For an even better experience in Python development, check out UV. It’s a more powerful and versatile tool that i highly recommend. I will keep this repository publicly available for those who on the off chance may wish to adapt or build upon it. I will continue to make updates for myself if I find more use cases or get bored.
The dev_template tool is designed with simplicity and speed in mind, providing a streamlined approach to setting up new Python projects. Unlike other feature-rich tools, dev_template focuses on quick development, allowing you to get started without the need to wade through extensive documentation (hopefully).
This tool was created to help enforce better development standards, even for quick tools and hobbyist programs. It offers essential features that facilitate a consistent project structure and dependency management, making it ideal for developers who need a reliable setup process without the overhead of complex configurations.
For those who want a bit more customization, the project's README provides clear instructions on how to modify templates and configuration settings. Everything you need to know is right there, making it easy to tailor the tool to fit your specific needs. (If you still have/find issues please submit an issue).
With dev_template, you can start your projects quickly, maintain good development practices, and avoid the hassle of extensive setup processes and documentation crawling.
this tool is for those of us that are lazy
-
User-Friendly
-
Interactive Prompts:
- Utilizes interactive prompts with directory path completion.
-
Cross-Platform Compatibility:
- Handles platform-specific differences for paths and commands (e.g., Windows vs. Unix-like systems).
-
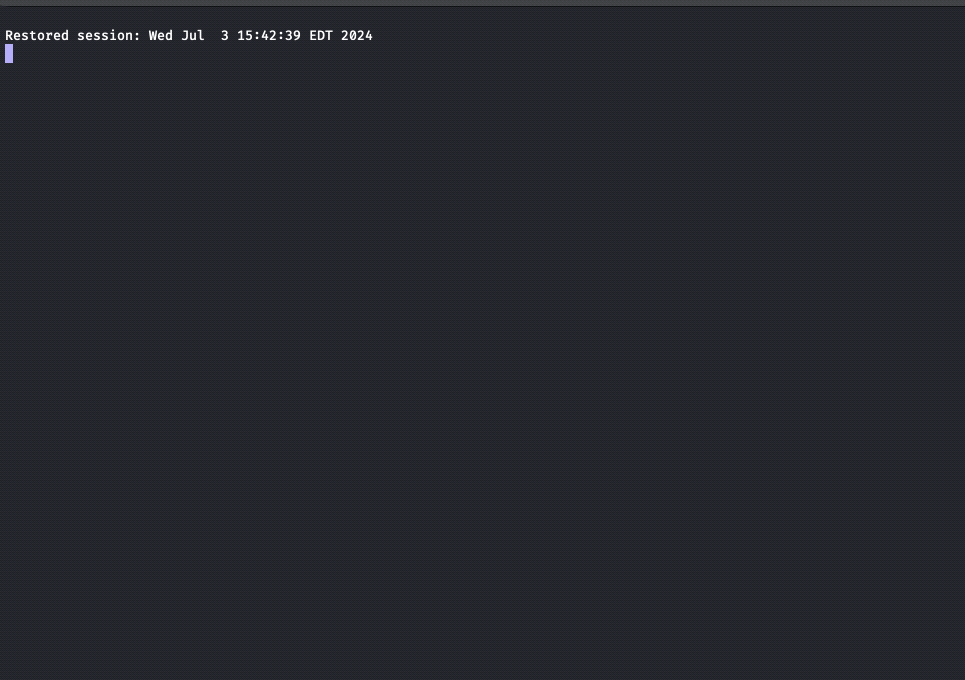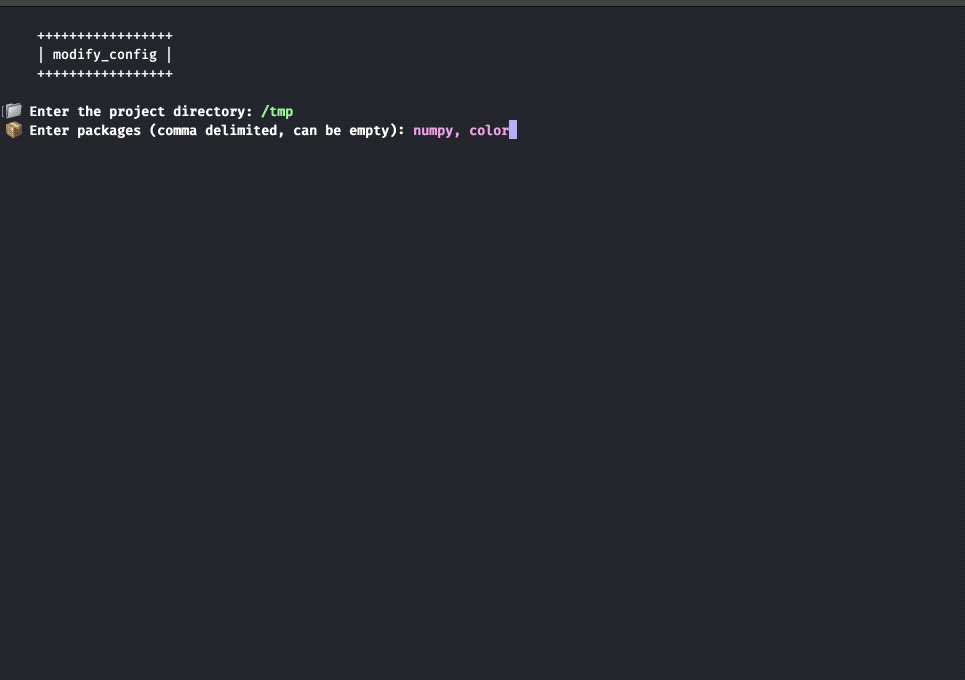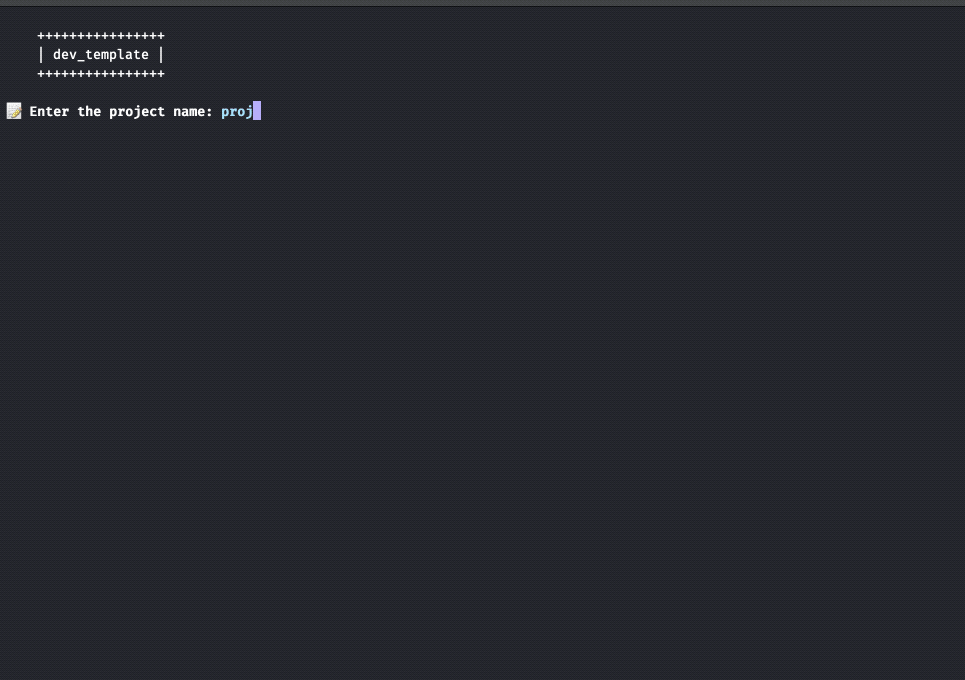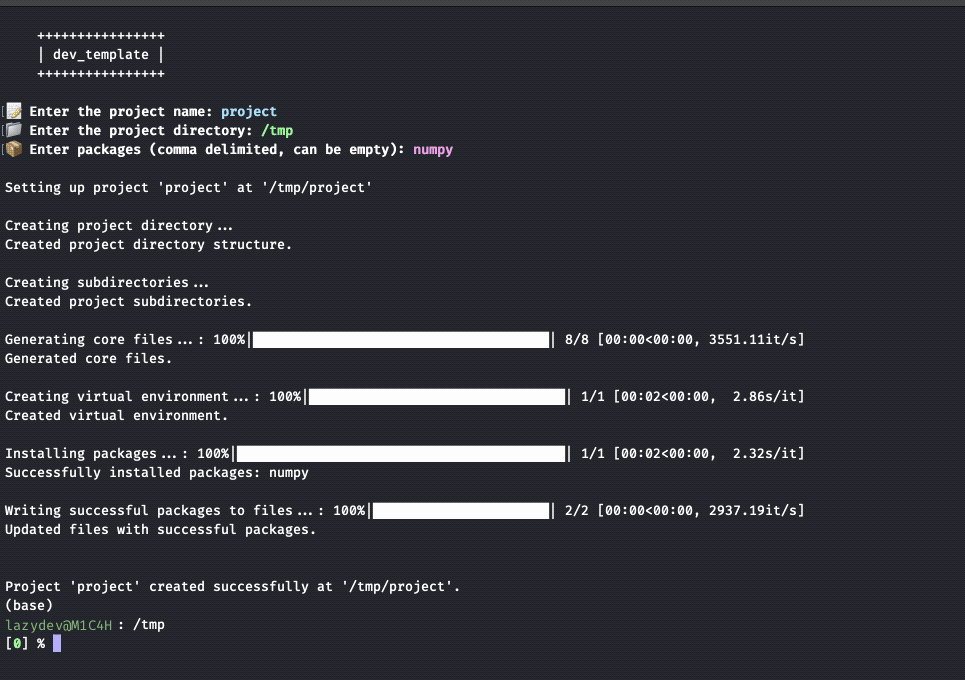
Project Directory Creation:
- Creates a new project directory structure, including subdirectories (
src,tests) and basic files (README.md,.gitignore,requirements.txt, etc.). - Optionally creates
setup.pyandpyproject.tomlbased on configuration settings.
- Creates a new project directory structure, including subdirectories (
-
Configuration Management:
- Uses a configuration file to manage default settings like packages to install, project path, and templates.
- Provides an interactive setup configuration option to modify default settings.
-
Template Copying:
- Copies predefined templates for project files from a configured templates directory.
- Ability to replace template files in the config directory with their own personalized versions.
-
Virtual Environment Management:
- Automatically creates a virtual environment for the new project.
- Installs specified packages into the virtual environment.
-
Package Management:
- Installs packages specified by the user or from the default configuration.
- Allows specifying exact package versions during creation.
- Updates
requirements.txtandpyproject.tomlwith successfully installed packages and their versions.
-
Error Handling:
- Provides comprehensive error handling and logging for various operations, including directory creation, package installation, and user input validation.
-
Logging:
- Supports debug logging for detailed execution trace.
project
├── project_venv
├── src
│ └── project
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── main.py
├── tests
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── test_main.py
├── .gitignore
├── README.md
├── requirements.txt
├── setup.py (creation disabled by default)
└── pyproject.toml (creation enabled by default)
To install the package using pip, run the following command:
pip install dev-templateOnce installed, you can start the tool by typing the following command in your terminal:
dev_templateAlternatively, you can run it as a Python module:
python -m dev_template.dev_templateAfter setting up your project, navigate into the project directory and activate the virtual environment.
- The virtual environment folder is named after your project (e.g., project_venv).
For Linux/macOS:
source project_venv/bin/activateFor Windows (Powershell):
.\project_venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1To deactivate the virtual environment, simply type:
deactivate- Clone the repository, navigate to the project directory, create and activate a virtual environment:
- On MacOS/Linux:
git clone https://github.com/http-kennedy/dev_template.git
cd dev_template
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate- On Windows (Powershell):
git clone https://github.com/http-kennedy/dev_template.git
cd dev_template
python -m venv venv
.\venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1- Install the requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt- Install the package:
- For interactive development (editable mode):
pip install -e .- To install directly:
pip install .Once installed, you can start the tool by typing the following command in your terminal:
dev_templateAlternatively, you can run the script directly:
python src/dev_template/dev_template.pyAfter setting up your project, navigate into the project directory and activate the virtual environment.
- The virtual environment folder is named after your project (e.g., project_venv).
For Linux/macOS:
source project_venv/bin/activateFor Windows (Powershell):
.\project_venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1To deactivate the virtual environment, simply type:
deactivateThe dev_template tool can be ran with various flags to perform different actions. Here are the available options:
-
-h,--help:- Displays the help message with information about all available options.
-
-c,--config:- Enters configuration mode, allowing you to customize default settings such as default packages to install, default directory for projects, and whether to create
setup.pyandpyproject.tomlfiles.
- Enters configuration mode, allowing you to customize default settings such as default packages to install, default directory for projects, and whether to create
-
-d,--debug:- Enables debug logging for more detailed output during execution.
- Log File Locations
- Linux/macOS:
- Log files:
~/.config/dev_template/logs
- Log files:
- Windows:
- Log files:
%LOCALAPPDATA%\dev_template\logs
- Log files:
- Linux/macOS:
The dev_template tool offers a configuration mode to customize default settings. You can enter configuration mode by running:
dev_template -cor
dev_template --configWhen in configuration mode you can set the following values:
-
Default packages to install:
- Packages must be
commma delimited. - Can be modified during normal execution of
dev_template - If defining a specific version use pip's version specifier syntax.
'package_name'=='version'- For example:
pandas==2.1.4
- Packages must be
-
Absolute path for default project directory creation:
- Sets default input for where to create the project.
- Can be modified during normal execution of
dev_template
-
Create
setup.pyfor new project directories:- Choose whether to create a
setup.pyfile in new project directories. - Default is set to
No
- Choose whether to create a
-
Create
pyproject.tomlfor new project directories:- Choose whether to create a
pyproject.tomlfile in new project directories. - Default is set to
Yes
- Choose whether to create a
Configuration File Locations
-
Linux/macOS:
- Configuration file:
~/.config/dev_template/config.ini - Templates directory:
~/.config/dev_template/templates/
- Configuration file:
-
Windows:
- Configuration file:
%LOCALAPPDATA%\dev_template\config.ini - Templates directory:
%LOCALAPPDATA%\dev_template\templates\
- Configuration file:
- If you replace or modify any of the template files in the templates directory using the same filename/s, the customized files will be used during project setup.
- Logging Wrapper: Implement a standardized logging wrapper.
- Typer Package: Enhance the command-line interface using the
typerpackage.
- Store virtual environments in the project directory or a user-specified location.
- Add version management and update notifications.
- Add an argument to remake the configuration directory.
- Allow custom project structures via the templates directory.
- If you need to install a specific package verison, use pip's version specifier syntax.
'package_name'=='version'- For example:
pandas==2.1.4
-
pyproject.toml: The
dependenciessection must be present in thepyproject.tomlfile. The absence of this section can cause installation issues. -
Config Template Directory: Problems may arise if not all expected files are present in the templates directory. Ensure that all necessary template files are included to avoid errors.
- Workaround: Delete
config directoryand re-rundev_template.- For Linux/macOS:
~/.config/dev_template - For Windows:
%LOCALAPPDATA%\dev_template
- For Linux/macOS:
- Workaround: Delete