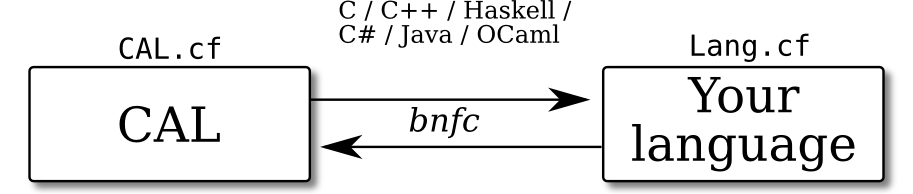
This repository contains CAL.cf, a labelled BNF grammar file
defining syntax of the CAL actor programming language. The
BNFC software generates compiler
components for C, C++, C#, Haskell, Java, and OCaml, i.e. compilers
written in these languages can parse and generate CAL actor source
code.
The labelled BNF rules are based on Annex D of the Internation
Standard ISO/IEC 23001-4, Information technology — MPEG systems
technologies - Part 4: Codec configuration representation 3rd
edition, with modifications to conform to expectations of the CAL
frontend of the Orcc compiler. From
these BNF rules, the bnfc executable generates:
- an abstract syntax implementation
- a case skeleton for the abstract syntax in the same language
- an Alex, JLex, or Flex lexer generator file
- a Happy, CUP, or Bison parser generator file
- a pretty-printer as a Haskell/Java/C++/C module
- a Latex file containing a readable specification of the language
More information about BNFC is at http://bnfc.digitalgrammars.com.
The source files generated by bnfc enables the parsing of a CAL
actor file into an AST, or the pretty-printing of an AST to CAL syntax
as a string which can then be written to a .cal file. This supports
compilers that use CAL dataflow as a language backend for multicore or
embedded processors, and also supports writing new CAL backends. This
is shown here:
The following example shows how to create a .cal file for a simple
CAL actor. First, we create our compiler components:
bnfc -m --haskell CAL.cf
Then we can programmatically construct a CAL actor using data type
constructors to construct an AST for the actor. We can then use the
printTree to create a string we can write to a .cal file:
module Main where
import qualified PrintCAL as C
import qualified AbsCAL as C
main :: IO ()
main = do
let actorCode = C.printTree actor
writeFile "my_actor.cal" actorCode
actor :: C.Actor
actor = actorAST
where
actorAST = C.Actr (C.PathN [C.PNameCons (C.Ident "cal")]) imports (C.Ident "my_actor") actorPar ioSig varDecl [action] priorityBlock
priorityBlock = []
actorPar = []
imports = []
varDecl = [ C.VDecl (intCalType 8) (C.Ident "i") [] ]
ioSig = C.IOSg [C.PortDcl (intCalType 8) (C.Ident "In")] [C.PortDcl (intCalType 8) (C.Ident "Out")]
inputPattern = [ C.InPattTagIds (C.Ident "In") [(C.Ident "x")] ]
outputPattern = [ C.OutPattTagIds (C.Ident "Out") [(C.Ident "i")] ]
actionHead = C.ActnHead inputPattern outputPattern
action = C.AnActn (C.ActnTagsStmts (C.ActnTagDecl [C.Ident "the_action"]) actionHead stmts)
stmts = [ C.SemiColonSeparatedStmt (C.AssignStt (C.AssStmt (C.Ident "i") (C.BEAdd (C.EIdent (C.Ident "i")) (C.EIdent (C.Ident "x"))))) ]
intCalType i = C.TypParam C.TUint [C.TypeAttrSizeDf (C.LitExpCons (C.IntLitExpr (C.IntegerLit i)))]Compiling and running this Haskell program generates the
following my_actor.cal file:
package cal ;
actor my_actor () uint (size = 8)In ==> uint (size = 8)Out :
uint (size = 8) i;
the_action : action In : [x]==> Out : [i]
do i := i + x ;
end
end
This repository also exposes a cabal project called cal-src for
compiler related Haskell projects that wish to use CAL as either a
frontend or a backend. Once in the repository, simply run:
$ cabal install
Once you add cal-src as a build depdendency in your cabal-ised
project, you should be able to import all relevant modules, i.e.
import qualified LexCAL as C
import qualified ParCAL as C
import qualified SkelCAL as C
import qualified PrintCAL as C
import qualified AbsCAL as C