Implementation of CSMA/CD 1-Persistent Method using Java programming language
- The Data Link Layer is responsible for transmission of data between two nodes. Its main functions are-
- Data Link Control
- Multiple Access Control
- If there is a dedicated link between the sender and the receiver then data link control layer is sufficient, however if there is no dedicated link present then multiple stations can access the channel simultaneously. Hence multiple access protocols are required to decrease collision and avoid crosstalk.
- Carrier Sense Multiple Access/ Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is one of the multiple access protocols in computer networks. More accurately, it is a random access protocol.
- In a random access protocol, all stations have same superiority that is no station has more priority than another station. Any station can send data depending on medium’s state( idle or busy). It has two features:
- There is no fixed time for sending data
- There is no fixed sequence of stations sending data
- CSMA/CD is short for Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection, CSMA/CD is a MAC (media access control) protocol. It defines how network devices respond when two devices attempt to use a data channel simultaneously and encounter a data collision. The CSMA/CD rules define how long the device should wait if a collision occurs. The medium is often used by multiple data nodes, so each data node receives transmissions from each of the other nodes on the medium. There are several CSMA access modes: 1- persistent, P-persistent, and O-persistent.
- Variations of CSMA use different algorithms to determine when to initiate transmission onto the shared medium. A key distinguishing feature of these algorithms is how aggressive or persistent they are in initiating transmission. A more aggressive algorithm may begin transmission more quickly and utilize a greater percentage of available bandwidth of the medium. This is typically at the expense of increased likelihood of collision with other transmitters
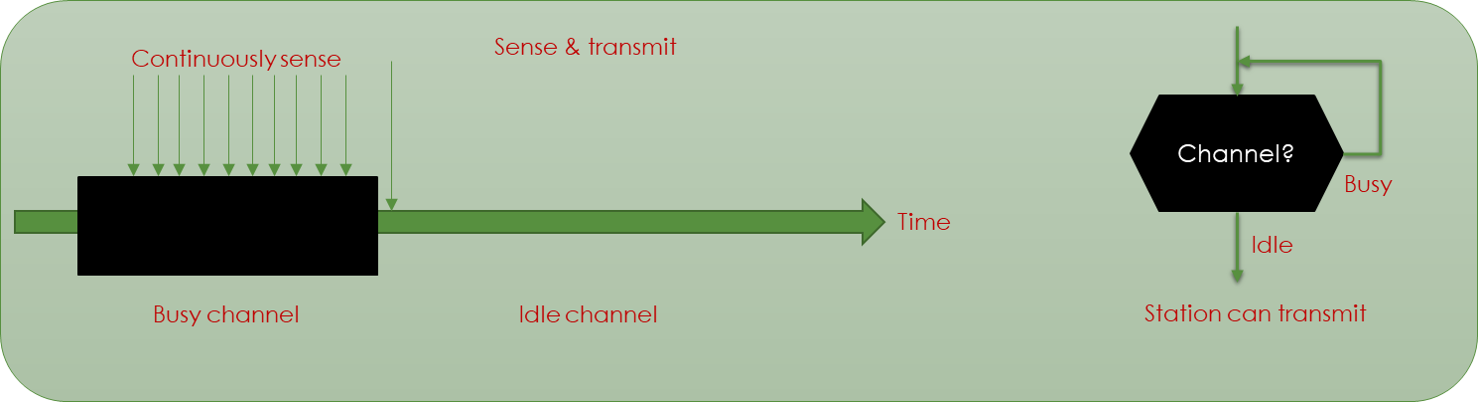
1-persistent CSMA is an aggressive transmission algorithm. When the transmitting node is ready to transmit, it senses the transmission medium for idle or busy. If idle, then it transmits immediately. If busy, then it senses the transmission medium continuously until it becomes idle, then transmits the message (a frame) unconditionally (i.e. with probability=1). In case of a collision, the sender waits for a random period of time and attempts the same procedure again. 1-persistent CSMA is used in CSMA/CD systems including Ethernet.
As a team, we decided to use Java as our programming language of choice. Few of the reasons we opted for
Java over C/C++ include the Java concept of “Threads” that was not available in C/C++ programming
languages, as well as the OOP feature of classes and objects that are absent in the C programming language.
Using the multithreading concept, we were able to implement a CSMA/CD 1-persistent model using in-built
thread functions such as join().
We also put to use other core Java concepts such as Exception Handling, Inheritance and Synchronization.
Our problem statement also specified that the minimum number of stations to be implemented in this model
are six and hence, we developed a model that would do so
The algorithm used to develop the required 1-persistent CSMA/CD model is as follows
Step 1: When a frame is ready, the transmitting station checks whether the channel is idle or busy.
Step 2: If the channel is busy, the station waits and continually checks until the channel becomes idle.
Step 3: If the channel is idle then it transmits the frame immediately, with a probability 1.
Step 4: A collision may occur if two or more channels transmit simultaneously. If collision occurs, the station waits for a random period of time and restarts the algorithm all over again.