These are my personal notes from Adrian Cantrill's (SAP-C01) course. There may be errors, so please purchase his course to get the original content and show support https://learn.cantrill.io.
- Generates Temporary Credentials.
- Similar to access keys but they EXPIRE and do not belong to the identity.
- Limited Access.
- Use to access AWS Resources.
- Requested by an Identity (AWS or External).
What will you do if temporary credentials leaked and compromised?
- You can delete the role but it will impact ALL identity that assume that role.
- You can change the TRUST policy but it has no impact to the existing credentials that has been generated.
- Changing the PERMISSIONS policy will impact ALL credentials.
Resolution:
Use Revoke Sessions in the role, this will add an AWSRevokeOlderSessions inline policy onto that IAM role which will DENY sessions in a point in time and because of this the credentials that has been generated will be expired and only the identities included in the trust policy can renew the role.
Use to limit what permissions an identity can receive. NOTE: They do not grant access.
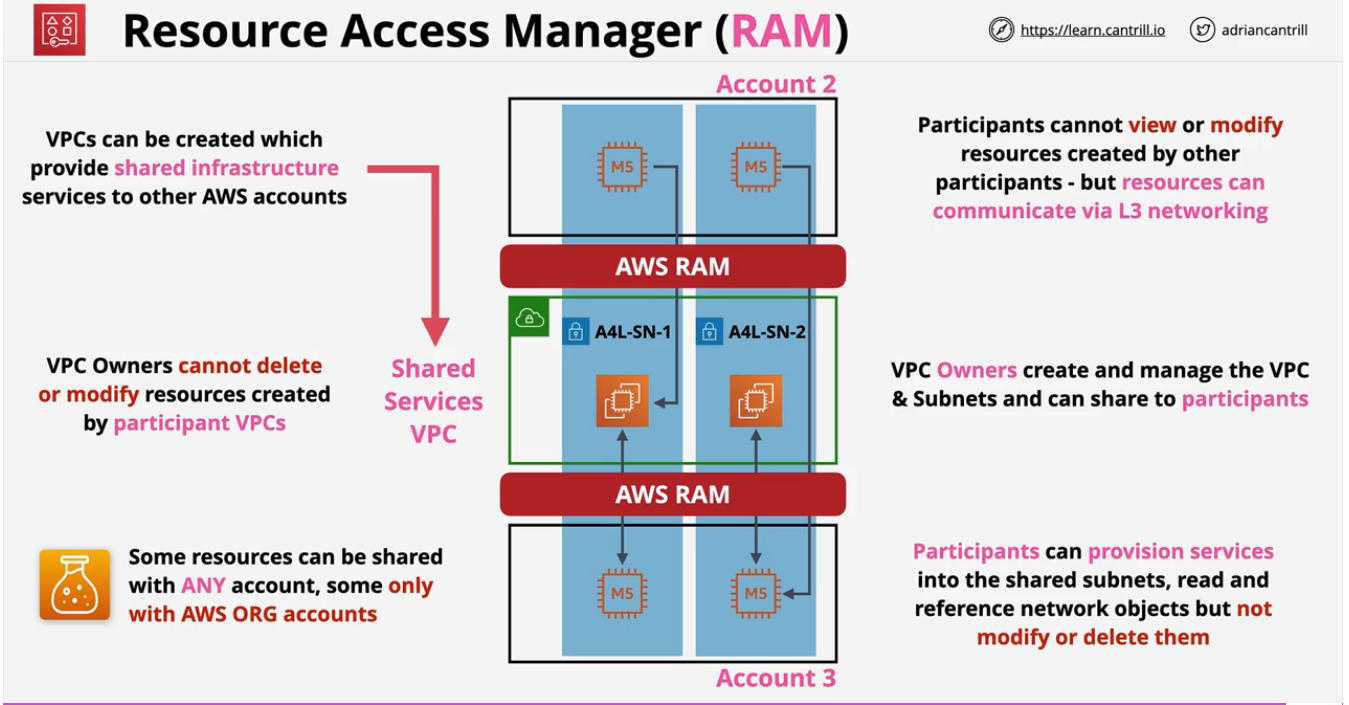
- Use to share AWS resources between AWS accounts.
- Products need to be supported by RAM.
- This can be shared with Principals (e.g. Accounts, Organization Units or ORG's).
- Shared resources can be accessed natively - as if they are in the same network.
- No charges for using the service - only the underlying services that it leverages.
- This are unique identifiers for a given Availability Zone.
- AWS rotates physical facilities that are used by Availability Zones and this are not consistent in each AWS account. For example
us-east-1ain an AWS account is not the same as other AWS accountus-east-1a.- This may cause issue when sharing resources to other AWS account.
- To resolve this, AWS used AZ IDs as an identifier for a specific Availability Zone and this is utilize by AWS RAM.
- Owner account creates a share. Utilizes AZ IDs to identify on which resources will be shared.
- Owner will retain full ownership of the resources.
- Defines a principal to whom to share.
- IF participant is inside an AWS Organization with Sharing enabled, resouces will be automatically shared.
- IF participant is NOT inside an AWS Organization OR AWS Organization Sharing is disabled, principal need to accept the invite.
Notes:
- Shared resouces using AWS RAM cannot be modified or deleted by the account to whom you shared your resources.
- Shared principals can interact with the resources but cannot edit or modify them.
- AWS Resources that has been created by the owner account or each member account are cannot be seen by other accounts except to the account where they are created.
- You cannot share VPC using AWS RAM but you can share the resources inside the VPC (e.g. Subnets, etc.). See list here.
- Each service has a default per region quota.
- Some service quota can be per account.
- Most service quotas can be increased as needed.
- Some cannot be increased due to architectural impacts.
- High quota increase == more processing and time needed.
Notes:
- AWS Service Quotas can be also used to request to increase service quotas in each service.
- This also has Quota request template for AWS Organization to request a bulk increase for your AWS Organization member accounts.
- You can build an CloudWatch Alarm based on a particular service quota.
- SAML 2.0 is an open standard for many Identity Providers (e.g MS ADFS, etc.)
- Mostly used for Enterprise Identity Provider - SAML 2.0 Compatible.
- This is used when you already have an existing identity management team.
- Single source of truth - can hanlde more than 5000 users.
- Leverages IAM Role and AWS Temporary Credentials (STS) with 12 hour of validity by default.
Notes:
- For API, you need to establish TRUST between your SAML 2.0 Compatible Identity Provider and IAM
- For Console, you need to establish TRUST between your SAML 2.0 Compatible Identity Provider and the SAML/SSO Endpoint.
- The Client Identity Provider Portal where you authenticate identifies the roles which are available for the authenticating user.
- Uses STS:AssumeRoleWithSAML that exchanges SAML assertion with temporary credentials that will be use to access an AWS service or the AWS console.
- Managed SSO access.
- Can be use for AWS accounts and External applications.
- Flexible Identity Source, you can use:
- AWS SSO built-in Identity Source
- AWS Managed Microsoft AD
- On-premises Microsoft AD (using 2-way trust (AWS Managed Microsoft AD) or AD connector)
- External Identity Provider (SAML 2.0)
- Preferred by AWS vs Traditional workforce identity federation.
Notes:
- Requirement of AWS SSO is you need to have AWS Organization enabled.
- Permission Sets - are way to define role-based permissions that can be assigned to an user or a group over a certain AWS account.
- You can use existing or custom permission sets.
- Handles authentication, authorization and user management.
- use for Web and Mobile applications.
- You can login directly to Cognito or other identity providers.
- Handles the exchange for AWS credentials.
- Access AWS resources using credentials.
- Handle Data Synchornization, Identity Merging, Managed Login UI.
- Data Synchornization is useful when you access an application using multiple devices as it sync's the data on all of those devices.
- Use for authentication, users can sign in through the user pool or federate through a third-party identity provider (IdP).
- Authenticate using federated identities (e.g. FB, Google, etc.) and a successful authentication can return a JSON Web Token (JWT).
- JWT will be send to Identity Pool and the Identity Pool swaps these JWT with temporary AWS credentials via AssumeRole.
- These credentials will be use to access AWS resources.
- JWT will be send to Identity Pool and the Identity Pool swaps these JWT with temporary AWS credentials via AssumeRole.
- Use for authorization, you can use identity pools to create unique identities for users and give them access to other AWS services.
- Can be used on both authenticated and unauthenticated identities.
- These identities will have separate role each.
- These roles are created during Identity Pool creation.
- These roles can be modified later or after creation.
- These identities will have separate role each.
Notes:
- When you establish Web Identity Federation where Google IDF is configured, AWS trust that Google to authneitcate, AWS accepts google proof of login then AWS exchanges this proof of login into temporary credentials which are used to access AWS resources.
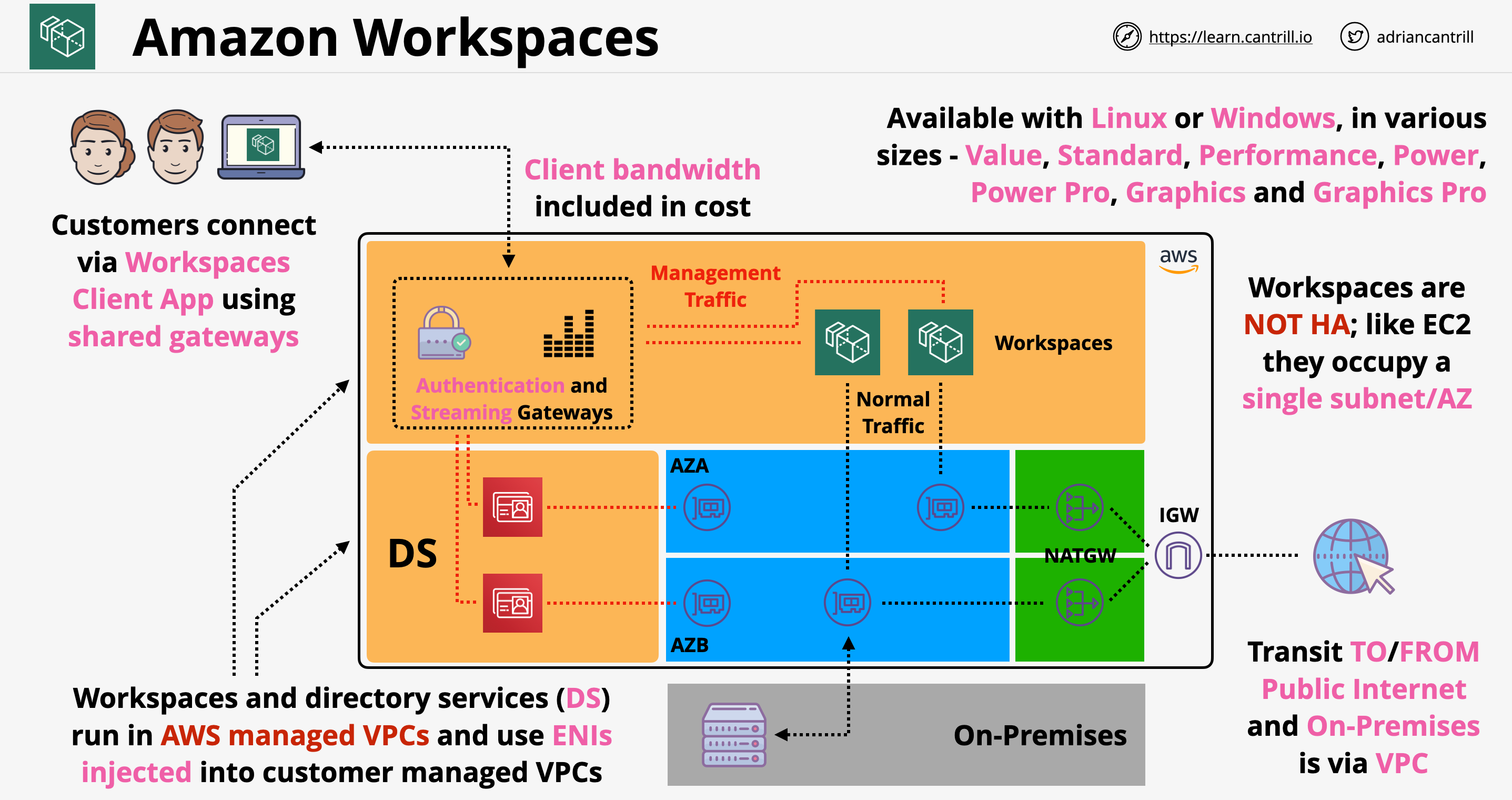
- Desktop-As-A-Service - primarily use for Home-working/Office.
- Similar to Citrix / Remote Desktop - but it's hosted by AWS.
- Consistent desktop from anywhere - apps and state.
- Can provision Windows and Linux desktop comes with various sizes.
- Monthly or Hourly Pricing (+ base infra costs).
- Uses Directory Service (Simple AD, Managed AD, AD Connector) for authentication and user management.
- The Directory Service is a requirement when using Workspaces.
- Windows Workspaces can access AWS FSx and EC2 Windows Resources.
- It can also access on-premises resources over VPN or Dirrect Connect (DX)
- Provides EBS-based volumes (can be encrypted at rest).
Notes:
- Workspaces and Directory Services run in AWS Managed VPC (controlled by AWS - not customer managed) and use Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs) that will be injected into customer-managed VPCs.
- Workspaces are not highly-available - uses ENI that only occupies a single subnet or AZ.
- Workspaces has 2 running modes:
- AlwaysOn - billed monthly. Always running Workspaces.
- AutoStop - billed hourly. Start Workspaces when you login then stops when no longer being used.
- AWS Workspaces can only be integrated with AWS Directory Service (e.g. Managed AD, AD Connector, Simple AD).
- When you create Workspaces and selected directory to use, Workspaces creates a number of security groups.
- These security groups will be attached to the Workspaces.
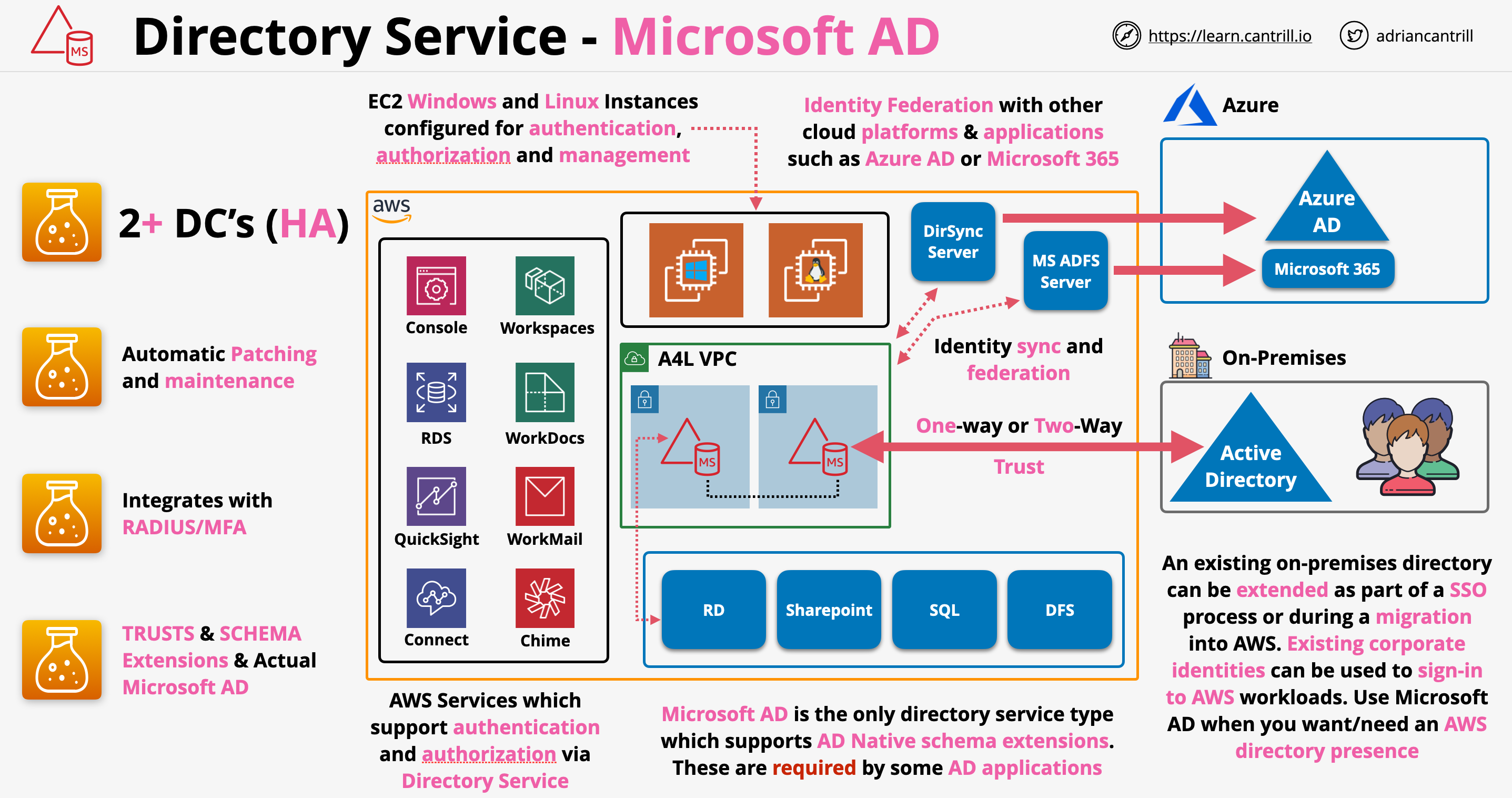
- Built using Microsoft Active Direcotry 2012 R2
- Managed using Standard Active Directory Tools.
- Supports Group policy and Single Sign-On (SSO).
- Supports Schema Extension - MS AD Aware Apps.
- Such as SharePoint, SQL, Distributed File System (DFS).
- Has 2 Sizes:
- Standard - can store up to 30,000 Objects.
- Enterprise - can store up to 500,000 Objects.
- Used for AD Authentication or Authorization of products and services within AWS.
- Highly available by default - provision 2 Domain Controllers that expands to 2 or more AZs.
- Includes monitoring, recovery, replication, snapshots and maintenance that is configurable and managed by AWS.
- Includes automatic patching and maintenance.
- Supports one-way and two-way external and forest with on-premise active directory
- Can operate independently. It can work through network link failure to any connected on-premises systems.
- Supports RADIUS-based MFA
- Can also be integrated with on-premises RADIUS server.
- Best choice if you need to establish TRUST relationship between AWS and you On-premises directories.
- The on-premises directory and Microsoft Managed Directory are 2 separate directories where you can establish either one-way or two-way trust.
Notes:
- AWS DS Managed Microsoft AD - To establish a 2-way Forest Trust between on-prem and AWS, you need to ensure that Kerberos pre-authentication settings is correct and enabled on both on-prem and AWS Domain Controller and conditional DNS Forwarder.
- You can establish 2-way trust and because of this you can create a Distributed File System (DFS) which is a File Server that can be reached either in AWS or On-premises.
- When integrating AWS & On-premises directories, AWS expects well-cared for directories.
- Well-cared for directories means that any identities within AD is define with First Name, Last Name and Email.
- These configuration is required when using Workspaces.
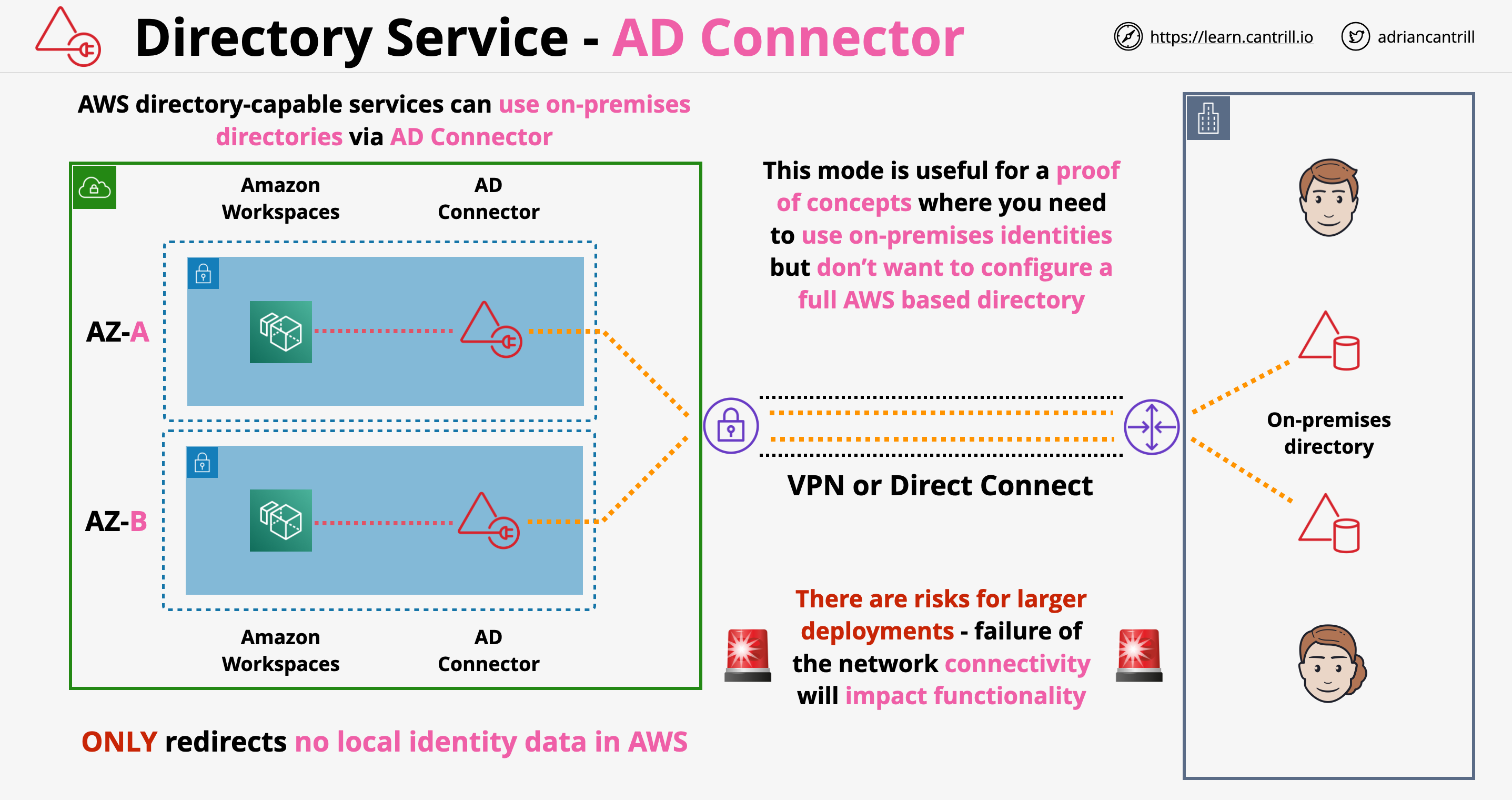
- A pair of directory endpoints running in AWS (ENI injected in a VPC).
- Supports directory-aware products
- Redirect requests to existing directory service.
- No directory data stored in AWS - All redirected (from AWS to On-premises).
- Use existing on-prem AD with directory compatible AWS services.
- Without any identity data in AWS.
- Mostly use for Proof of Concepts (POC).
- Has 2 sizes, Small and Large - no explicit limits but controls the amount of compute allocated.
- Multiple AD connectors can be created to spread load.
- Requires 2 subnets within a VPC - must be in different AZs.
- Requires 1 or more directory servers to be configured.
- Requires a working networking connection between AWS and on-premises.
- It will not function if this is not met.
- This can be a network connectivity in private via DX or VPN.
Notes:
- AWS DS AD Connector is reliant on network connectivity, if the network link between AWS and On-prem fails then the Domain Controller and Workspaces will also fail.
- Autonomous Systems (AS) - routers controlled by one entity - it's a network in BGP.
- BCP overates over TCP/179 - reliable.
- Not automatic - peering is manually configured.
- BGP is also known as Path vector protocol as it exvhanges the best path to a destination between peers.
- The path is called ASPATH.
- BGP does not consider the speed, it just based on ASPATH.
- The path is called ASPATH.
- iBGP - Internal BGP - Routing within an AS's.
- eBGP - External BGP - Routing between AS's.
- BGP always advertises the shortest path.
- Moves the actual AWS network closer to customers.
- Connection enters at edge (Global Accelerator Edge Location) using Anycast IPs.
- These Anycast IPs are mapped on each Global Accelerator Edge Location and users connect to the neareast Global Accelerator POP.
- Once the traffic enter the Global Accelerator Edge Location it then transit over AWS network to 1 or more locations.
- Used for Non HTTP or HTTPS traffics (UDP / TCP)
- Does not cache anything.
- Cannot be used for HTTP / HTTPS.
- Used for Global TCP / UDP Optimization.
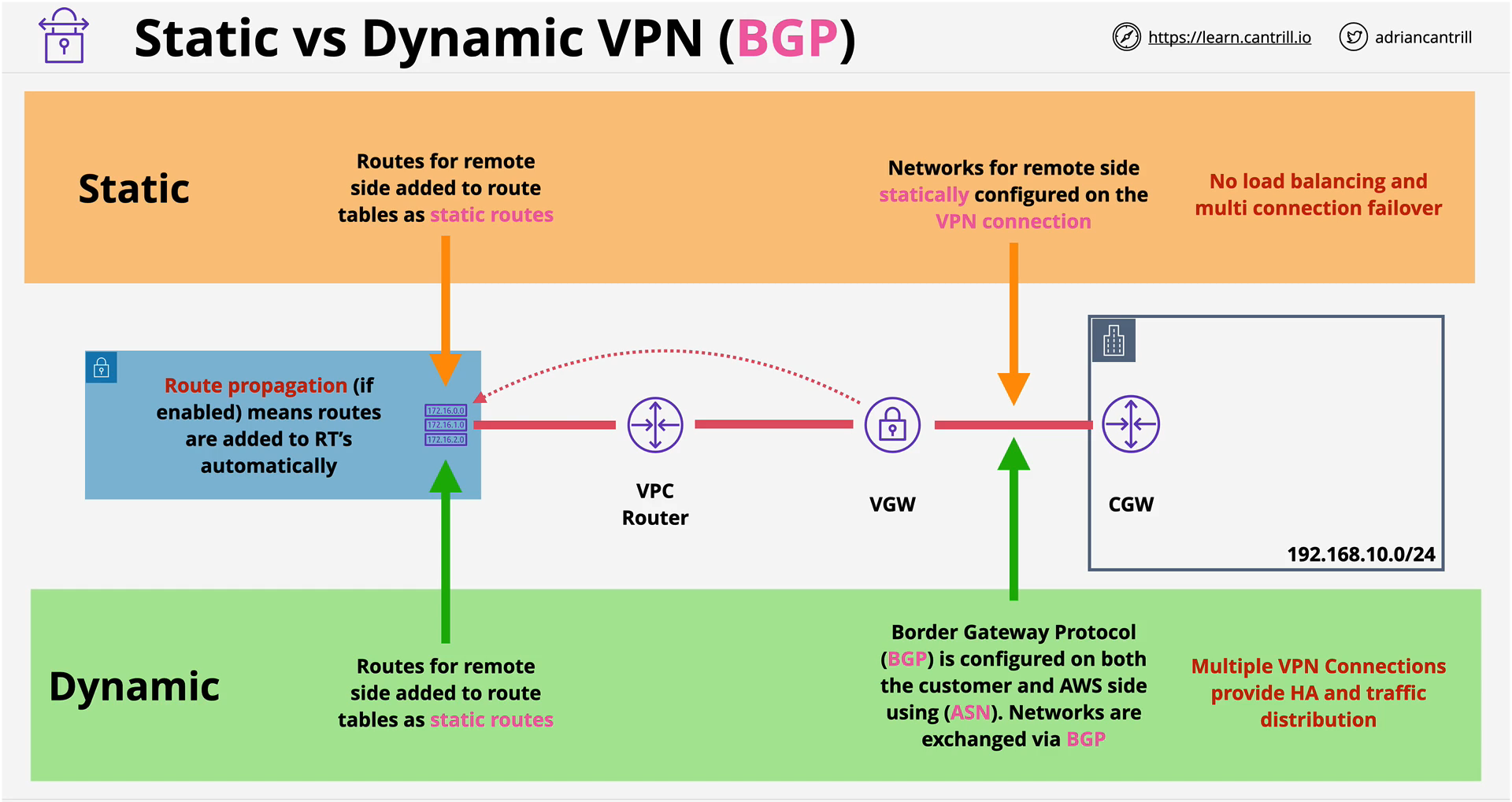
- A logical connection between a VPC and On-premises network that is encrypted using IPSec which runs over the public internet.
- Can be configured to be fully Highly available.
- Quick to provision - faster than Direct Connect.
- Requirements:
- VPC
- VGW - reside in the VPC, target of one or more RTs
- CGW - Logical config in AWS and the configuration that represents the physical on-premises router.
- Dynamic VPN setup will only work if your router supports BGP.
- In this setup, it's a full-mesh topology between VPC's and lots of Admin overhead.
- Speed Limit of 1.25GBPS only.
- Also CGW router as VPN use encryption and theres a processing overhaed for cryptographic operations.
- Speed of setup - can be setup just hours because its all software configurations.
Notes:
- VGW is HA by design, it provisions 2 endpoints located in 2 different subnets.
- VPN is linked to VGW and it use the endpoints that VGW provides then you specify an CGW and after this VPN tunnel will be establish between 2 VGW endpoints and CGW.
- One VGW : One CGW
- When you created a new VPN connection to your existing VGW that has VPN link existing, VGW will create 2 more endpoints.
- Can be used with DX or backup connection for DX.
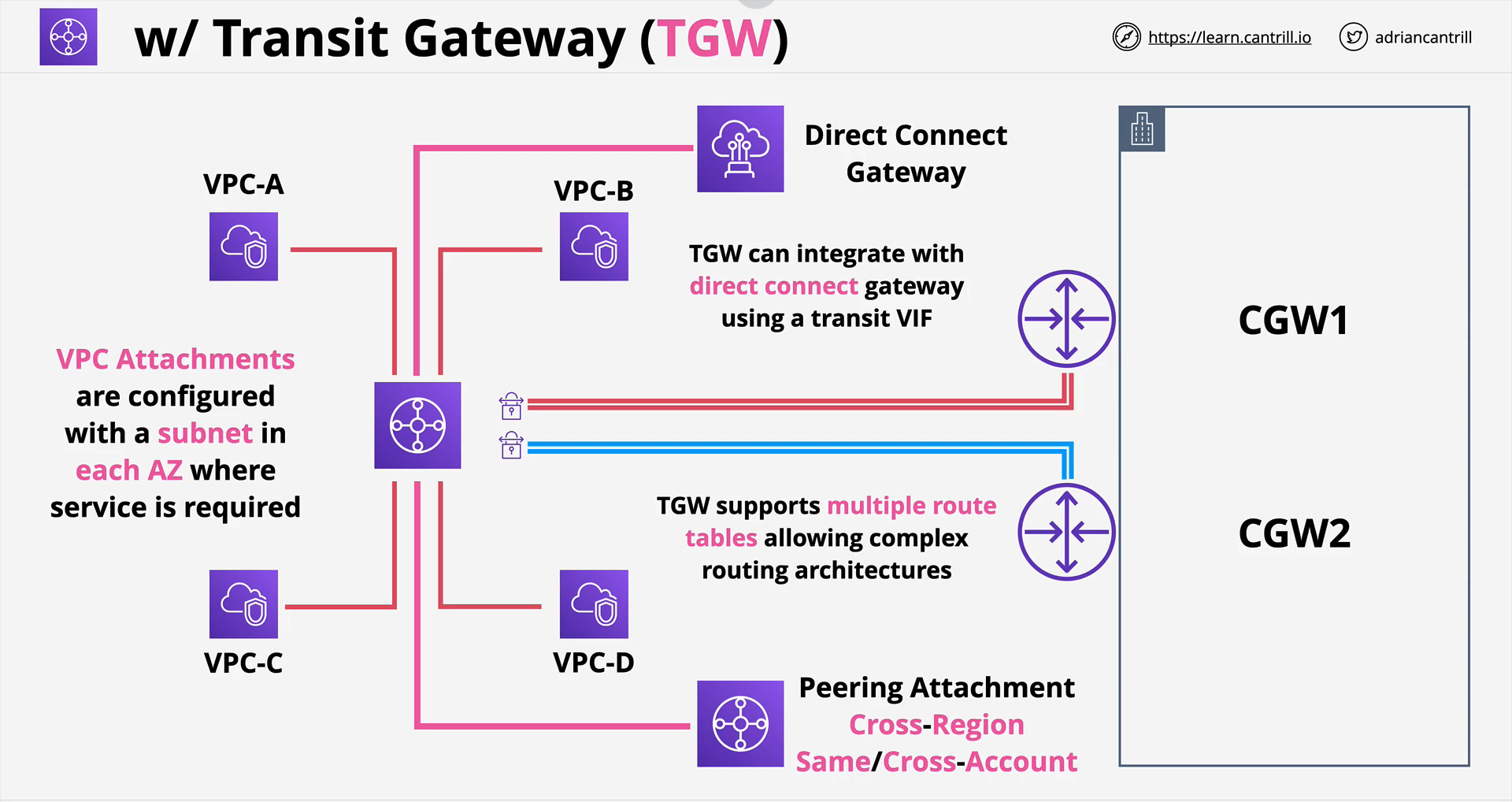
- Supports transitive routing.
- Can be used to create Global networks.
- Can be shared between accounts using AWS RAM.
- Can be peered with TGW in different Regions - same or cross accounts.
- Can also be peered with DX (using Transit VIF).
- Offers less complexity in network topology compared to full mesh topology offered by VPC Peers or other services.
Notes:
- Transit Gateway needs to have attachments to everything that it will route traffice between.
- Transit Gateway topology is better than static VPN in full HA setup.
- TGW support transitive routting that simplifies that management of multiple route tables allowing complex routing architectures.
- Subnets are associated with one Route Table (RT) only.
- Either implicitly associated with Main Route Table or explicitly associated with custom Route Table.
- IF there no explicit association of RT in a subnet, the subnet will have the implicait Main RT associated.
- IF explicitly associated with custom RT, implicit association with Main RT will be removed.
- Either implicitly associated with Main Route Table or explicitly associated with custom Route Table.
- IPv4 and IPv6 are handle separately within a RT.
- Routes send traffic based on Destination to a Target.
- All routes are evaluated - highest priority machings is used.
- Longest Prefix - highest CIDR prefix wins.
- Static Routes
- Propagated Routes
- 3.a. Routes learned via DX.
- 3.b. Routes learned via Static VPN.
- 3.c. Routes learned via Dynamic (BGP) VPN.
- 3.d. AS_PATH
- This are used to control inbound traffic coming from the outside.
- Remember that Subnet Route Tables only controls traffic going out (outbound) and not going in (inbound).
- This can be attached to Internet Gateway or Virtual Private Gateway that is used to direct inbound traffic and take actions.
- Actions such as forwarding traffice to a software appliance, etc.
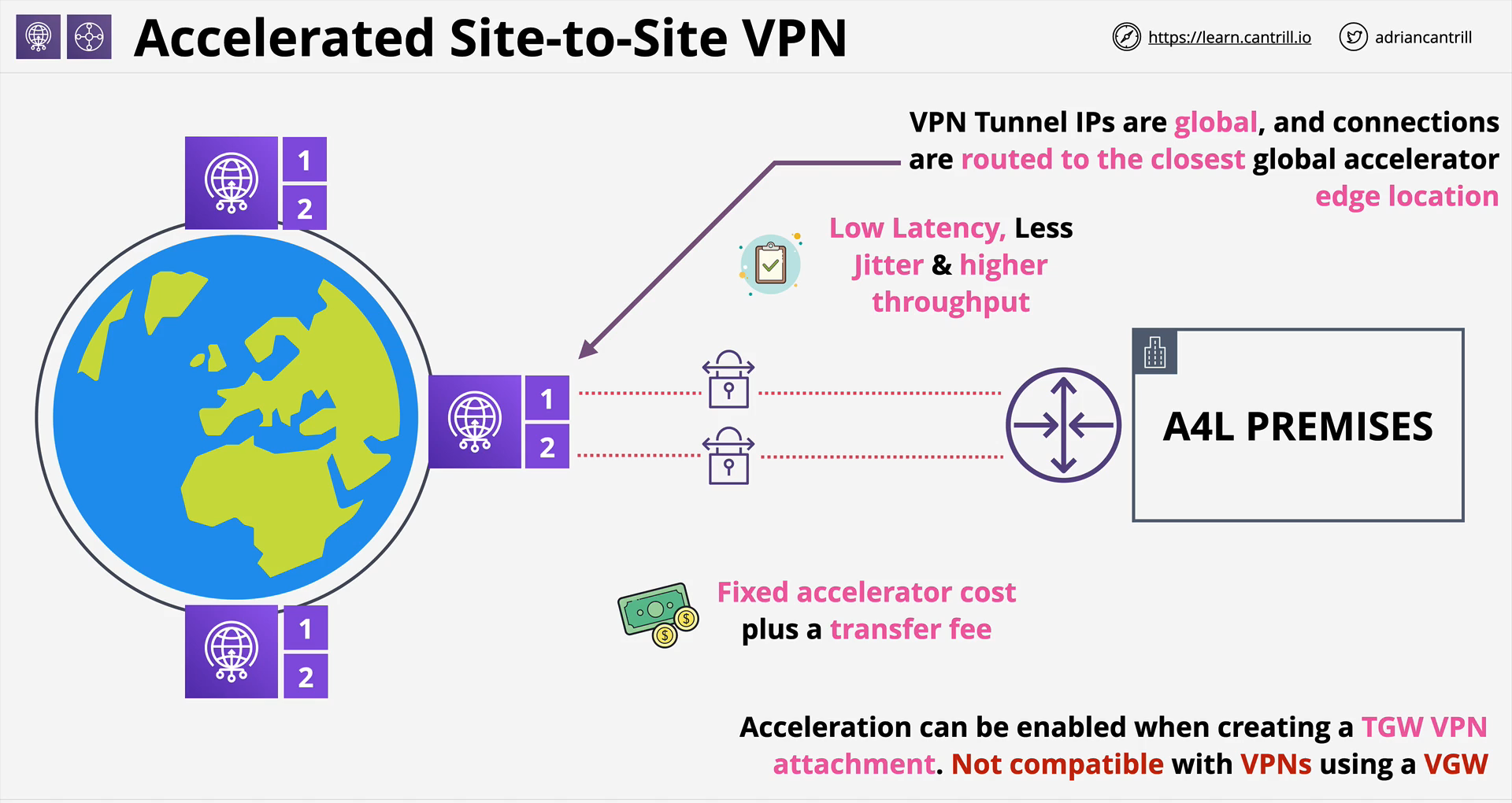
- Use to optimize the connectivity between on-premises to your AWS VPC by leveraging the combination of Global Accelerator, Transit Gateway and Site-to-Site VPN.
- On-premises <-> VPN <-> Global Accelerator POP <-> Transit Gateway <-> Your VPC.
- Cannot be used by Virtual Private Gateway.
Notes:
- TGW attachments with VPN setup will create Site-to-Site VPN connections.
- In these Site-to-Site VPN Connections you can download the connection configuration to be use in setups.
- When you create 1 VPN connection or 1 TGW VPN attachment, these will create 2 tunnels.
- Both tunnels go to AWS and 1 CGW.
- Tunnel is a network connection between 2 location which is encrypted and this tunnel goes between 2 endpoints.
- VPN Tunnel inside IPs are associate with the actual data being transffered and the BGP connection which exchanges routing information.
- VPN Tunnel outside IPs are associated with the tunnel intself the encrypted connections between AWS and On-premises.
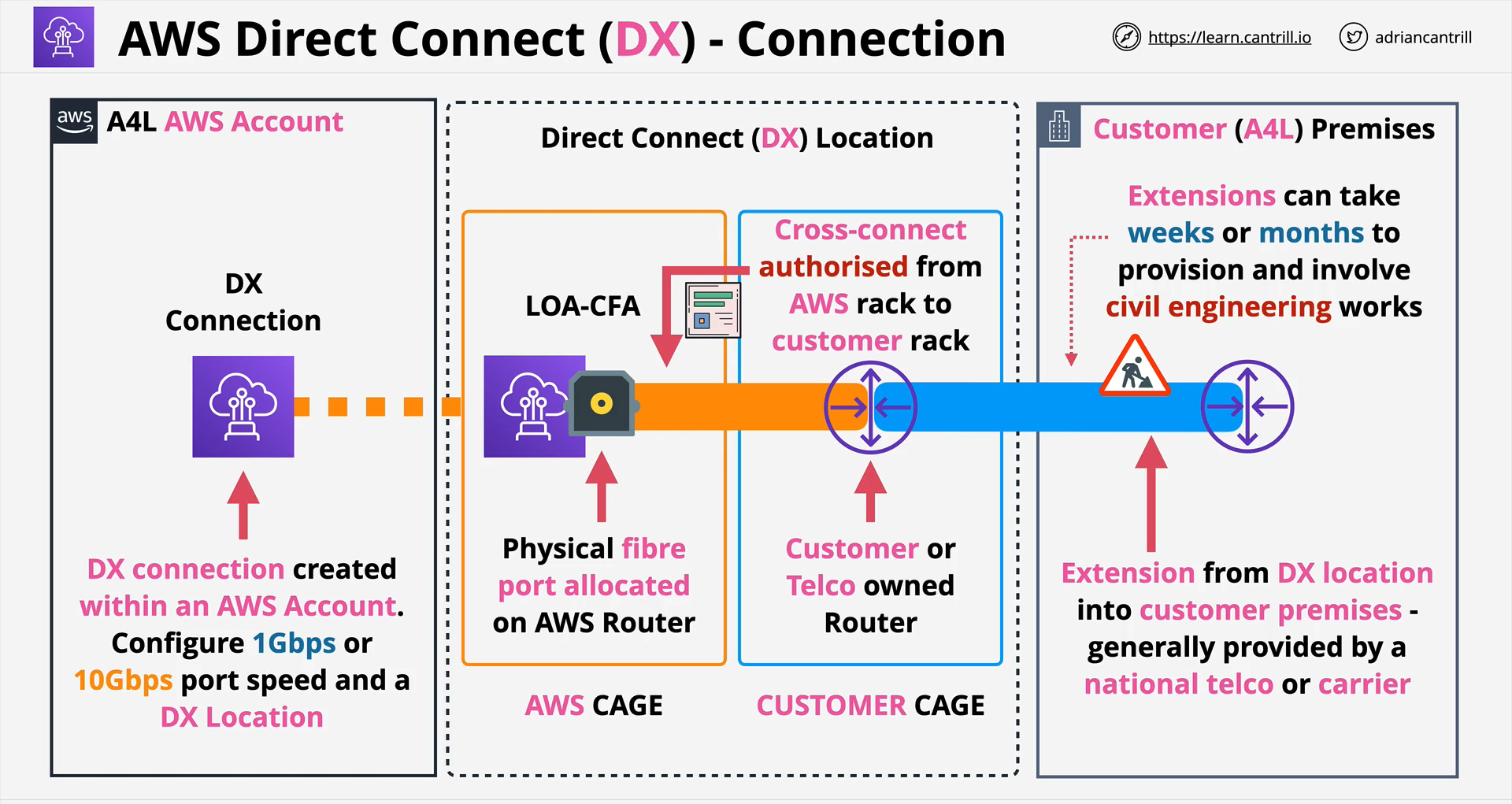
- DX lins your on-premises network to AWS, it does it physically with fibr cables.
- To create DX connection, you need to:
- Create a connection within you AWS account.
- Choose speed, either 1Gbps or 10Gbps.
- Choose DX location.
- After this, AWS will allocate a DX port in that DX location.
- Depends on the speed you selected, you'll be given either:
- 1000-Base-LX
- 10GBASE-LR
- To connect to the DX port that AWS allocated and to the router that your internet provider allocated inside the DX Location, you need to arrange cross-connect between.
- This will establish connection between your DX port on the AWS DX router and your Customer DX router.
- There's an authorization needed to perform cross-connect from AWS Rack and Customer Rack.
- Cross-connect happens at the DX Location.
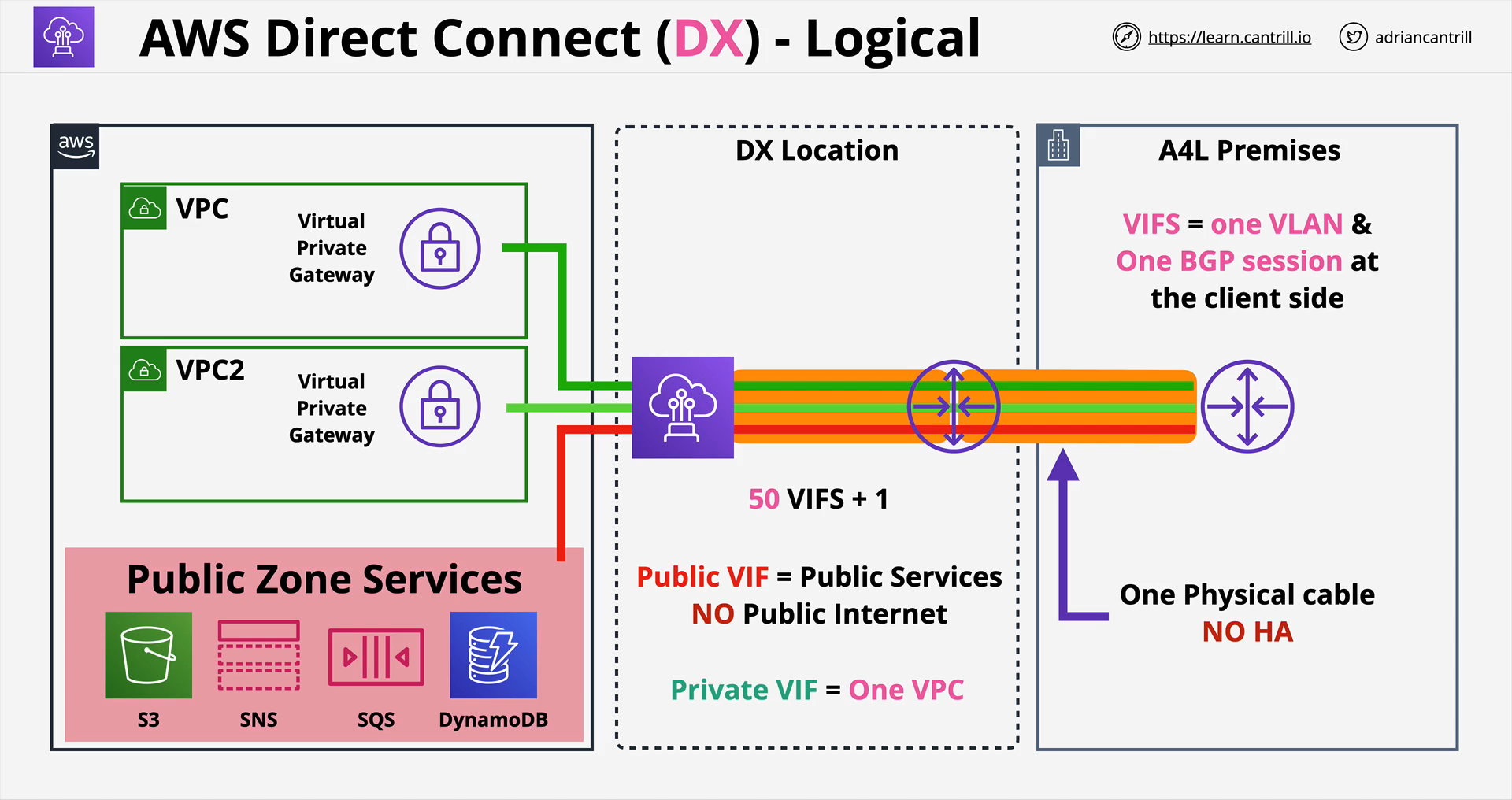
- Virtual Interface (VIF) - the thing that transfer data.
- VLAN and BGP session.
- 3 Types of VIF
- Private VIF
- use to access AWS VPC using Private IP addresses.
- By default, it can connect to VPC as the same Region.
- Connects to the VGW that is attached on the VPC.
- Public VIF
- use to access AWS Public Services using their Public IP addresses.
- Cannot be used to access the Public internet, its for AWS Public Zone Services only.
- Transit VIF
- use to access one or more AWS VPC Transit Gateway associated with DX Gateway.
- Private VIF
- via AWS
- Dedicated connection - direct from AWS.
- Speed: 1GB / 10GBPS
- via Partner
- Ranges of speed between 50MBPS -> 10GBPS.
- Types:
- Hosted Connection
- a DX Connection with one VIF.
- All the bandwidth is dedicated with a single VIF.
- If you require more VIF, you need an additional hosted connection.
- Hosted VIF
- Cannot specify speed as it is shared connection.
- It shares the bandwidth of the parent DX connection which is in the partner account.
- Hosted Connection
Notes:
- DX is not encrypted.
- To encrypt it, you can use the Public VIF + S2S VPN.
- DX does not shares your internet data cap.
- DX does not shares your internet bandwidth.
- No transit over the internet - low / consistent latency.
- Cheaper data transfer - faster speeds.
- LAG is for improving speed and manageability.
- Combines 2 DX connection to 1, to achieve high speed connection.
- 4 DX Max, must be at the same speed and same DX location.
- Multiple Physical Connection act as one - Speed * n.
- Active / Active Architecture.
- Maximum of 4 Connection per LAG
- All connection need to be the same speed.
- and also be terminated at the same DX location.
- A LAG has a minimumLinks attribute - the LAG is considered Active as long this attribute or more connections are active.
- e.g. if minimumLinks is set to 2 then you have 3 active connection the LAG is still active; if the active connection decreased to 2, the LAG is still active; if the active connection decreased to 1, the LAG is considered Failed.
- if active connections are less than the minimumLinks the LAG will Fail.
- e.g. if minimumLinks is set to 2 then you have 3 active connection the LAG is still active; if the active connection decreased to 2, the LAG is still active; if the active connection decreased to 1, the LAG is considered Failed.






.PNG)