|
| 1 | +### 题目描述 |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +这是 LeetCode 上的 **[749. 隔离病毒](https://leetcode.cn/problems/contain-virus/solution/by-ac_oier-l9ya/)** ,难度为 **困难**。 |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +Tag : 「模拟」、「图论搜索」、「BFS」 |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | + |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +病毒扩散得很快,现在你的任务是尽可能地通过安装防火墙来隔离病毒。 |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +假设世界由 $m \times n$ 的二维矩阵 `isInfected` 组成,`isInfected[i][j] == 0` 表示该区域未感染病毒,而 `isInfected[i][j] == 1` 表示该区域已感染病毒。可以在任意 $2$ 个相邻单元之间的共享边界上安装一个防火墙(并且只有一个防火墙)。 |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +每天晚上,病毒会从被感染区域向相邻未感染区域扩散,除非被防火墙隔离。现由于资源有限,每天你只能安装一系列防火墙来隔离其中一个被病毒感染的区域(一个区域或连续的一片区域),且该感染区域对未感染区域的威胁最大且 保证唯一 。 |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +你需要努力使得最后有部分区域不被病毒感染,如果可以成功,那么返回需要使用的防火墙个数; 如果无法实现,则返回在世界被病毒全部感染时已安装的防火墙个数。 |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +示例 1: |
| 18 | +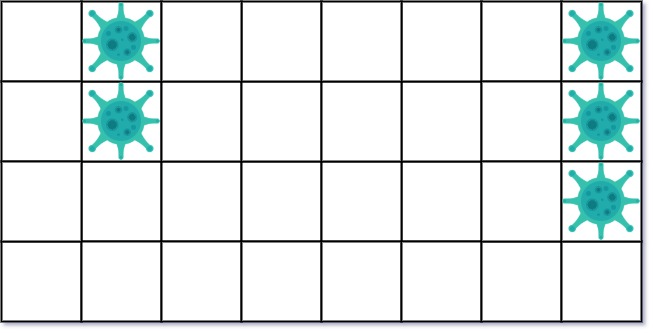 |
| 19 | +``` |
| 20 | +输入: isInfected = [[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1],[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]] |
| 21 | +
|
| 22 | +输出: 10 |
| 23 | +
|
| 24 | +解释:一共有两块被病毒感染的区域。 |
| 25 | +在第一天,添加 5 墙隔离病毒区域的左侧。病毒传播后的状态是: |
| 26 | +
|
| 27 | +第二天,在右侧添加 5 个墙来隔离病毒区域。此时病毒已经被完全控制住了。 |
| 28 | +``` |
| 29 | +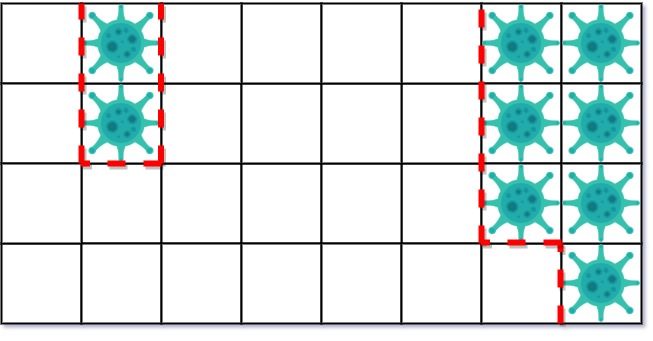 |
| 30 | +示例 2: |
| 31 | +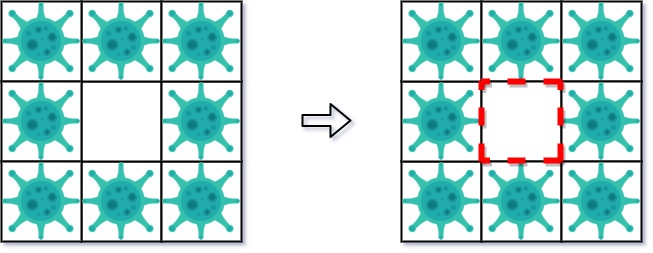 |
| 32 | +``` |
| 33 | +输入: isInfected = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]] |
| 34 | +
|
| 35 | +输出: 4 |
| 36 | +
|
| 37 | +解释: 虽然只保存了一个小区域,但却有四面墙。 |
| 38 | +注意,防火墙只建立在两个不同区域的共享边界上。 |
| 39 | +``` |
| 40 | +示例 3: |
| 41 | +``` |
| 42 | +输入: isInfected = [[1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0],[1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0]] |
| 43 | +
|
| 44 | +输出: 13 |
| 45 | +
|
| 46 | +解释: 在隔离右边感染区域后,隔离左边病毒区域只需要 2 个防火墙。 |
| 47 | +``` |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +提示: |
| 50 | +* $m == isInfected.length$ |
| 51 | +* $n == isInfected[i].length$ |
| 52 | +* $1 <= m, n <= 50$ |
| 53 | +* `isInfected[i][j]` is either `0` or `1` |
| 54 | +* 在整个描述的过程中,总有一个相邻的病毒区域,它将在下一轮 严格地感染更多未受污染的方块 |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | +--- |
| 57 | + |
| 58 | +### 搜索模拟 |
| 59 | + |
| 60 | +根据题意,我们可以按天进行模拟,设计函数 `getCnt` 用于返回当天会被安装的防火墙数量,在 `getCnt` 内部我们会进行如下操作: |
| 61 | + |
| 62 | +* 找出当天「对未感染区域的威胁最大」的区域,并将该区域进行隔离(将 $1$ 设置为 $-1$); |
| 63 | +* 对其他区域,进行步长为 $1$ 的感染操作。 |
| 64 | + |
| 65 | +考虑如何实现 `getCnt`:我们需要以「连通块」为单位进行处理,因此每次的 `getCnt` 操作,我们先重建一个与矩阵等大的判重数组 `vis`,对于每个 $g[i][j] = 1$ 且未被 $vis[i][j]$ 标记为 `True` 的位置进行搜索,搜索过程使用 `BFS` 实现。 |
| 66 | + |
| 67 | +**在 `BFS` 过程中,我们除了统计该连通块所需要的防火墙数量 $b$ 以外,还需要额外记录当前连通块中 $1$ 的点集 `s1`(简称为原集,含义为连通块的格子集合),以及当前连通块相邻的 $0$ 的点集 `s2`(简称为扩充集,含义为将要被感染的格子集合)。** |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +根据题意,在单次的 `getCnt` 中,我们需要在所有连通块中取出其 `s2` 大小最大(对未感染区域的威胁最大)的连通块进行隔离操作,而其余连通块则进行扩充操作。 |
| 70 | + |
| 71 | +因此我们可以使用两个变量 `max` 和 `ans` 分别记录所有 `s2` 中的最大值,以及取得最大 `s2` 所对应连通块所需要的防火墙数量,同时需要使用两个数组 `l1` 和 `l2` 分别记录每个连通块对应的「原集」和「扩充集」,方便我们后续进行「隔离」和「感染」。 |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | +Java 代码: |
| 74 | +```Java |
| 75 | +class Solution { |
| 76 | + int[][] g; |
| 77 | + int n, m, ans; |
| 78 | + int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; |
| 79 | + boolean[][] vis; |
| 80 | + int search(int _x, int _y, Set<Integer> s1, Set<Integer> s2) { |
| 81 | + int ans = 0; |
| 82 | + Deque<int[]> d = new ArrayDeque<>(); |
| 83 | + vis[_x][_y] = true; |
| 84 | + d.addLast(new int[]{_x, _y}); |
| 85 | + s1.add(_x * m + _y); |
| 86 | + while (!d.isEmpty()) { |
| 87 | + int[] info = d.pollFirst(); |
| 88 | + int x = info[0], y = info[1]; |
| 89 | + for (int[] di : dirs) { |
| 90 | + int nx = x + di[0], ny = y + di[1], loc = nx * m + ny; |
| 91 | + if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m || vis[nx][ny]) continue; |
| 92 | + if (g[nx][ny] == 1) { |
| 93 | + s1.add(loc); |
| 94 | + vis[nx][ny] = true; |
| 95 | + d.addLast(new int[]{nx, ny}); |
| 96 | + } else if (g[nx][ny] == 0) { |
| 97 | + s2.add(loc); |
| 98 | + ans++; |
| 99 | + } |
| 100 | + } |
| 101 | + } |
| 102 | + return ans; |
| 103 | + } |
| 104 | + int getCnt() { |
| 105 | + vis = new boolean[n][m]; |
| 106 | + int max = 0, ans = 0; |
| 107 | + // l1: 每个连通块的点集 s2: 每个连通块的候选感染点集 |
| 108 | + List<Set<Integer>> l1 = new ArrayList<>(), l2 = new ArrayList<>(); |
| 109 | + for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { |
| 110 | + for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { |
| 111 | + if (g[i][j] == 1 && !vis[i][j]) { |
| 112 | + // s1: 当前连通块的点集 s2: 当前连通块的候选感染点集 |
| 113 | + Set<Integer> s1 = new HashSet<>(), s2 = new HashSet<>(); |
| 114 | + int b = search(i, j, s1, s2), a = s2.size(); |
| 115 | + if (a > max) { |
| 116 | + max = a; ans = b; |
| 117 | + } |
| 118 | + l1.add(s1); l2.add(s2); |
| 119 | + } |
| 120 | + } |
| 121 | + } |
| 122 | + for (int i = 0; i < l2.size(); i++) { |
| 123 | + for (int loc : l2.get(i).size() == max ? l1.get(i) : l2.get(i)) { |
| 124 | + int x = loc / m, y = loc % m; |
| 125 | + g[x][y] = l2.get(i).size() == max ? -1 : 1; |
| 126 | + } |
| 127 | + } |
| 128 | + return ans; |
| 129 | + } |
| 130 | + public int containVirus(int[][] _g) { |
| 131 | + g = _g; |
| 132 | + n = g.length; m = g[0].length; |
| 133 | + while (true) { |
| 134 | + int cnt = getCnt(); |
| 135 | + if (cnt == 0) break; |
| 136 | + ans += cnt; |
| 137 | + } |
| 138 | + return ans; |
| 139 | + } |
| 140 | +} |
| 141 | +``` |
| 142 | +TypeScript 代码: |
| 143 | +```TypeScript |
| 144 | +let g: number[][] = null |
| 145 | +let n: number = 0, m: number = 0 |
| 146 | +let vis: boolean[][] = null |
| 147 | +const dirs: number[][] = [[1,0],[-1,0],[0,1],[0,-1]] |
| 148 | +function dfs(_x: number, _y: number, s1: Set<number>, s2: Set<number>): number { |
| 149 | + let he = 0, ta = 0, ans = 0 |
| 150 | + let d: Array<number> = new Array<number>() |
| 151 | + s1.add(_x * m + _y) |
| 152 | + vis[_x][_y] = true |
| 153 | + d[ta++] = _x * m + _y |
| 154 | + while (he < ta) { |
| 155 | + const poll = d[he++] |
| 156 | + const x = Math.floor(poll / m), y = poll % m |
| 157 | + for (const di of dirs) { |
| 158 | + const nx = x + di[0], ny = y + di[1], loc = nx * m + ny |
| 159 | + if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m || vis[nx][ny]) continue |
| 160 | + if (g[nx][ny] == 1) { |
| 161 | + s1.add(loc) |
| 162 | + vis[nx][ny] = true |
| 163 | + d[ta++] = loc |
| 164 | + } else if (g[nx][ny] == 0) { |
| 165 | + s2.add(loc) |
| 166 | + ans++ |
| 167 | + } |
| 168 | + } |
| 169 | + } |
| 170 | + return ans |
| 171 | +} |
| 172 | +function getCnt(): number { |
| 173 | + vis = new Array<Array<boolean>>(n) |
| 174 | + for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) vis[i] = new Array<boolean>(m).fill(false) |
| 175 | + let max = 0, ans = 0 |
| 176 | + let l1: Array<Set<number>> = new Array<Set<number>>(), l2: Array<Set<number>> = new Array<Set<number>>() |
| 177 | + for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { |
| 178 | + for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) { |
| 179 | + if (g[i][j] == 1 && !vis[i][j]) { |
| 180 | + let s1 = new Set<number>(), s2 = new Set<number>() |
| 181 | + const b = dfs(i, j, s1, s2), a = s2.size |
| 182 | + if (a > max) { |
| 183 | + max = a; ans = b |
| 184 | + } |
| 185 | + l1.push(s1); l2.push(s2) |
| 186 | + } |
| 187 | + } |
| 188 | + } |
| 189 | + for (let i = 0; i < l2.length; i++) { |
| 190 | + for (let loc of l2[i].size == max ? l1[i] : l2[i]) { |
| 191 | + const x = Math.floor(loc / m), y = loc % m |
| 192 | + g[x][y] = l2[i].size == max ? -1 : 1 |
| 193 | + } |
| 194 | + } |
| 195 | + return ans |
| 196 | +} |
| 197 | +function containVirus(_g: number[][]): number { |
| 198 | + g = _g |
| 199 | + n = g.length; m = g[0].length |
| 200 | + let ans: number = 0 |
| 201 | + while (true) { |
| 202 | + const cnt = getCnt() |
| 203 | + if (cnt == 0) break |
| 204 | + ans += cnt |
| 205 | + } |
| 206 | + return ans |
| 207 | +}; |
| 208 | +``` |
| 209 | +* 时间复杂度:最多有 $n + m$ 天需要模拟,每天模拟复杂度 $O(n \times m)$,整体复杂度为 $O((n + m) \times nm)$ |
| 210 | +* 空间复杂度:$O(nm)$ |
| 211 | + |
| 212 | +--- |
| 213 | + |
| 214 | +### 最后 |
| 215 | + |
| 216 | +这是我们「刷穿 LeetCode」系列文章的第 `No.749` 篇,系列开始于 2021/01/01,截止于起始日 LeetCode 上共有 1916 道题目,部分是有锁题,我们将先把所有不带锁的题目刷完。 |
| 217 | + |
| 218 | +在这个系列文章里面,除了讲解解题思路以外,还会尽可能给出最为简洁的代码。如果涉及通解还会相应的代码模板。 |
| 219 | + |
| 220 | +为了方便各位同学能够电脑上进行调试和提交代码,我建立了相关的仓库:https://github.com/SharingSource/LogicStack-LeetCode 。 |
| 221 | + |
| 222 | +在仓库地址里,你可以看到系列文章的题解链接、系列文章的相应代码、LeetCode 原题链接和其他优选题解。 |
| 223 | + |
0 commit comments