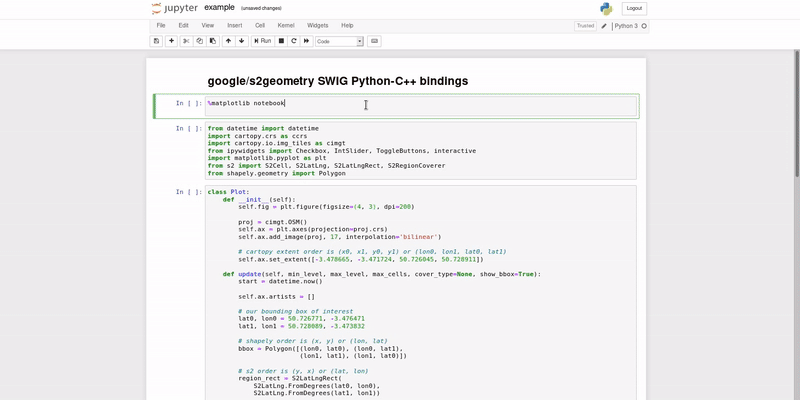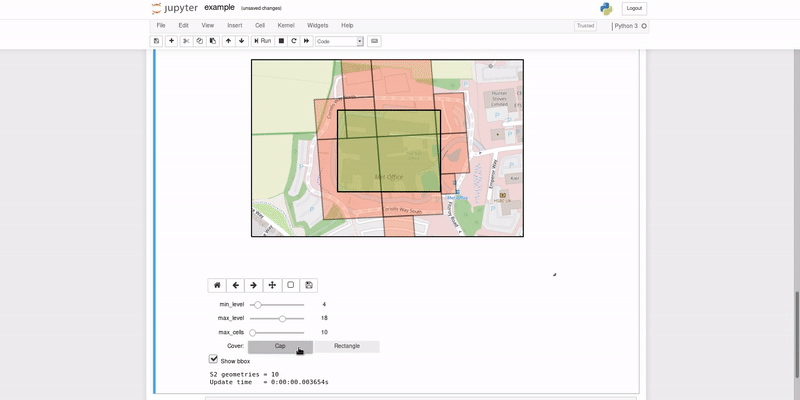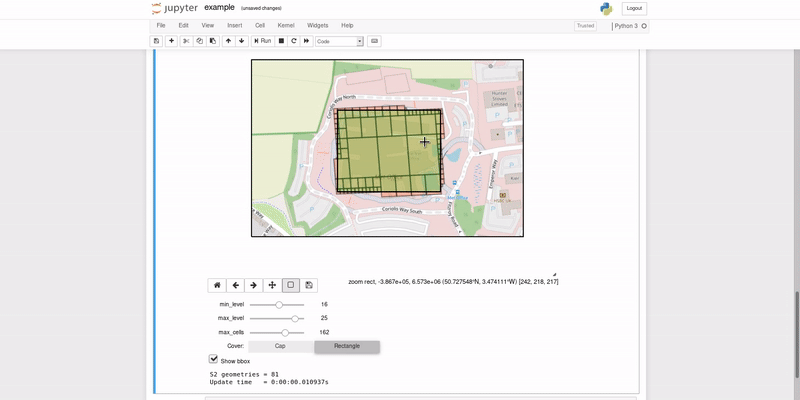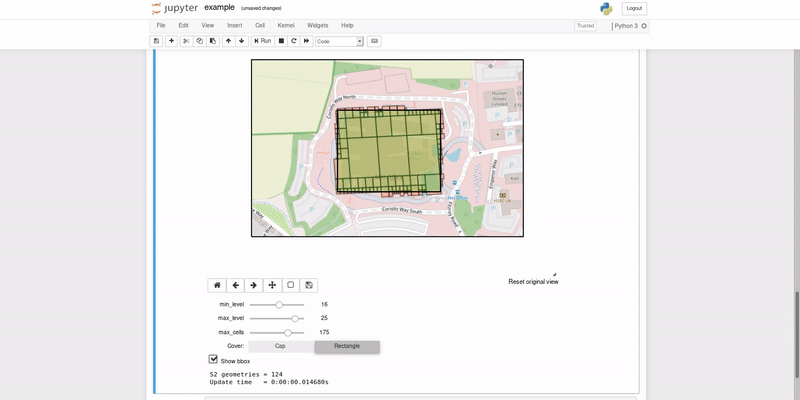
This repository contains a recipe for building a Docker ubuntu:bionic base image with layers containing the Python3.6 SWIG bindings for google/s2geometry, and SciTools/cartopy.
By default, the recipe configures an entrypoint to stand-up a jupyter notebook in the running container and will expose the service over container port 8888.
Simply build the Docker image as follows:
> cd context
> sudo docker build -t s2geometry .
If necessary, override the default ARG port for the jupyter notebook:
> sudo docker build -t s2geometry --build-arg port=<container-port> .
Run the built s2geometry Docker image as follows:
> sudo docker container run -it -p 8888:8888 --rm s2geometry
Providing no [COMMAND] after the Docker s2geometry image will result in the jupyter notebook entrypoint executing in --no-browser mode.
Connect to the jupyter notebook running within the container on your host through your browser of choice on port 8888.
If you want to use a different host port e.g., 9999, then start the Docker container as follows:
> sudo docker container run -it -p 9999:8888 --rm s2geometry
To override the entrypoint for an interactive bash session in a running container, simply:
> sudo docker container run -it -p 8888:8888 --entrypoint "/usr/bash" --rm s2geometry
For convenience, simply pull the bjlittle/s2geometry image from Dockerhub and run the container (in daemon-mode) as follows:
> sudo docker image pull bjlittle/s2geometry:latest
> sudo docker container run -d -it -p 8888:8888 --rm bjlittle/s2geometry
> firefox localhost:8888
The s2geometry Docker image is configured with the jupyter notebook password hello-s2!.
See the config/root-jupyter-notebook-config.py.
The default working directory for the jupyter notebook instance is /root/work, which conatains an example notebook to whet your appetite.
To bind mount a volume from the host into the container, simply start the container as follows:
> sudo docker container run -it -p 8888:8888 -v </absolute/path/to/host/dir>:/root/work/host s2geometry
This will allow you to create and save jupyter notebooks within the container into the /root/work/host directory, and those notebooks will then be available in your host </absolute/path/to/host/dir> directory.
- Constructing the Hilbert Curve
- Mapping points in a line to points in a square
- Planetary View
- Region Coverer
- Nick Johnson, Nick's Blog blog post: Damn Cool Algorithms: Spatial indexing with Quadtrees and Hilbert Curves
- Sven Kreiss, Medium blog post: S2 cells and space-filling curves: Keys to building better digital map tools for cities
- Christian Peroni, Terra Incognita blog post: Google's S2, geometry on the sphere, cells, and Hilbert curve
- Antoine Sinton, Zenly blog post: Geospatial indexing on Hilbert curves
- Push a tagged version of this
s2geometryimage on Dockerhub - Build and push automatically to Dockerhub with CI
- Provision a Docker image with default google/s2geometry SWIG Python bindings within a conda environment
- 17 Feb 2020 - WIP
- Provision a Docker image with full API google/s2geometry Python bindings within a conda environment
- the goal is to provision a conda package on
conda-forgecontaining the Python3.x-C++ bindings for the full google/s2geometry API
- the goal is to provision a conda package on
Enjoy 😀