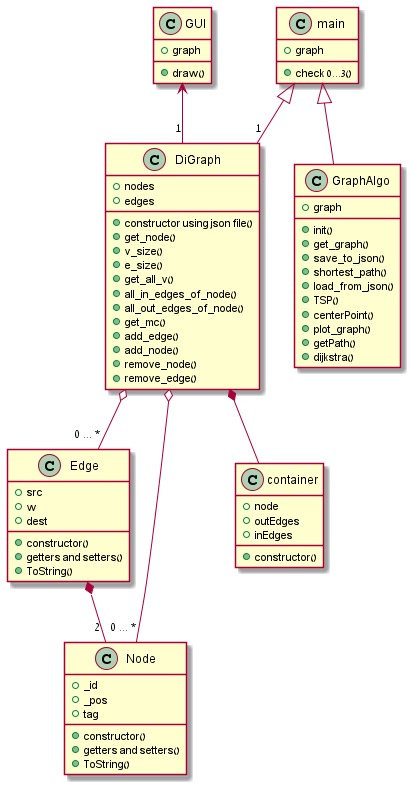
Graph calculator is a simple program that can create, load(via JSON file) , and edit directed weighted graphs. After receiving/loading a graph from a JSON file it can be used as the basis for many graph operations, such as finding the shortest path between two nodes, finding the center, etc...
The manipulated graph can be saved to json file.
- Shortest path: We call Dijkstra's algorithm on the source node, fetch the parents array it returns, and use it to calculate the path to the destination vertex Then, using backtracking we construct the path between these two nodes.
- Center: The implementation is rather simple, we first compute the eccentricity of each node (eccentricity:wikipedia) using Dijkstra's algorithm on each vertex and taking the max distance. then, we pick the vertex with the smallest eccentricy as the center
- Tsp-Traveling salesmen problem: We start from some random node from the list, perform the Dijkstra algorithm, and travel to the closest Unvisited node from the list, we keep doing that until we reached all the nodes from the list. following this method will yield us a valid path, albeit not necessarily the shortest. we repeat this process for each node in the list, each time picking another vertex as a starting point. in the end we return the shortest path we've found
- Extract the downloaded zip file, and open the project in Python environment workspace (VERY IMPORTANT TO DOWNLOAD THE LIBRARY "MATPLOTLIB").
- In class "main" you run the project itself as described:
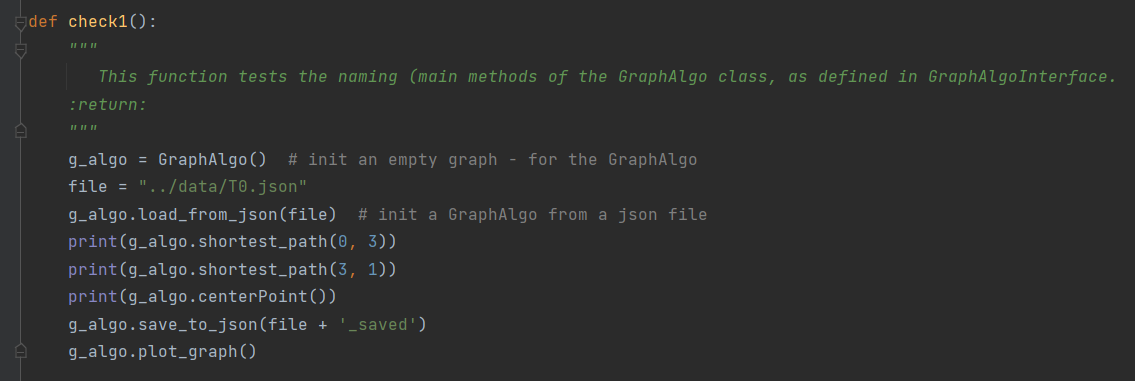
- There are 4 check functions that are already in the project. you can change each one of them as you desire, or to create a new check function.
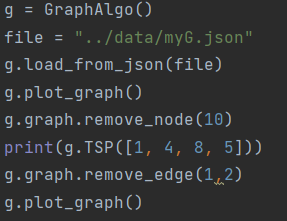
- example of a check function:
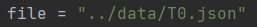
- To upload a graph from a Json file do the following:
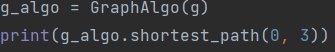
- Init an empty graph - for the GraphAlgo:
- To create a graph (not via upload), do the following:
- Create an empty directed graph:
- Example: Here we call the algorithm "shortest path"
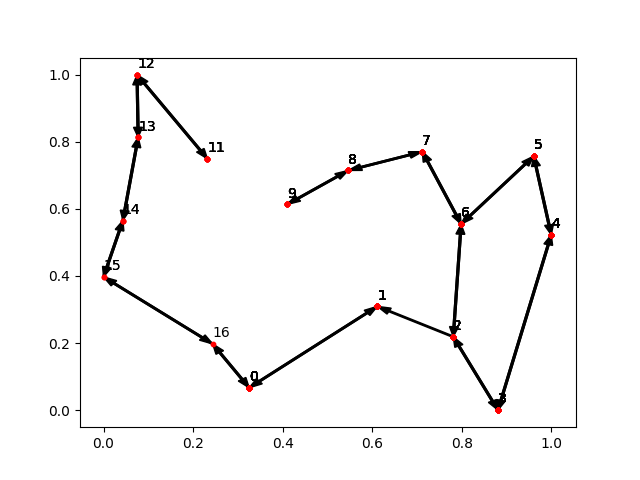
- Example: first picture shows the graph before the changes, the second shows the graph after we called the function "remove edge":
Dijkstra's algorithm played a major part in our work, being part of every algorithm. After our first implementation of the algorithm (using regular priority queue) proved to be too slow for our purposes, we implemented it again using python's min heap Queue library - heapq. Using the new implementation and after little bit of profiling, we managed to greatly improve our running time.
First, download/clone the project from git. Afterwards do the following:
- Write the path to where the file is at:
- Init a GraphAlgo from a json file:
To run the algorithms, just call the algorithm function that you would like to activate, inside a print call, so you will get the answer of the algorithm.
To run changes on the graph, call the function that you would like to, and don't forget to call right afterwards to the function plot_graph() in order to see the changes.
Example of how to write the changes and plotting the graph:
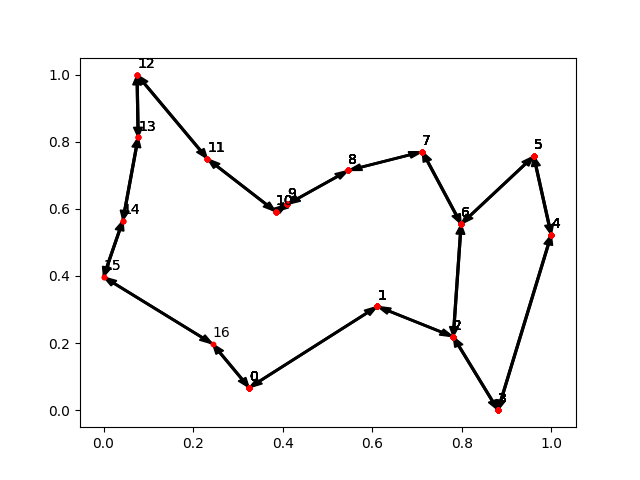
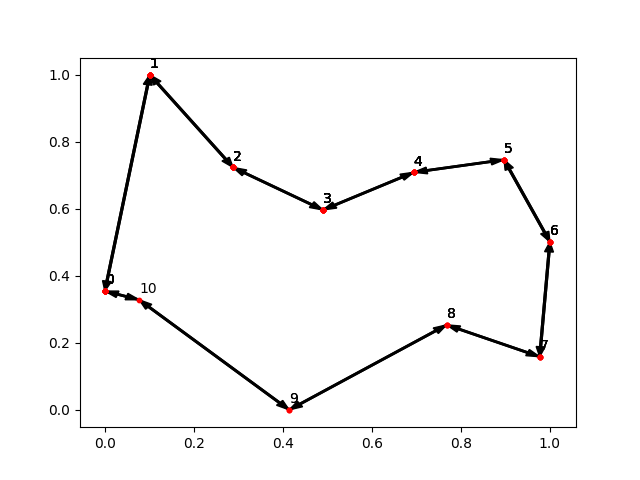
Some examples of graphs visualizations: