A toolbox for creating, maintaining, and querying Semantic Object Maps (SOMAs). SOMAs can include objects, regions of interest (ROI), and trajectories.
Currently there are two modeling tools:
- the SOMA object manager
- the SOMA ROI manager (ROI = regions of interest)
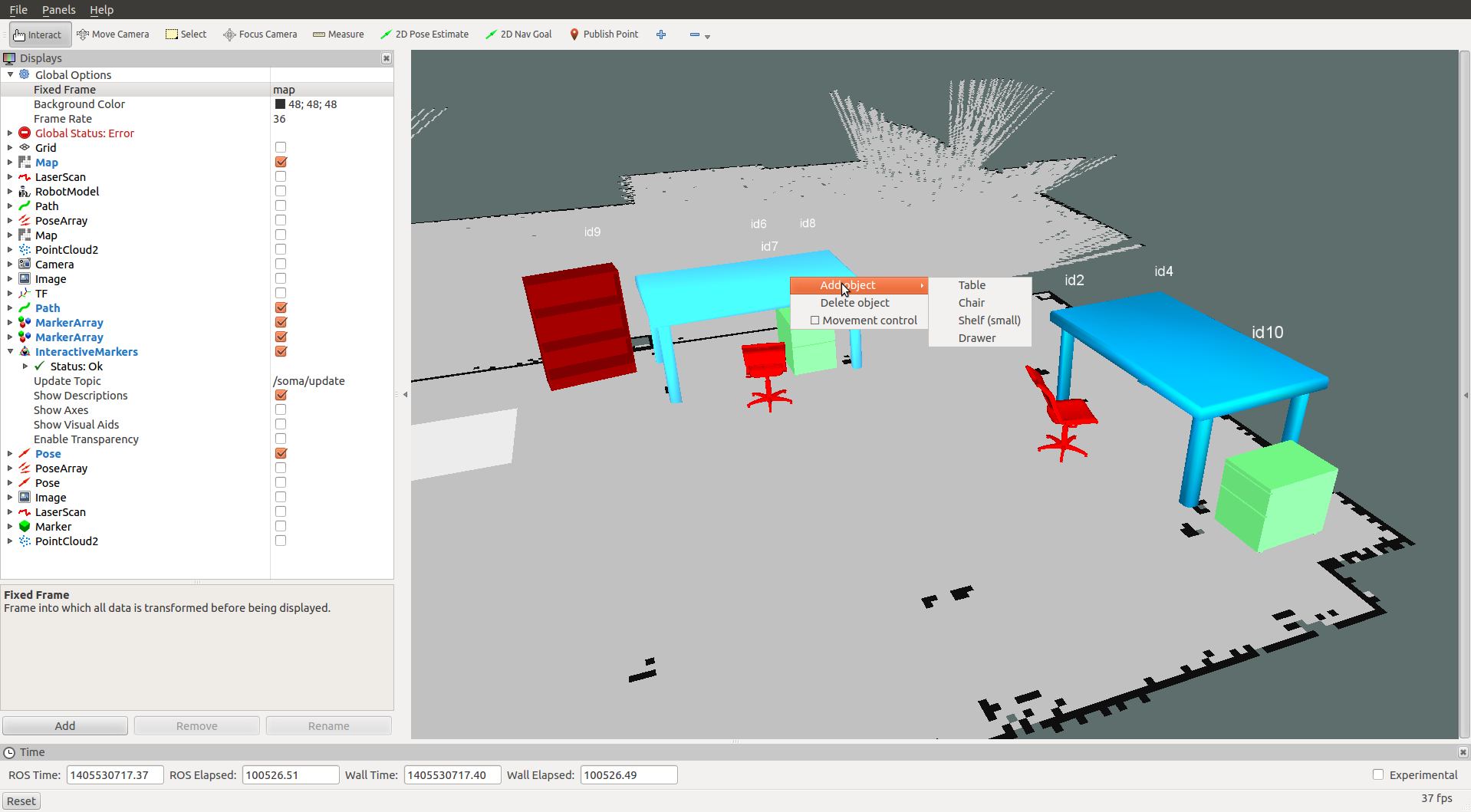
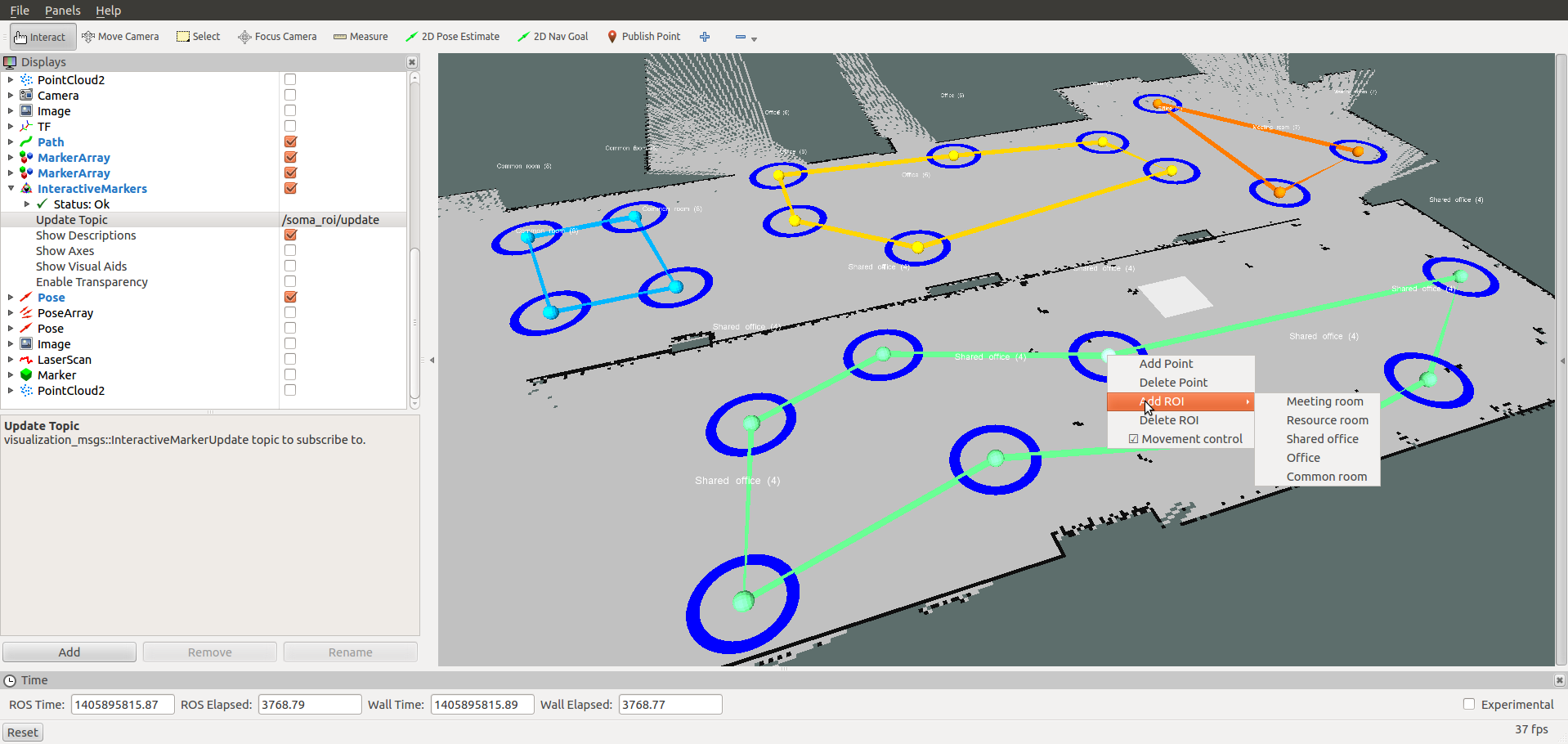
The SOMA manager for objects visualizes objects in RVIZ where the user can add, delete, move, and rotate them interactively. The SOMA manager for ROIs visualizes regions in RVIZ where the user can add, delete, and modify them. Both the object and the ROI configurations are immediately stored and updated in the ROS datacentre (MongoDB).
Trajectories can be added to a SOMA using an import tool. These trajectories are generated from the output of the bayes_people_tracker in (strands_perception_people).
A query service (ROS Service) allows a caller to extract a set of trajectories based on spatial-temporal restritions. For example, a query can filter out trajectories that are near an object, within a region, or intersect with another object (region, trajectory). Additionally, temporal constraints can be specified to select only trajectories that were observed during a certain interval.
- MongoDB (>=2.4)
- mongodb_store
- ROS's navigation stack (only map server)
- strands_perception_people
-
Start the ros core:
$ roscore -
Launch the ROS datacentre:
$ roslaunch mongodb_store datacentre.launch -
Run the map_server with a 2D map:
$ rosrun map_server map_server <map.yaml>
where map.yaml specifies the map you want to load.
- Start RVIZ, add a Map display type and subsribe to the
/maptopic:
$ rosrun rviz rviz
-
Run the SOMA object manager:
$ rosrun soma_manager soma.py <map> <config>
where map denotes the name of the 2D map (Step 3) and config denotes an object configuration within this map. By default, the configuration file soma_objects/config/default.json is used to initialize the list of available object types. Alternatively, the following command can be used to use a different configuration file:
```
$ rosrun soma_manager soma.py -t /path/to/config/file <map> <config>
```
- In RVIZ, add an InteractiveMarker display type, and subsribe to the
/soma/updatetopic: - Add, delete, move, and rotate objects in RVIZ using the interactive marker and the context menu (right-mouse-click)
-
Run the SOMA ROI manager:
$ rosrun soma_roi_manager soma_roi.py <map> <config>
where map denotes the name of the 2D map (Step 3) and config denotes an object configuration within this map. By default, the configuration file soma_roi_manager/config/default.json is used to initialize the list of available ROI types. Alternatively, the following command can be used to use a different configuration file:
```
$ rosrun soma_roi_manager soma_roi.py -t /path/to/config/file <map> <config>
```
- In RVIZ, add an InteractiveMarker display type, and subsribe to the
/soma_roi/updatetopic: - Add, delete, modify ROIs in RVIZ using the interactive marker and the context menu (right-mouse-click)
-
Trajectories can be impoerted as follows:
$ rosrun soma_trajectory trajectory_importer.py
-
The service can be started as follows:
$ rosrun soma_trajectory trajectory_query_service.py
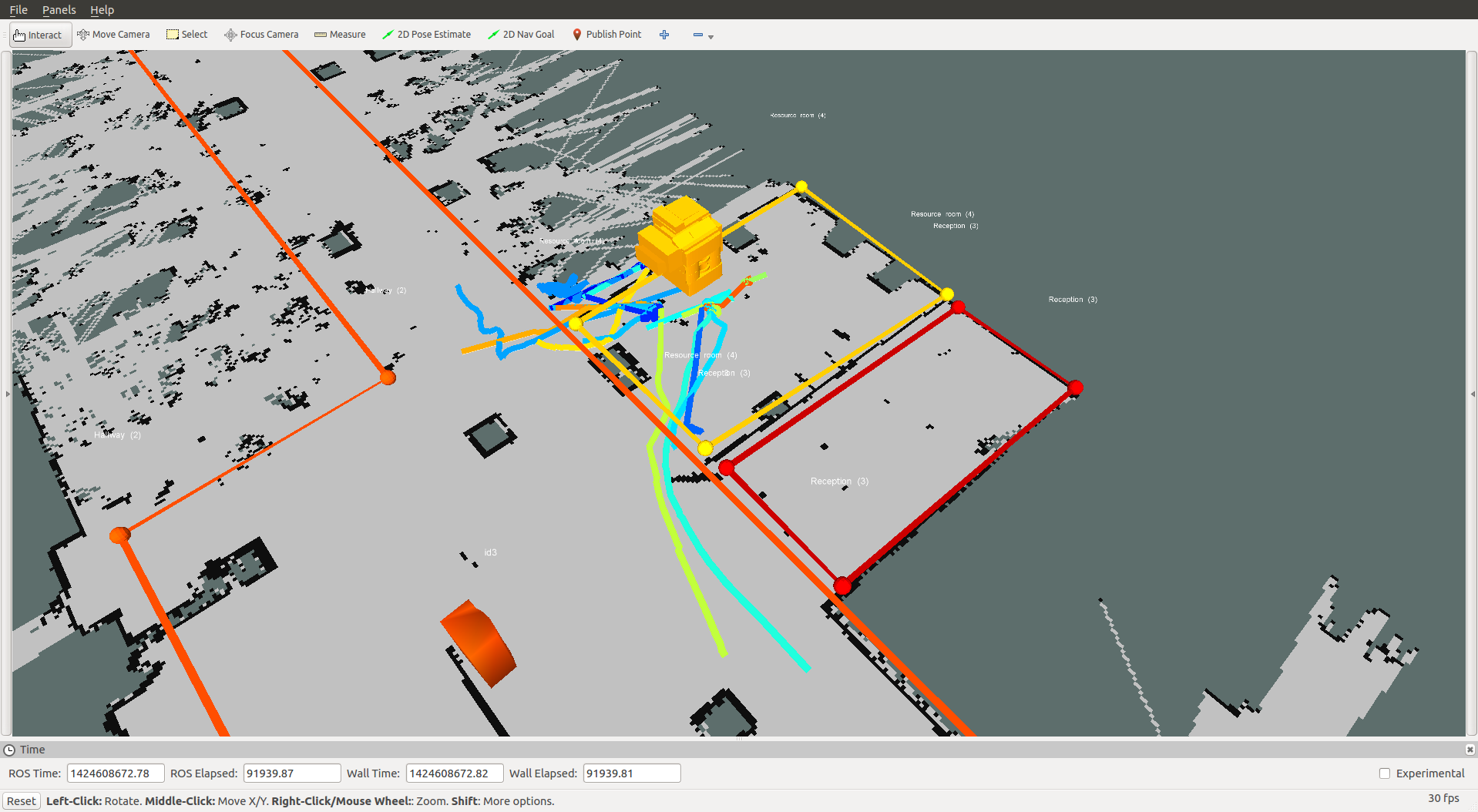
The service request includes a MongoDB query in json format and a boolean flag whether the result should be visualized (see image below). The response has a boolean error flag (in case the JSON was invalid) and list of trajectories that match the query specification.
Here is an example query:
{"loc": {"$nearSphere": { "$geometry":
{ "type" : "Point",
"coordinates" :
[ -0.0002281133006505343, -4.632269674686995e-05 ]
},
"$maxDistance": 1
}
}
}
Further examples are here: https://github.com/kunzel/soma/blob/master/soma_trajectory/scripts/query_examples.py