Bellman–Ford is based on the principle of relaxation, in which an approximation to the correct distance is gradually replaced by more accurate values until eventually reaching the optimum solution.[1] The approximate distance to each vertex is always an overestimate of the true distance, and is replaced by the minimum of its old value and the length of a newly found path. It is capable of handling graphs in which some of the edge weights are negative numbers. Negative edge weights are found in various applications of graphs, hence the usefulness of this algorithm. If a graph contains a "negative cycle" (i.e. a cycle whose edges sum to a negative value) that is reachable from the source, then there is no cheapest path: any path that has a point on the negative cycle can be made cheaper by one more walk around the negative cycle. In such a case, the Bellman–Ford algorithm can detect negative cycles and report their existence.
Bellman-Ford algorithm is a procedure used to find all shortest path in a graph from one source to all other nodes. The algorithm requires that the graph does not contain any cycles of negative length, but if it does, the algorithm is able to detect it.
The Bellman–Ford algorithm simply relaxes all the edges, and does this |V|-1 times, where |V| is the number of vertices in the graph. In each of these repetitions, the number of vertices with correctly calculated distances grows, from which it follows that eventually all vertices will have their correct distances. This method allows the Bellman–Ford algorithm to be applied to a wider class of inputs than Dijkstra. Bellman–Ford runs O(|V|.|E|) time, where |V| and |E| are the number of vertices and edges respectively.
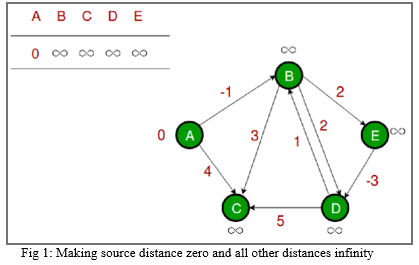
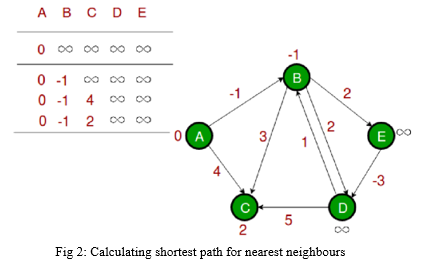
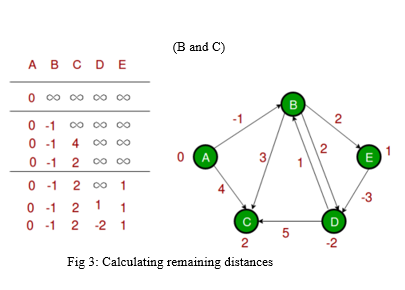
The algorithm initializes the distance to the source to 0 and all other nodes to infinity. Then for all edges, if the distance to the destination can be shortened by taking the edge, the distance is updated to the new lower value. At each iteration i that the edges are scanned, the algorithm finds all shortest paths of at most length i edges (and possibly some paths longer than i edges). Since the longest possible path without a cycle can be |V|-1 edges, the edges must be scanned |V|-1 times to ensure the shortest path has been found for all nodes. A final scan of all the edges is performed and if any distance is updated, then a path of length |V| edges has been found which can only occur if at least one negative cycle exists in the graph.
The required shortest path is calculated by entering the number of Vertices, Edges, Source node number and the respective source to destination distances of each edge. Hence, we use Ford Algorithm to calculate the shortest path in our code.