Examples of Object Classfication and Detection using OpenCV with Deep Learning in C++
In a regular basis, work with classifiers as neural networks requires the execution of the following steps: training and classification.
- Training step
Tiven a set of examples (the training dataset) the training step consists of build the classifier using some learning algorithm. The trainig dataset must be labeled. For example, a dataset containing a set of pics and a text file listing the content of each pic. Both the classifier structure and parameters can be set in this step but more often just the parameters are fitted for a pre defined well know structure. The most popular example is to training the neural network's weight matrix using the backpropagation algorithm for a 1-hidden layer architecture.
This step is also known as learning step and usually demand a lot of time for running the learning algorithm along the dataset and adjusting the training parameters (learning rate, max number of epochs and so on). Often the training dataset must be modified, what is know as data preparation, in order to obtain a better the classifier. Depending how much data to training and the complexity of the data preparation and training settings calibration, the training step can spent just a bunch of seconds or minutes up to hours, days, weeks or even months of work of a multidisciplinary team.
The output of the trainning step is a Network Configuration (also known as netowrk structure or network topology) and a Network Model (the values of the network parameters).
The classfier's performance is measured usually in terms of its accuracy and generalization. The classifier training step is done when both accuracy and generalization power are acceptable.
- Classification step
Once the classifier is done it is ready for use in realtime classification. In the classification step, a single or a small batch of unlabeled instances are classified. For example, the classifier identify what is showed in a given picture just evaluating its contents.
If the training step is a complex and costly task, the classification step is often fast and straigforward. In this step, as know as inferece step, the classifier outputs one or more class (or label) for each instance. The time took on each classification execution is usaully of the order of few milliseconds. Sometimes, the classifier requires that the input data must be pre formated before the classification which is performed for low cost operations like resize a image or change it for gray scale.
Binary classification problems (Yes/No, True/False, Present/Absent) or even problems with a small number of classes (< 10) can be handled by convetional artificial neural networks with a small number of layers. But if you take a real appliation, for example when you need to identify an arbitrary object in a image, the support of those regular architectures is not enough. For our lucky, the Deep Learning provides a way to go if you have hundred or more different classes to choose in a classification problem.
The most popular frameworks for Deep Learning are TensorFlow and Caffe. However every day a new alternative is provided by the Machine Learning community in a field that evolves continuously. In other tutorial I explain how to use TensorFlow to build a classifier from scratch.
Since version 3.1 OpenCV supports Deep Learning first as a contrib feature but today inside the core of the package. Indeed the support is limited: do not expect to training the classifier directly in OpenCV. The OpenCV team understand that the training step of a (image based) classifier is not a role of OpenCV. Thus, to use OpenCV with Deep Learning you will perform just the classification step. Indeed it is not a problem so far. The community has shared great ready-to-use networs, trained by the experts in the field after a demand time of efforts. So our job is just to plug those networks into our programs and voila. In another tutorial I show how to build a complete pipeline of a Deep Learning solution since the data preparation and network training and use in a real time application.
It could be frustrating for some C++ programmers try to learning more about Deep Learning (and OpenCV) nowadays. The most of tutorial and examples in internet I found are written in Python. Thus I decided to write down some straightforward examples in C++ to help people getting starting to apply OpenCV and Deep Learning in their projects.
The first example is pretty basic and show how to load the GoogleNet Classification Network using Caffe Engine into a single pic classification program. The ideia is to be really plain and easy to read, avoiding to include complex out-of-concern things like Webcam capture or parameter tunning.
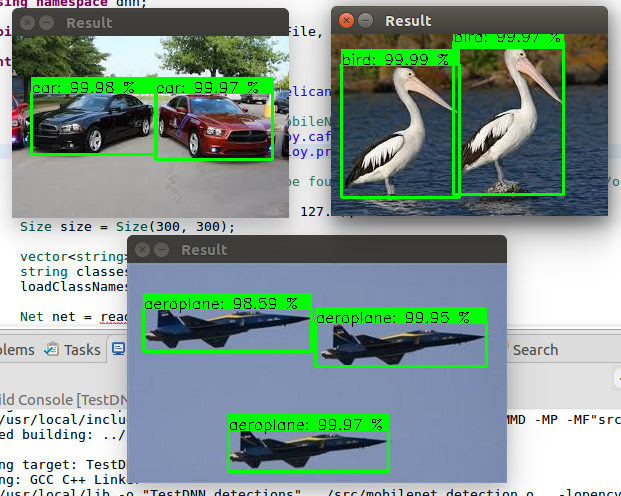
The second example is also easy to read and explain how to perform object detection. In object detection it isn't said just WHAT is the object (like in classification) but also WHERE is the object (or objects) in the image. Object detection indeed is not a classification task. To perform it the network use a single-shot detector algorithm but it is done internatly by the framework. The second example use another prebuilt Google network called MobileNet and also uses the Caffe framework.
OpenCV is a very active project and Deep Learning is eveolves every day. So, be careful to get your environment updated before try to run these examples. My current setup is ready with OpenCV 4.0.0-pre grabbed from the sources. It requires a C++11 at least compatible compiler and I had used the GCC for that. There are lot of ways to know what is the OpenCV version running in your environment. Use the following code if you want to use C++ to get it:
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
cout << "OpenCV version : " << CV_VERSION << endl;
return 0;
}
In my setup it outputs:
OpenCV version : 4.0.0-pre
You needn't an IDE to build and run the examples but if you are wondering about a good option I could recommend you start with Eclipse CDT IDE. Another good option is the Visual Studio Code. OpenCV can be installed in Windows, Linux and OSX. My suggestion is to try an Ubuntu 16.04 OS running inside a virtualization environment like Virtual Box. Look here for instructions how to install OpenCV from sources in Ubuntu: https://github.com/doleron/installopencv3.2ubuntu