-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 25.2k
Description
❓ Questions and Help
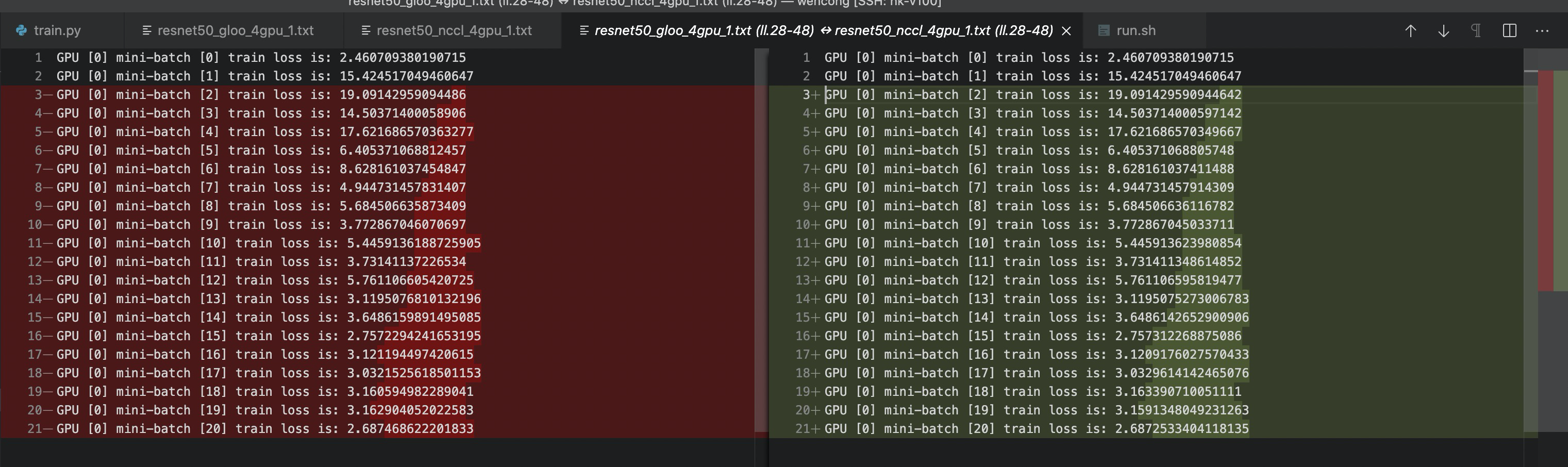
Why changing the backends of ddp from NCCL to GLOO introduces a significant difference in train loss (model accuracy)
I run a resnet50 model on cifar10 dataset for 20 mini-batch and print out the train loss of the first 20 mini-batches.
Using the script below for running the application of ddp in 4 GPUs
array=( resnet50 )
epoch=10
for i in "${array[@]}"
do
echo $i
for j in 1 2 3 4 5
do
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 MASTER_PORT=20480 python -u train.py -n 1 -g 4 -nr 0 -e ${epoch} --batch-size 32 -m $i --backend nccl &> ./${i}_nccl_4gpu_${j}.txt
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3 MASTER_PORT=20481 python -u train.py -n 1 -g 4 -nr 0 -e ${epoch} --batch-size 32 -m $i --backend gloo &> ./${i}_gloo_4gpu_${j}.txt
done
doneThe results of the same type of communication backend can be reproduced deterministically (thanks to https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html ).
However, the results of different backends (NCCL/GLOO) are different and spreading out by iterations.
Moreover, I find that such an issue can only be observed with more than 2 GPUs ( > two workers for ddp ).
For ddp of two GPUs, the train losses are exactlly the same for both two backends. Two-gpu script is listed as below.
array=( resnet50 )
epoch=10
for i in "${array[@]}"
do
echo $i
for j in 1 2 3 4 5
do
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 MASTER_PORT=20480 python -u train.py -n 1 -g 2 -nr 0 -e ${epoch} --batch-size 32 -m $i --backend nccl &> ./${i}_nccl_2gpu_${j}.txt
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 MASTER_PORT=20481 python -u train.py -n 1 -g 2 -nr 0 -e ${epoch} --batch-size 32 -m $i --backend gloo &> ./${i}_gloo_2gpu_${j}.txt
done
doneThe main code is here.
import os
import sys
from datetime import datetime
import argparse
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.distributed as dist
import numpy as np
import random
from models.resnet import ResNet50
def set_seed(seed):
# CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG=:4096:8 (will increase library footprint in GPU memory by approximately 24MiB)
# CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG=:16:8 (may limit overall performance)
os.environ['CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG'] = ":4096:8"
torch.manual_seed(seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
np.random.seed(seed)
random.seed(seed)
os.environ['PYTHONHASHSEED'] = str(seed)
torch.set_deterministic(True)
torch.set_default_tensor_type(torch.DoubleTensor)
torch.autograd.set_detect_anomaly(True)
# torch.set_printoptions(precision=10)
torch.set_printoptions(profile="full")
# note that it will dump too large files !!!
# np.set_printoptions(threshold=sys.maxsize)
# torch.set_printoptions(profile="default")
set_seed(0)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('-n', '--nodes', default=1, type=int, metavar='N',
help='number of data loading workers (default: 4)')
parser.add_argument('-g', '--gpus', default=1, type=int,
help='number of gpus per node')
parser.add_argument('-nr', '--nr', default=0, type=int,
help='ranking within the nodes')
parser.add_argument('-e', '--epochs', default=5, type=int, metavar='N',
help='number of total epochs to run')
parser.add_argument('-m', '--model', default="lenet",
help='the neural network model')
parser.add_argument('-bs', '--batch-size', default=64, type=int,
help='training batch size')
parser.add_argument('-ba', '--backend', default="nccl",
help='communication approach')
args = parser.parse_args()
args.world_size = args.gpus * args.nodes
os.environ['MASTER_ADDR'] = '127.0.0.1'
# os.environ['MASTER_PORT'] = '20480'
mp.spawn(train, nprocs=args.gpus, args=(args,))
def train_a_step(model, images, labels, criterion, optimizer, args, gpu_id, mini_batch_id):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(images)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# Backward and optimize
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
return outputs, loss
def train(gpu, args):
rank = args.nr * args.gpus + gpu
backend = args.backend
print(backend)
dist.init_process_group(backend, init_method='env://', world_size=args.world_size, rank=rank)
if args.model == "resnet50":
model = ResNet50()
else:
print("unrecognized model type")
return
torch.cuda.set_device(gpu)
model.cuda(gpu)
print("batch size: {}".format(args.batch_size))
batch_size = args.batch_size
# define loss function (criterion) and optimizer
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda(gpu)
model = nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model, device_ids=[gpu])
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-1)
# Data loading code
data_path = "./data/"
transform_train = transforms.Compose([
transforms.CenterCrop(32),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
])
transform_test = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)),
])
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root=data_path,
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transform_train)
train_sampler = torch.utils.data.distributed.DistributedSampler(train_dataset,
num_replicas=args.world_size,
rank=rank,
shuffle=False)
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=0,
pin_memory=True,
sampler=train_sampler,
drop_last=True)
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root=data_path,
train=False,
transform=transform_test,
download=True)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset,
batch_size=1000,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=0,
pin_memory=True,
drop_last=True)
start = datetime.now()
func = train_a_step
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
for i, (images, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
model.train()
images = images.to(torch.float64)
images = images.cuda(non_blocking=True)
labels = labels.cuda(non_blocking=True)
outputs, loss = func(model, images, labels, criterion, optimizer, args, gpu, i)
dist.all_reduce(loss, op=dist.reduce_op.SUM)
if gpu == 0:
loss /= args.world_size
print("GPU [{}] mini-batch [{}] train loss is: {}".format(gpu, i, loss.item()))
if i == 20:
return
if gpu == 0:
print("Training complete in: " + str(datetime.now() - start))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()For your convenience, all the code and logs are attached. resnet50.tar.gz
All the experiments are conducted on an 8 V100-GPU cloud server, using the official pytorch 170 docker (pytorch/pytorch:1.7.0-cuda11.0-cudnn8-devel).
As the other parts of the code are exactly the same, I think the difference should come from the allreduce of gradients.
However, the gradient synchronization is to just average the gradients of all workers, which should not introduce the difference in my view. Moreover, I am confused about the results. Which one is correct?
Thanks!
Wencong