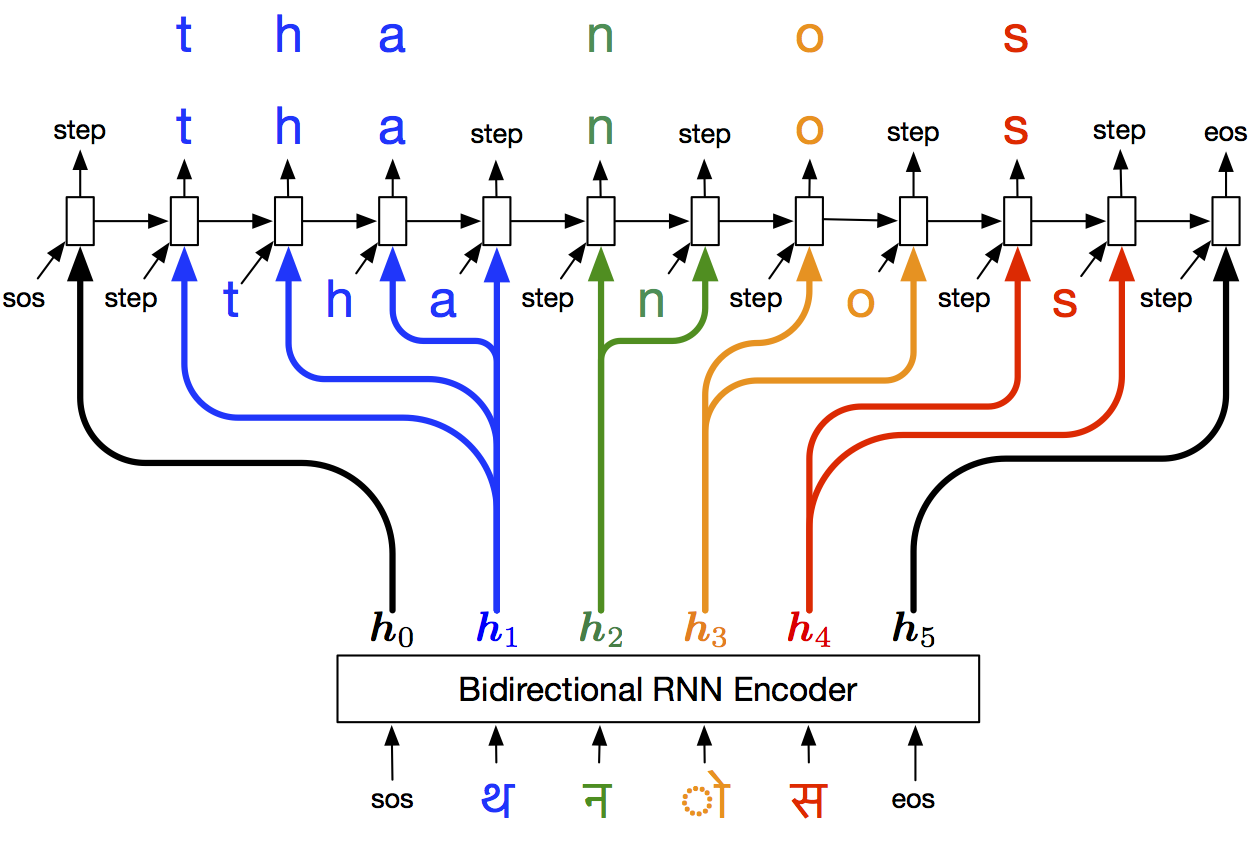
Code for the EMNLP paper, "Bootstrapping Transliteration with Guided Discovery for Low-Resource Languages".
- python3
- pytorch version '0.3.1'. Can be installed using the following command,
conda install -c pytorch pytorch=0.3.1
- editdistance
pip install editdistance
Download and untar the relevant trained model. Right now the models for bengali, kannada or hindi trained on the NEWS2015 datasets are available.
Each tarball contains the vocab files and the pytorch model.
To run in interactive mode
./load_and_test_model_interactive.sh hindi_data.vocab hindi.modelYou will see a prompt to enter surface forms in the source writing script (see below)
...
...
:INFO: => loading checkpoint hindi.model
:INFO: => loaded checkpoint!
enter surface:ओबामा
ओ ब ा म ा
[(-0.4624647759074629, 'o b a m a')]
- First prepare a test file (let's call it
hindi.test) such that each line contains a sequence of space separated characters of each input token,
आ च र े क र
आ च व ल
- Then run the trained model on it using the following command,
./load_and_test_model_on_files.sh hindi_data.vocab hindi.model hindi.test hindi.test.outThis will generate output in the test file as follows,
आ च र े क र a c h a r e k a r;a c h a b e k a r;a a c h a r e k a r -0.6695770507547368;-2.079195646460341;-2.465612842870943
where the 2nd column is the (';' delimited) output from the beam search (using beam_width of 3) and 3rd column contains the (';' delimited) corresponding scores for each item.
That is, the model score for a c h a r e k a r was -0.6695770507547368.
- First compile the C code for the aligner.
cd baseline/
make- write you train, dev and test data in the following format,
x1 x2 x3<tab>y1 y2 y3 y4 y5
where x1x2x3 is the input word (xi is the character), and y1y2y3y4y5 is the desired output (transliteration). Example train and test files for bengali are in data/ folder. There is a optional 3rd column marking whether the word is native or foreign (see the paper for these terms); this column can be ignored for most purposes.
- Create the vocab files and aligned data using
prepare_data.sh
./prepare_data.sh hindi_train.txt hindi_dev.txt 100 hindi_data.vocab hindi_data.aligned This will create two vocab files hindi_data.vocab.envoc and hindi_data.vocab.frvoc, and a file hindi_data.aligned containing the (monotonically) aligned training data .
- Run
train_model_on_files.shon your train (say train.txt) and dev file (dev.txt) as follows,
./train_model_on_files.sh hindi_data.vocab hindi_data.aligned hindi_dev.txt 100 hindi.modelwhere 100 is the random seed and hindi.model is the output model.
Other parameters like embedding size, hidden size (see utils/arguments.py for all options) can be specified by modifying the train_model_on_files.sh script appropriately.
- Test the trained model as follows,
./load_and_test_model_on_files.sh hindi_data.vocab hindi.model hindi_test.txt output.txtThe output should report relevant metrics,
...
...
:INFO: --------------------TEST--------------------
:INFO: running infer on example 200
:INFO: running infer on example 400
:INFO: running infer on example 600
:INFO: running infer on example 800
:INFO: accuracy 367/997=0.37
:INFO: accuracy (nat) 308/661=0.47
:INFO: accuracy (eng) 59/336=0.18
:INFO: ********************total********************
:INFO: ACC: 0.371457 (367/988)
:INFO: Mean F-score: 0.910995
:INFO: Mean ED@1: 1.136640+-1.167
:INFO: Mean NED@1: 0.084884
:INFO: Median ED@1: 1.000000
...
...