke ###########")
// Get the function and arguments from the request
function, args := stub.GetFunctionAndParameters()
// Check whether it is an invoke request
if function != "invoke" {
return shim.Error("Unknown function call")
}
// Check whether the number of arguments is sufficient
if len(args) < 1 {
return shim.Error("The number of arguments is insufficient.")
}
// In order to manage multiple type of request, we will check the first argument.
// Here we have one possible argument: query (every query request will read in the ledger without modification)
if args[0] == "query" {
return t.query(stub, args)
}
// If the arguments given don’t match any function, we return an error
return shim.Error("Unknown action, check the first argument")
}
// query
// Every readonly functions in the ledger will be here
func (t *HeroesServiceChaincode) query(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
// Check whether the number of arguments is sufficient
if len(args) < 2 {
return shim.Error("The number of arguments is insufficient")
}
// Like the Invoke function, we manage multiple type of query requests with the second argument.
// We also have only one possible argument: hello
if args[1] == "hello" {
// Get the state of the value matching the key hello in the ledger
state, err := stub.GetState("hello")
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Failed to get state of hello")
}
// Return this value in response
return shim.Success(state)
}
// If the arguments given don’t match any function, we return an error
return shim.Error("Unknown query action, check the second argument.")
}
func main() {
// Start the chaincode and make it ready for futures requests
err := shim.Start(new(HeroesServiceChaincode))
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error starting Heroes Service chaincode: %s\n", err)
}
}
The file is available here: chaincode/main.go
We choose to put the chaincode here to make the application simpler, but from an architecture point of view, it will be better to use the architectural given by the SDK and put the chaincode in the
srcfolder offixtures. The chaincode isn't really related to the application, we can have one repository for the app and another for the chaincode. For your information, in a near future, the chaincode could be written in other languages.
For now, the chaincode does nothing extraordinary, just put the key/value hello/world in the ledger at initialisation. In addition, there is one function that we can call by an invoke: query hello. This function gets the state of the ledger, i.e. hello and give it in response. We will test this in the next step, after successfully install and instantiate the chaincode.
In order to install and instantiate the chaincode, we need to add some code in the application. Edit the blockchain/setup.go and add this following lines:
line 3 of
blockchain/setup.go: we add the OS import to get access to the GOPATH variable in the environment
import (
api "github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/api"
fsgConfig "github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/pkg/config"
bccspFactory "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/bccsp/factory"
fcutil "github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/pkg/util"
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/pkg/fabric-client/events"
"fmt"
"os"
)
line 13 of
blockchain/setup.go: we add chaincode parameters
// FabricSetup implementation
type FabricSetup struct {
Client api.FabricClient
Channel api.Channel
EventHub api.EventHub
Initialized bool
ChannelId string
ChannelConfig string
ChaincodeId string
ChaincodeVersion string
ChaincodeGoPath string
ChaincodePath string
}
line 28 of
blockchain/setup.go: we set new parameters
func Initialize() (*FabricSetup, error) {
// Add parameters for the initialization
setup := FabricSetup{
// Channel parameters
ChannelId: "mychannel",
ChannelConfig: "fixtures/channel/mychannel.tx",
// Chaincode parameters
ChaincodeId: "heroes-service",
ChaincodeVersion: "v1.0.0",
ChaincodeGoPath: os.Getenv("GOPATH"),
ChaincodePath: "github.com/chainhero/heroes-service/chaincode",
}
[...]
}
line 156 of
blockchain/setup.go: we add the function that will install and instantiate the chaincode
// Install and instantiate the chaincode
func (setup *FabricSetup) InstallAndInstantiateCC() error {
// Check if chaincode ID is provided
// otherwise, generate a random one
if setup.ChaincodeId == "" {
setup.ChaincodeId = fcutil.GenerateRandomID()
}
fmt.Printf(
"Chaincode %s (version %s) will be installed (Go Path: %s / Chaincode Path: %s)\n",
setup.ChaincodeId,
setup.ChaincodeVersion,
setup.ChaincodeGoPath,
setup.ChaincodePath,
)
// Install ChainCode
// Package the go code and make a proposal to the network with this new chaincode
err := fcutil.SendInstallCC(
setup.Client, // The SDK client
setup.Channel, // The channel concerned
setup.ChaincodeId,
setup.ChaincodePath,
setup.ChaincodeVersion,
nil,
setup.Channel.GetPeers(), // Peers concerned by this change in the channel
setup.ChaincodeGoPath,
)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("Send install proposal return error: %v", err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Chaincode %s installed (version %s)\n", setup.ChaincodeId, setup.ChaincodeVersion)
}
// Instantiate ChainCode
// Call the Init function of the chaincode in order to initialize in every peer the new chaincode
err = fcutil.SendInstantiateCC(
setup.Channel,
setup.ChaincodeId,
setup.ChannelId,
[]string{"init"}, // Arguments for the invoke request
setup.ChaincodePath,
setup.ChaincodeVersion,
[]api.Peer{setup.Channel.GetPrimaryPeer()}, // Which peer to contact
setup.EventHub,
)
if err != nil {
return err
} else {
fmt.Printf("Chaincode %s instantiated (version %s)\n", setup.ChaincodeId, setup.ChaincodeVersion)
}
return nil
}
The file is available here: blockchain/setup.go
Tips: take care of the chaincode version, if you want to update your chaincode, increment this number. Otherwise the network will keep the same chaincode.
Finally, we add the call to this function in the main.go after the SDK initialisation:
line 38 of
main.go: we add the function that will install and instantiate the chaincode
func main() {
[...]
// Initialize the Fabric SDK
fabricSdk, err := blockchain.Initialize()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Unable to initialize the Fabric SDK: %v\n", err)
}
// Install and instantiate the chaincode
err = fabricSdk.InstallAndInstantiateCC()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Unable to install and instantiate the chaincode: %v\n", err)
}
}
The file is available here: main.go
We can test this, just with the make command setup in the previous step:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
make
Tips: the installation and the instantiation don't need to be run at every start of the application. Only when we update the chaincode (and the chaincode version). A solution is to provide an argument when we run the application to tell to do this additional procedure before move on. Since in this tutorial we will clean up the environment every time we don't really care about that.
Like a database, the chaincode is plugged and ready to answer. Let's try the hello query.
We will put all query functions in a new file named query.go in the blockchain folder:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
vi blockchain/query.go
package blockchain
import (
fcutil "github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/pkg/util"
api "github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/api"
"fmt"
)
// QueryHello query the chaincode to get the state of hello
func (setup *FabricSetup) QueryHello() (string, error) {
// Prepare arguments
var args []string
args = append(args, "invoke")
args = append(args, "query")
args = append(args, "hello")
// Make the proposal and submit it to the network (via our primary peer)
transactionProposalResponses, _, err := fcutil.CreateAndSendTransactionProposal(
setup.Channel,
setup.ChaincodeId,
setup.ChannelId,
args,
[]api.Peer{setup.Channel.GetPrimaryPeer()}, // Peer contacted when submitted the proposal
nil,
)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("Create and send transaction proposal return error in the query hello: %v", err)
}
return string(transactionProposalResponses[0].ProposalResponse.GetResponse().Payload), nil
}
The file is available here: blockchain/query.go
Add the call to this new function in the main.go:
line 49 of
main.go
func main() {
[...]
// Query the chaincode
response, err := fabricSdk.QueryHello()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Unable to query hello on the chaincode: %v\n", err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Response from the query hello: %s\n", response)
}
}
The file is available here: main.go
Let's try:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
make
The next thing to do in order to make a basic tour of the Fabric SDK Go, is to make a request to the chaincode in order to change the ledger state.
First, we will add this ability in the chaincode. Edit the chaincode/main.go file:
line 97 of
chaincode/main.go
// invoke
// All functions that read and write in the ledger will be here
func (t *HeroesServiceChaincode) invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
if len(args) < 2 {
return shim.Error("The number of arguments is insufficient, you need to provide the function for the invoke.")
}
if args[1] == "hello" && len(args) == 3 {
//
err := stub.PutState("hello", []byte(args[2]))
if err != nil {
return shim.Error("Failed to update state of hello")
}
// Return this value in response
return shim.Success(nil)
}
// If the arguments given don't match any function, we return an error
return shim.Error("Unknown invoke action, check the second argument.")
}
line 57 of
chaincode/main.go
func (t *HeroesServiceChaincode) Invoke(stub shim.ChaincodeStubInterface) pb.Response {
[...]
if args[0] == "query" {
return t.query(stub, args)
}
// The update argument will manage all update in the ledger
if args[0] == "invoke" {
return t.invoke(stub, args)
}
[...]
}
The file is available here: chaincode/main.go
From the application side, we add a new interface to make the invocation of the chaincode. Add a file named invoke.go in the blockchain folder:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
vi blockchain/invoke.go
package blockchain
import (
fcutil "github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/pkg/util"
api "github.com/hyperledger/fabric-sdk-go/api"
"fmt"
"time"
)
// InvokeHello
func (setup *FabricSetup) InvokeHello(value string) (string, error) {
// Prepare arguments
var args []string
args = append(args, "invoke")
args = append(args, "invoke")
args = append(args, "hello")
args = append(args, value)
// Add data that will be visible in the proposal, like a description of the invoke request
transientDataMap := make(map[string][]byte)
transientDataMap["result"] = []byte("Transient data in hello invoke")
// Make a next transaction proposal and send it
transactionProposalResponse, txID, err := fcutil.CreateAndSendTransactionProposal(
setup.Channel,
setup.ChaincodeId,
setup.ChannelId,
args,
[]api.Peer{setup.Channel.GetPrimaryPeer()},
transientDataMap,
)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("Create and send transaction proposal in the invoke hello return error: %v", err)
}
// Register the Fabric SDK to listen to the event that will come back when the transaction will be send
done, fail := fcutil.RegisterTxEvent(txID, setup.EventHub)
// Send the final transaction signed by endorser
if _, err := fcutil.CreateAndSendTransaction(setup.Channel, transactionProposalResponse); err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("Create and send transaction in the invoke hello return error: %v", err)
}
// Wait for the result of the submission
select {
// Transaction Ok
case <-done:
return txID, nil
// Transaction failed
case <-fail:
return "", fmt.Errorf("Error received from eventhub for txid(%s) error(%v)", txID, fail)
// Transaction timeout
case <-time.After(time.Second * 30):
return "", fmt.Errorf("Didn't receive block event for txid(%s)", txID)
}
}
The file is available here: blockchain/invoke.go
Add the call to this function in the main.go:
line 49 of
main.go
func main() {
[...]
// Query the chaincode
response, err := fabricSdk.QueryHello()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Unable to query hello on the chaincode: %v\n", err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Response from the query hello: %s\n", response)
}
// Invoke the chaincode
txId, err := fabricSdk.InvokeHello("chainHero")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Unable to invoke hello on the chaincode: %v\n", err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Successfully invoke hello, transaction ID: %s\n", txId)
}
// Query again the chaincode
response, err = fabricSdk.QueryHello()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Unable to query hello on the chaincode: %v\n", err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Response from the query hello: %s\n", response)
}
}
The file is available here: main.go
Let's try:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
make
We also can make this usable for any user. The best choice is a web application and we are lucky because the Go language natively provides a web server handling HTTP requests and also templating for HTML.
For now, we have only two different actions: the query and the invocation of the hello value. Let's make two HTML pages for each action. We add a web directory with three other directories:
web/templates: contains all HTML pages (templates)web/assets: contains all CSS, Javascript, Fonts, Images...web/controllers: contains all functions that will render templates
We use the MVC (Model-View-Controller) to make it more readable. The Model will be the blockchain part, the View are templates and Controller are provided by functions in the controllers directory.
Populate each with the appropriate code (we also added Bootstrap to make the result a little prettier:
web/templates/layout.htmlweb/templates/home.htmlweb/templates/request.htmlweb/controllers/controller.goweb/controllers/home.goweb/controllers/request.goweb/app.goweb/assets
And finaly, we change the main.go, in order to use the web interface instead of directly query the blockchain.
Run the app and go to localhost:3000/home.html:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/chainhero/heroes-service && \
make
The home page make a query in in the blockchain to get the value of the hello key and display it.
The request page has a form to change the hello value. After a successful submission the transaction ID is given.
We can see the change by going back to the home page.
It's the end for the first part. A more complex application is coming.
- Hyperledger website
- Hyperledger Fabric online documentation
- Hyperledger Fabric on github
- Hyperledger Fabric Certificate Authority on github
- Hyperledger Fabric SDK Go on github
- Fabric SDK Go tests
- CLI: An example CLI for Fabric built with the Go SDK.