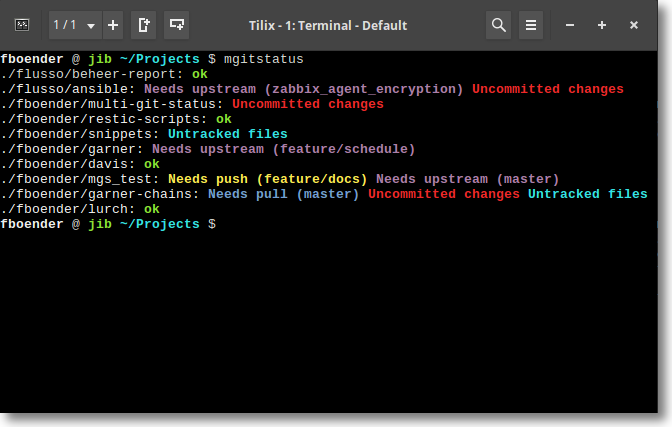
Show uncommited, untracked and unpushed changes in multiple Git repositories. Scan for .git dirs up to DEPTH directories deep. The default is 2. If DEPTH is 0, the scan is infinitely deep.
mgitstatus shows:
- Uncommitted changes if there are unstaged or uncommitted changes on the checked out branch.
- Untracked files if there are untracked files which are not ignored.
- Needs push (BRANCH) if the branch is tracking a (remote) branch which is behind.
- Needs upstream (BRANCH) if a branch does not have a local or remote upstream branch configured. Changes in the branch may otherwise never be pushed or merged.
- Needs pull (BRANCH) if the branch is tracking a (remote) branch which is
ahead. This requires that the local git repo already knows about the remote
changes (i.e. you've done a
fetch), or that you specify the-foption. mgitstatus does NOT contact the remote by default. - X stashes if there are stashes.
Since there are a lot of different states a git repository can be in, mgitstatus makes no guarantees that all states are taken into account.
mgitstatus can also list dirs that are not a repo, if given the -w
switch. To ignore certain repos, set the mgitstatus.ignore git config flag
for that repo to true. (See "usage" below for an example).
Usage: ./mgitstatus [--version] [-w] [-e] [-f] [--no-X] [-d/--depth=2] [DIR [DIR]...]
mgitstatus shows uncommited, untracked and unpushed changes in multiple Git
repositories. By default, mgitstatus scans two directories deep. This can be
changed with the -d (--depth) option. If DEPTH is 0, the scan is infinitely
deep.
--version Show version
-w Warn about dirs that are not Git repositories
-e Exclude repos that are 'ok'
-f Do a 'git fetch' on each repo (slow for many repos)
-c Force color output (preserve colors when using pipes)
-d, --depth=2 Scan this many directories deep
You can limit output with the following options:
--no-push
--no-pull
--no-upstream
--no-uncommitted
--no-untracked
--no-stashes
The following example scans all directories under the current dir, with a depth of 2. That means the current dir and all directories directly under it.
~/Projects/fboender $ mgitstatus
./mgitstatus: ok
./mdpreview: ok
./snippets: ok
./boxes: ok
./ansible-cmdb: Uncommitted changes Untracked files
./scriptform: Uncommitted changes
For more examples, see the manual page.
mgitstatus requires a POSIX compliant shell. Bash will do fine.
The following steps will install mgitstatus:
# Clone the repo
$ git clone https://github.com/fboender/multi-git-status.git
$ cd multi-git-status
# Install globally (all users)
$ sudo ./install.sh
# Install locally (only your user)
$ PREFIX=~/.local ./install.sh
mgitstatus is released under the MIT license.