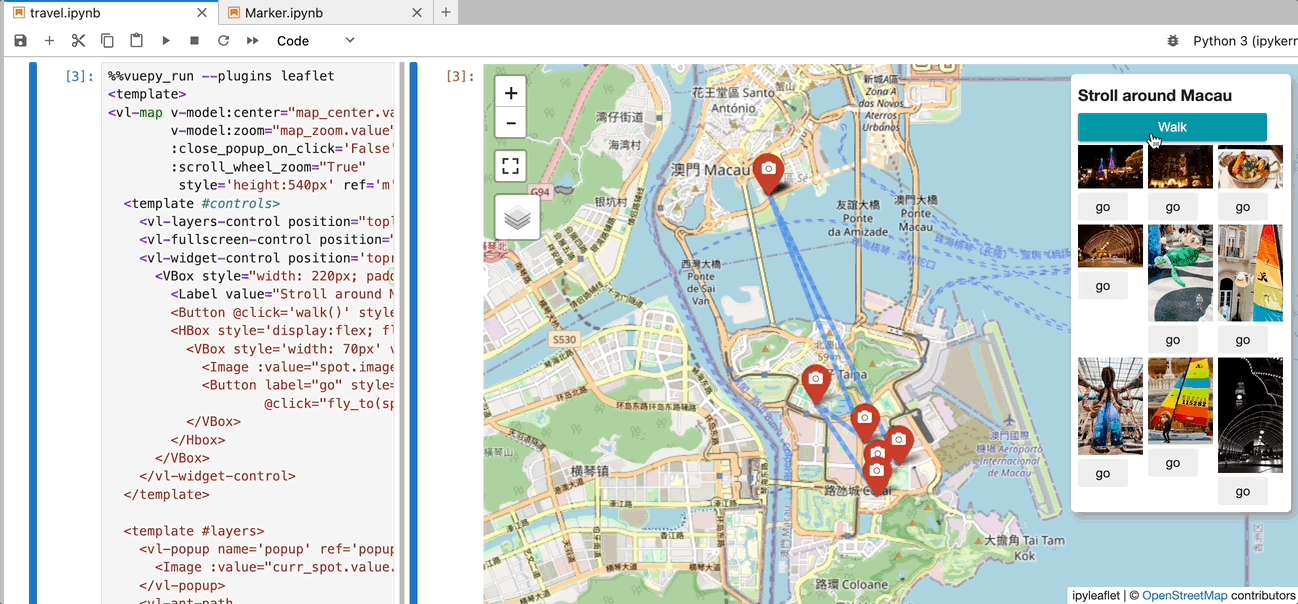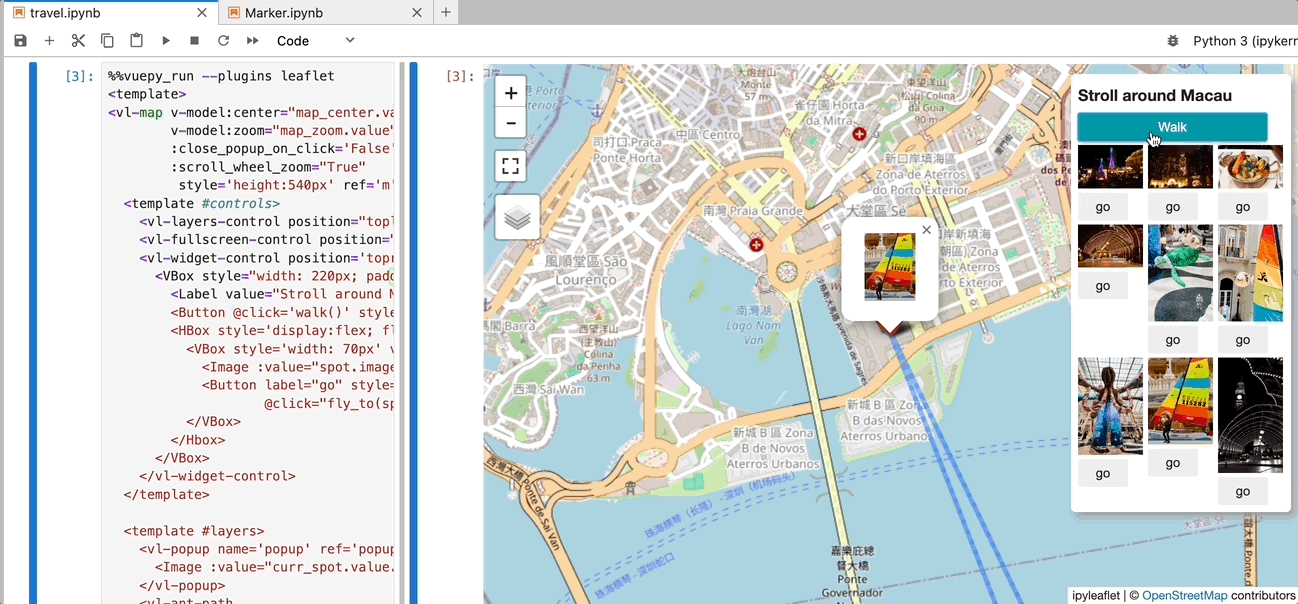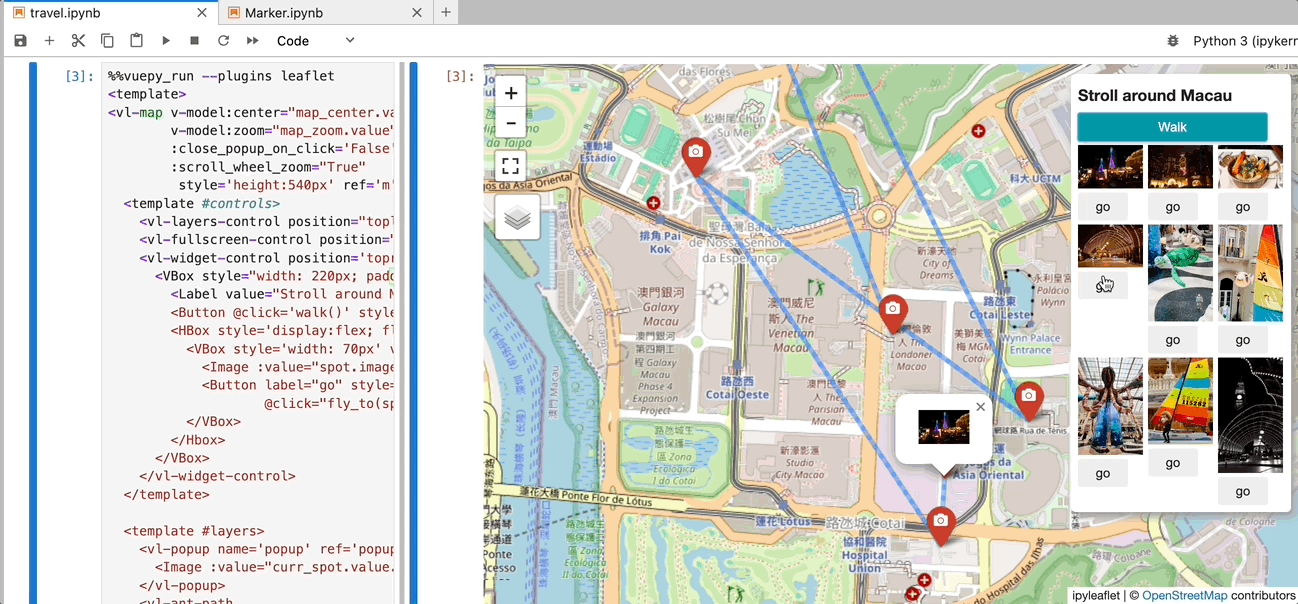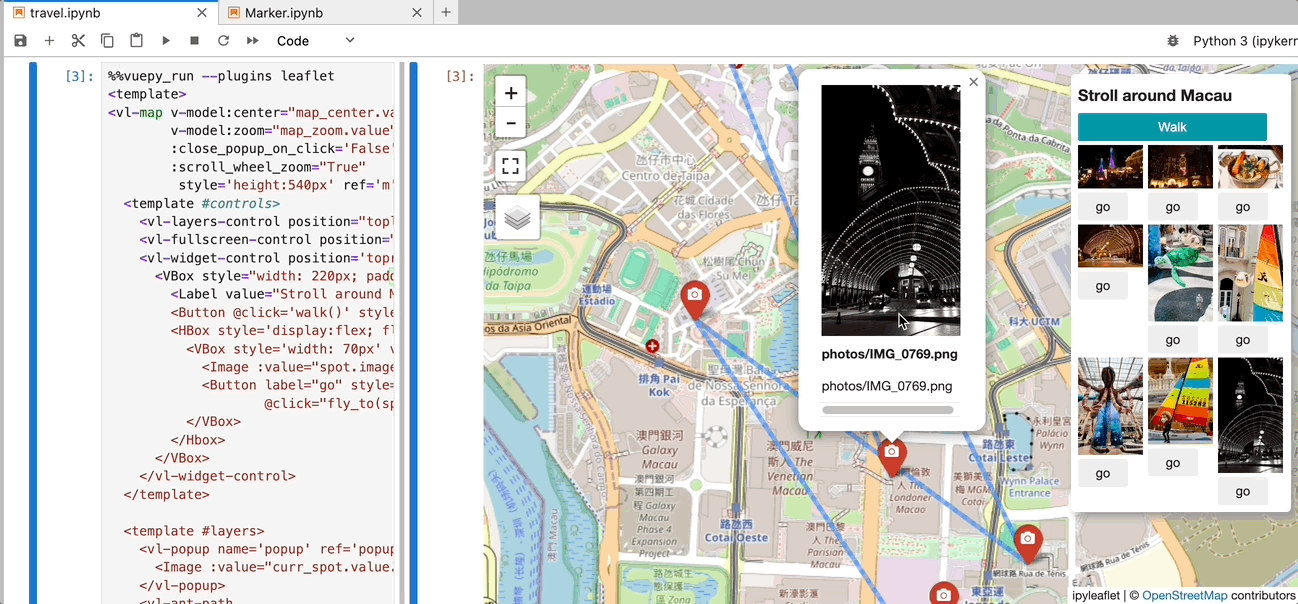
vleaflet is a responsive map component library built on top of Vue.py and ipyleaflet. It allows you to create interactive maps within Jupyter notebooks, where every object (including maps, TileLayers, layers, controls, etc.) is reactive. You can dynamically update properties from Python or the browser.
- Responsive and interactive maps
- Built on Vue.py and ipyleaflet
- Easy integration with Jupyter notebooks
- Reactive components for dynamic updates
- Leverages Vue.py's ecosystem for building interactive applications.
To install vleaflet, you can use pip:
pip install 'vuepy-core[vleaflet]'To get started with vleaflet, please refer to the Quick Start Guide for installation steps, prerequisites, and example code snippets.
You can use vleaflet in different ways depending on your workflow:
Using the use Plugin Method
from vuepy import create_app, import_sfc
from vleaflet import leaflet
App = import_sfc('App.vue') # Update with the actual path to App.vue
app = create_app(App)
app.use(leaflet)
app.mount()Using %vuepy_run
from vuepy.utils import magic
from vleaflet import leaflet
%vuepy_run app.vue --plugins leafletUsing %%vuepy_run
from vuepy.utils import magic
from vleaflet import leaflet
# -- cell --
%%vuepy_run --plugins leaflet
<template>
<vl-map :center="[53, 354]" />
</template>For more detailed information about the vleaflet component library, please check the following resources:
We welcome contributions to the vleaflet project! Please feel free to submit issues or pull requests.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more details.
Explore the Map Component Guide to dive deeper into vleaflet's features