-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 18.4k
Description
What version of Go are you using (go version)?
$ go version go version go1.12.1 linux/amd64
Does this issue reproduce with the latest release?
Yes
What operating system and processor architecture are you using (go env)?
go env Output
$ go env GOARCH="amd64" GOBIN="" GOCACHE="/root/.cache/go-build" GOEXE="" GOFLAGS="" GOHOSTARCH="amd64" GOHOSTOS="linux" GOOS="linux" GOPATH="/data/go_work" GOPROXY="" GORACE="" GOROOT="/usr/local/go" GOTMPDIR="" GOTOOLDIR="/usr/local/go/pkg/tool/linux_amd64" GCCGO="gccgo" CC="gcc" CXX="g++" CGO_ENABLED="1" GOMOD="" CGO_CFLAGS="-g -O2" CGO_CPPFLAGS="" CGO_CXXFLAGS="-g -O2" CGO_FFLAGS="-g -O2" CGO_LDFLAGS="-g -O2" PKG_CONFIG="pkg-config" GOGCCFLAGS="-fPIC -m64 -pthread -fmessage-length=0 -fdebug-prefix-map=/tmp/go-build134300587=/tmp/go-build -gno-record-gcc-switches"
What did you do?
At the very first time, we found that when I dig the backend dns server, which is written in go, we got an unexpect source alert, it seems that the reply came from another interface from the machine.

So I want to stimulate this issue with a tiny program like:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net"
)
func main() {
listener, err := net.ListenUDP("udp", &net.UDPAddr{IP: net.ParseIP("0.0.0.0"), Port: 9999})
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("Local: <%s> \n", listener.LocalAddr().String())
data := make([]byte, 1024)
for {
n, remoteAddr, err := listener.ReadFromUDP(data)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("error during read: %s", err)
}
fmt.Printf("<%s> %s\n", remoteAddr, data[:n])
_, err = listener.WriteToUDP([]byte("world"), remoteAddr)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf(err.Error())
}
}
}UDP server listen on (:9999 or 0.0.0.0:9999)

What did you expect to see?
The machine we are gonna access is bound with multiple interface, i.e. it has eth0/eth1/tun0/tun1 etc.
so when the client get access to this service from eth0, it is expect that the reply must be sent from interface eth0.

What did you see instead?
Udp server local ip (multi)
x.x.52.207
x.x.56.205
x.x.78.207
client (remote IP) : x.x.218.174
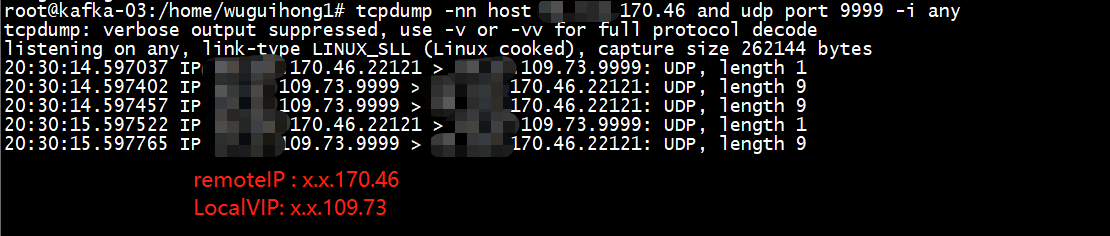
as you can see, the server always reply from the default interface, the steps are as belows:
- client(x.x.218.174) -> udp server(x.x.52.207) got reply from udp server(x.x.52.207)
- client(x.x.218.174) -> udp server(x.x.56.205) got reply from udp server(x.x.52.207)
TCP connections all work as expect except UDP connections.
However, when we test this scenario with Nginx, it works:
As you can see it reply the client with the incoming interface instead of the default one.
Here is the simplified config:
# nginx listen on 0.0.0.0:9999
stream {
upstream dns {
server x.x.41.44:9999;
}
server {
listen 9999 udp;
... ...
}
}