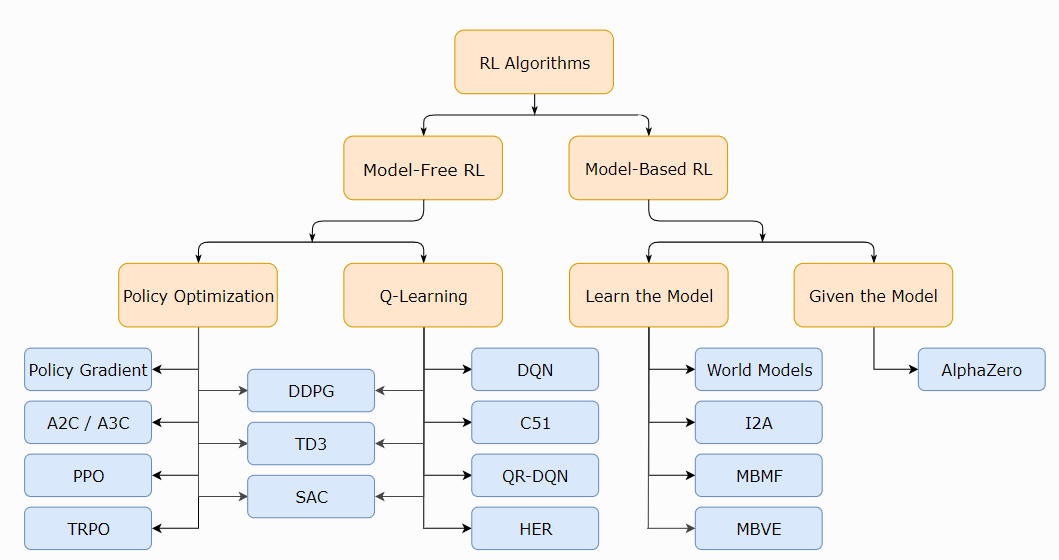
https://www.cloudcraftz.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/mind_map_rl_algos.png
the actor-critic method describes a method to approximate the value function to then derive an optimal policy the ac method consists of two DNNs: 1. used to approximate the agent's policy directly (actor) (policy is a prob distr) 2. used to approximate the value function (critic) both DNNs work together: the actor selects actions and the critic evaluates the states and the result is compared to the rewards from the environment belongs to Temporal Difference learning (since learning happpens in episodes)
algo overview:
- init actor critic network
- repeat for large number of episodes:
- reset the environment, score, terminal flag
- while state is not terminal:
- select action according to actor network
- take action and receive reward and new state
- plot scores over time for evidence of learning
- type of actor-critic method (two DNNs)
- critic evaluates state and action pairs
- actor decides what to do based on current state (or any other we pass through)
- network outputs action values, no probabilities here
- noise for explore-exploit dilemma
see paper 'Continuous Control with Deep Reinforcement Learning'
extension of 2. DDPG
-
in Q learning, there is bias from the max over actions
-
no max ni update rule for AC methods, so whats responsible for it?
-
overestimation (state is higher evaluated than it actually is thus resulting in a suboptimal solution) also comes from approximation errors
-
neural networks are a source of approximation error
-
AC methods are bootstrpped so errors accumulate
-
double Q learning uses two Q networks
-
can use clipped double Q which underestimates
-
delay policy updates to give Q time to converge
-
use target networks for actor and (both) critics (6 in total)
-
use soft updates to the target network
see paper 'Addressing Function Approximation Error in Actor-Critic Methods'
-
tries to resolve the issue that in AC methods performance can decline quickly and hardly recovers (due to the fact that ac methods is very sensitive to pertubations e.g. small change in networks weights can change the output significantly)
-
limits update to policy network by baseing the update on the ration of new policy to old
-
two distinct networks instead of shared inputs
-
critic evaluates states (not s,a pairs!)
-
actor decides what to do based on current state
- network outputs probs (softmax) for a distribution
- exploration due to nature of distribution
see paper 'Proximal Policy Optimization Algorithms'
-
how to use a maximum entropy framework in actor critic?
-
maximizes both long term rewards and entropy
-
similar to Q learning (epsilon greedy)
-
entropy modeled by reward scalling (inv. relationship)
-
leverages actor, value network and critic networks
-
actually uses two critics like double Q learning / TD3
-
also makes use of a target value function (soft update)
-
actor network models mean and sigma of distribution
see paper 'Soft Actor-Critic: Off-Policy Maximum Entropy Deep Reinforcement Learning with a Stochastic Actor'
- instead of Replaybuffer, allow multiple agents to play independently on separate environments
see paper 'Asynchronous Methods for Deep Reinforcement Learning'