This repository contains a collection of Android apps built on top of IPv8 (our P2P networking stack) and TrustChain (a scalable, distributed, pair-wise ledger). All applications are built into a single APK, following the concept of super apps – an emerging trend that allows to provide an ecosystem for multiple services within a single all-in-one app experience.
TrustChain Explorer allows to browse the TrustChain blocks stored locally on the device and crawl chains of other connected peers. It also demonstrates how to interact with TrustChainCommunity. It defines its own DemoCommunity to ensure that all users using the app are able to discover each other easily. The content of the app is split into several tabs:
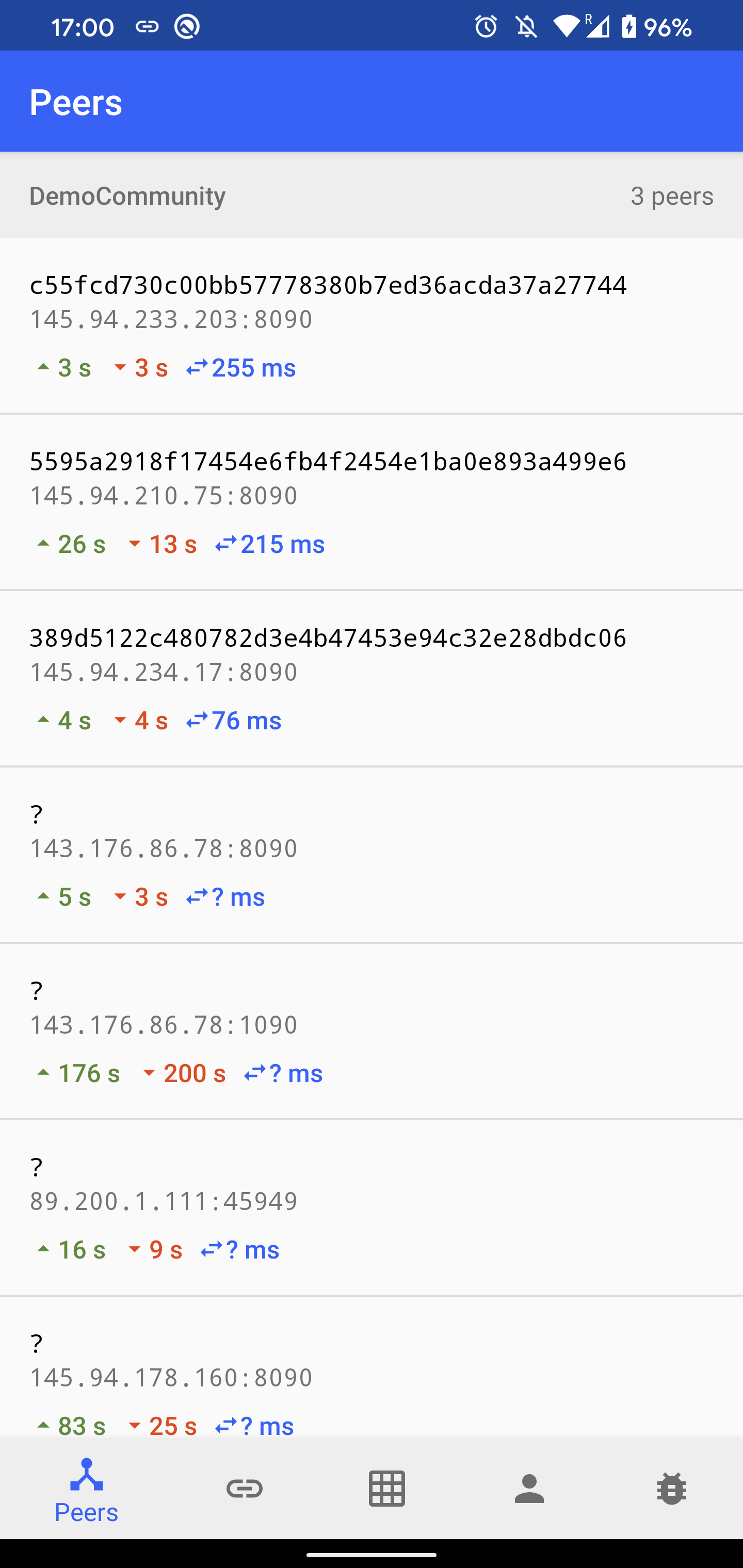
- Peers: A list of discovered peers in
DemoCommunity. For each peer, there is a time since the last sent and received message, and an average ping latency. After clicking on the peer item, a list of mutual blocks in TrustChain is shown. It is possible to create and send a new proposal block by clicking on the plus icon. A crawl request send be sent by clicking on the refresh button. - Chains: A list of discovered chains in
TrustChainCommunity, ordered by their length. After clicking on the item, the list of stored blocks is shown. - All Blocks: A stream of all received blocks, updated in real-time as new blocks are received from the network.
- My Chain: A list of blocks in which the current user is participating either as a sender or a receiver. It is possible to create a new self-signed block by clicking on the plus icon. It is posible to sign received blocks if they are not defined to be signed automatically.
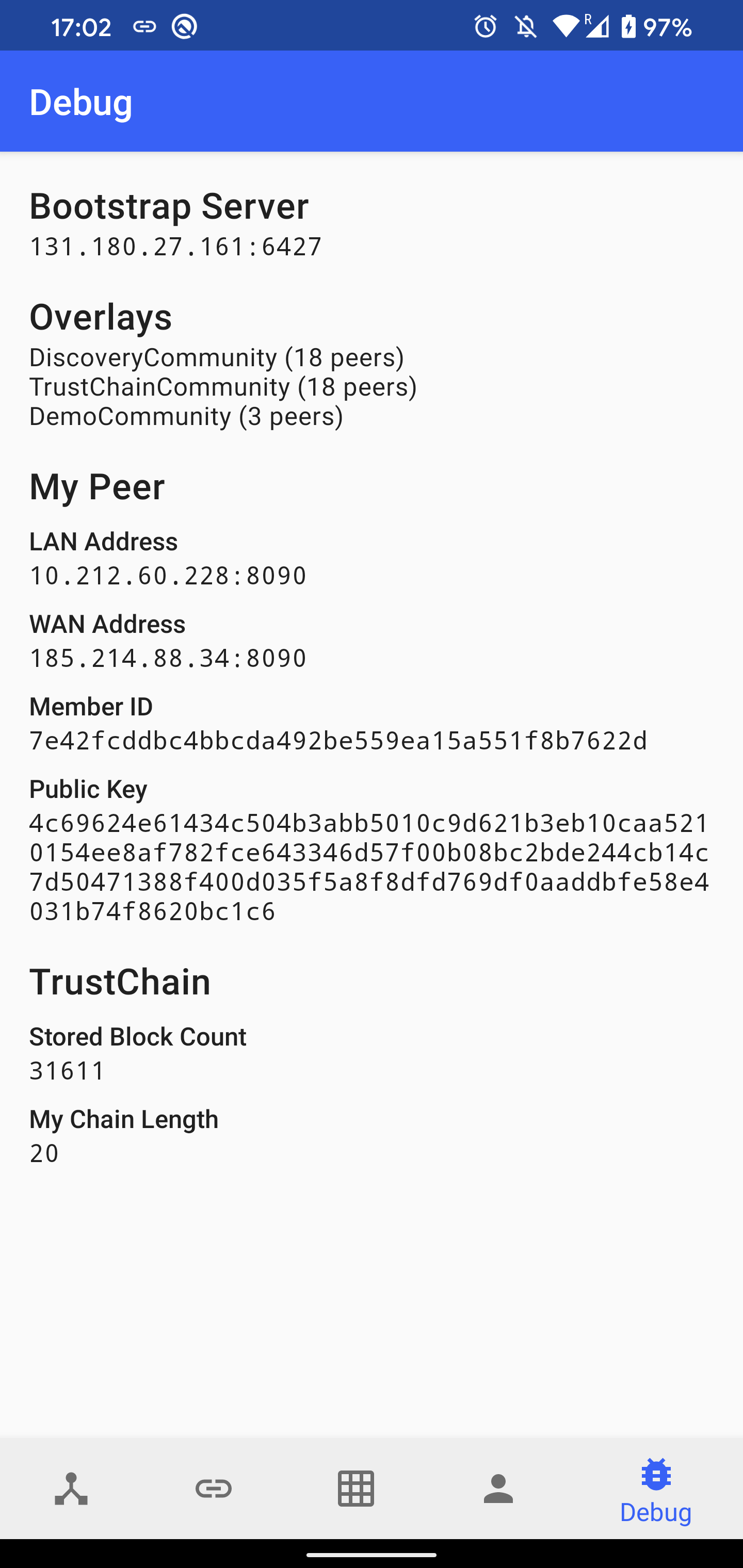
Debug shows various information related to connectivity, including:
- The list of bootstrap servers and their health. The server is considered to be alive if we received a response from it within the last 120 seconds.
- The number of connected peers in the loaded overlays.
- The LAN address estimated from the network interface and the WAN address estimated from the packets received from peers outside of our LAN.
- The public key and member ID (SHA-1 hash of the public key)
- TrustChain statistics (the number of stored blocks and the length of our own chain)
AI trading bot consist of two parts.
- An AI trading bot using a Naive Bayes Classifier which buys or sells Bitcoins in a decentralized market.
- Sending and receiving money to and from other peers.
Trading The AI trading bot app is visible upon opening the superapp. It receives bids and asks from other peers that want to buy or sell Bitcoins for Dymbe Dollars. Upon receiving a bid or ask, it decides to either execute the offer or not. The bot can be toggled on and off using the toggle on the home screen.
Send/Receive In the sending/receiving money tab one can send money to, or receive money from a different peer. There are two ways to find a public key:
- The receiving peer presses the send/receive toggle. His public key will be shown as a QR-code. Now pressing the "scan" button on the sender's device allows you can scan the QR code of the receiver.
- As a sender, go to the "Peers" fragment in the app, and press the public key of the receiver.
The market bot app can generate bids and asks which are received by the peers in the market community. The bid and asks can either be generated automatically or manually. Those bids and asks will be sent as IPv8 messages.
Luxury communism is an Android application built on top of IPv8 and Trustchain, and is integrated into the Trustchain Superapp. It is a proof-of-concept implementation of a DAO system using Trustchain and Bitcoin. Trustchain is used for communication and bookkeeping while the Bitcoin blockchain is used to have collective multi-signature wallets for each DAO. The content of the app is split up in several tabs:
- First Time Launch: The first time the app is launched, the user must setup his bitcoin wallet. Afterwhich the chain will sync and he is routed to the main screens.
- My DAO's: A list of all DAO's that the user participates in. Selecting a DAO will allow a user to create a transfer proposal from that DAO.
- All DAO's: A list of all discovered DAO's in the network which the user can propose to join.
- Proposals: A list of all proposals that the user can vote on. This can either be join proposals or proposals from someone else to transfer funds from one of the DAO's.
- My Wallet: Overview of the used Bitcoin wallet and the ability to chane this to another.
- Duplicate Wallet: In case the user has wallet files for both TestNet and Production, the user is allowed to select which one to keep. After the user selected either one, the files belonging to other network type are backed up. This, thus, ensures that the wallet is not lost.
The TrustChain Voter can be used to create a proposal on which the community can vote. The functionality has been split up in two parts: a Voting API, which provides the core voting functionality, and a TrustChain Voter submodule, which serves to demonstrate the capabilities of the voting API. Below, the process of creating a proposal (left) and casting a vote (right) can be seen.
Freedom-of-Computing is an extension-app of the trustchain app. It enables the users to share files in the forms of torrents, through a torrent peer-to-peer (P2P) network, which is the same peer-to-peer network that we call "DemoCommunity" within the app. More specifically though, the purpose of the torrent network is to enable users to freely distribute code in the form of .apk files. The code can be uploaded (seeded) and downloaded by the users, who can then dynamically load that code and execute it. The code, apart from being an .apk file, needs to have a specific format for its execution to work, the requirements/constraints are listed below.
The left demo shows the upload procedure, while the right demo shows the download and code execution procedure.
More about Freedom-of-Computing App
If you want to build an APK, run the following command:
./gradlew :app:buildDebug
The resulting APK will be stored in app/build/outputs/apk/debug/app-debug.apk.
You can also build and automatically install the app on all connected Android devices with a single command:
./gradlew :app:installDebug
Note: It is required to have an Android device connected with USB debugging enabled before running this command.
Run unit tests:
./gradlew test
Run instrumented tests:
./gradlew connectedAndroidTest
Ktlint is used to enforce a consistent code style across the whole project.
Check code style:
./gradlew ktlintCheck
Run code formatter:
./gradlew ktlintFormat