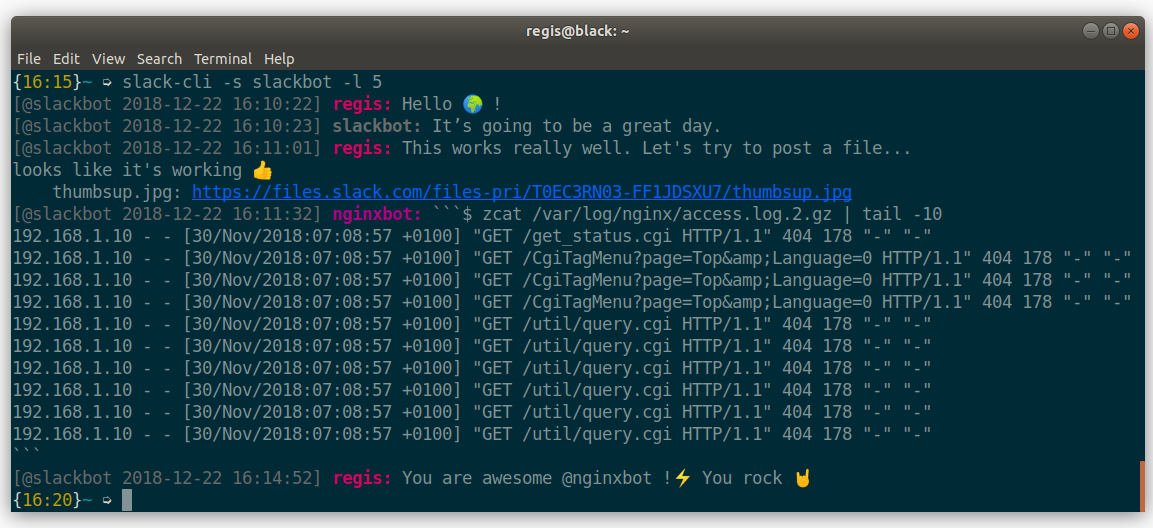
Effectively interact with Slack from the command line: send messages, upload files, send command output, pipe content... all from the confort of your terminal.
Member of dozens of Slack teams? No worries, with slack-cli you can easily switch from one team to another.
$ pip install slack-cli $ slack-cli -d general "Hello everyone!"
You will be asked to provide a Slack API token. It's easy, check out the Tokens section for a quickstart.
$ slack-cli -h
usage: slack-cli [-h] [-t TOKEN] [-T TEAM] [-d DST] [-f FILE] [--pre] [--run]
[-u USER] [-s SRC] [-l LAST]
[messages [messages ...]]
Send, pipe, upload and receive Slack messages from the CLI
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-t TOKEN, --token TOKEN
Explicitly specify Slack API token which will be
saved to /home/user/.config/slack-cli/slack_token.
-T TEAM, --team TEAM Team domain to interact with. This is the name that
appears in the Slack url: https://xxx.slack.com. Use
this option to interact with different teams. If
unspecified, default to the team that was last used.
Send messages:
-d DST, --dst DST Send message to a Slack channel, group or username
-f FILE, --file FILE Upload file
--pre Send as verbatim `message`
--run Run the message as a shell command and send both the
message and the command output
-u USER, --user USER Send message not as the current user, but as a bot
with the specified user name
messages Messages to send (messages can also be sent from
standard input)
Receive messages:
-s SRC, --src SRC Receive messages from a Slack channel, group or
username. This option can be specified multiple times.
When streaming, use 'all' to stream from all sources.
-l LAST, --last LAST Print the last N messages. If this option is not
specified, messages will be streamed from the
requested sources.
The destination argument may be any user, group or channel:
$ slack-cli -d general "Hello everyone!" $ slack-cli -d slackbot "Hello!"
Send message with a different username:
$ slack-cli -d general -u terminator "I'll be back"
$ slack-cli -d general "/status :office: In the office" $ slack-cli -d general "/status :house: At home" $ slack-cli -d general "/status Just chillin'" $ slack-cli -d general "/status clear"
$ cat /etc/hosts | slack-cli -d devteam
Usually you will want to format piped content as verbatim content with triple backticks ("```"). This is achieved with the --pre option:
$ tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log | slack-cli -d devteam --pre
$ slack-cli -f /etc/nginx/sites-available/default.conf -d alice
This is really convenient for showing both the result of a command and the command itself:
$ slack-cli -d john --run "git log -1"
will send to user john:
$ git log -1
commit 013798f5c85043d31f0221a9a32b39298e97fb08
Author: Régis Behmo <regis@behmo.com>
Date: Thu Jun 22 15:20:36 2017 +0200
Replace all commands by a single command
Our first 1.0 release!
Stream the content of a channel:
$ slack-cli -s general
Monitor all conversations:
$ slack-cli -s all
$ slack-cli -s general --last 10000 > general.log $ slack-cli -s myboss --last 10000 > covermyass.log
Switch to a different team anytime with the -T flag:
$ slack-cli -T family -d general "I'll be home in an hour"
The new team will become the new default team.
Note that the Slack token may optionally be stored in an environment variable (although it is not recommended for security reasons):
$ export SLACK_TOKEN="slack_token_string"
The slack-cli configuration is stored in a generic configuration directory -- by default, this is ~/.config/slack-cli on Linux. You can check the path of this directory by running:
python3 -c "from slackcli.token import CONFIG_ROOT; print(CONFIG_ROOT)"
This directory can be modified by setting the SLACK_CLI_CONFIG_ROOT environment variable. For instance:
export SLACK_CLI_CONFIG_ROOT=~/slackcli
Channel, group and user names can be autocompleted from the command line for bash users. Add the following line to ~/.bashrc:
eval "$(register-python-argcomplete slack-cli)"
Then, try autocompletion with:
$ slack -s gene<tab>
or:
$ slack -d <tab><tab>
Unfortunately, I did not manage to get autocompletion to work with zsh ¯\_( ͡° ͜ʖ ͡°)_/¯ Please let me know if you have more success.
Color output is activated by default in compatible terminals. To deactivate colors, define the SLACK_CLI_NO_COLOR environment variable:
export SLACK_CLI_NO_COLORS=1
Emoji short codes will be automatically replaced by their corresponding unicode value. For instance, :smile: will become 😄. However, these characters will display properly only if your terminal supports them! I stronly encourage you to download patched fonts from Nerd Fonts and to configure your terminal to use them. For instance, in Ubuntu this is how I downloaded the DejaVuSansMono fonts:
wget -O ~/.fonts/DejaVuSansMono.zip https://github.com/ryanoasis/nerd-fonts/releases/download/v2.0.0/DejaVuSansMono.zip cd ~/.fonts unzip DejaVuSansMono.zip fc-cache -vf ~/.fonts
If emojis are not your thing, you can disable them globally with the SLACK_CLI_NO_EMOJI environment variable:
export SLACK_CLI_NO_EMOJI=1
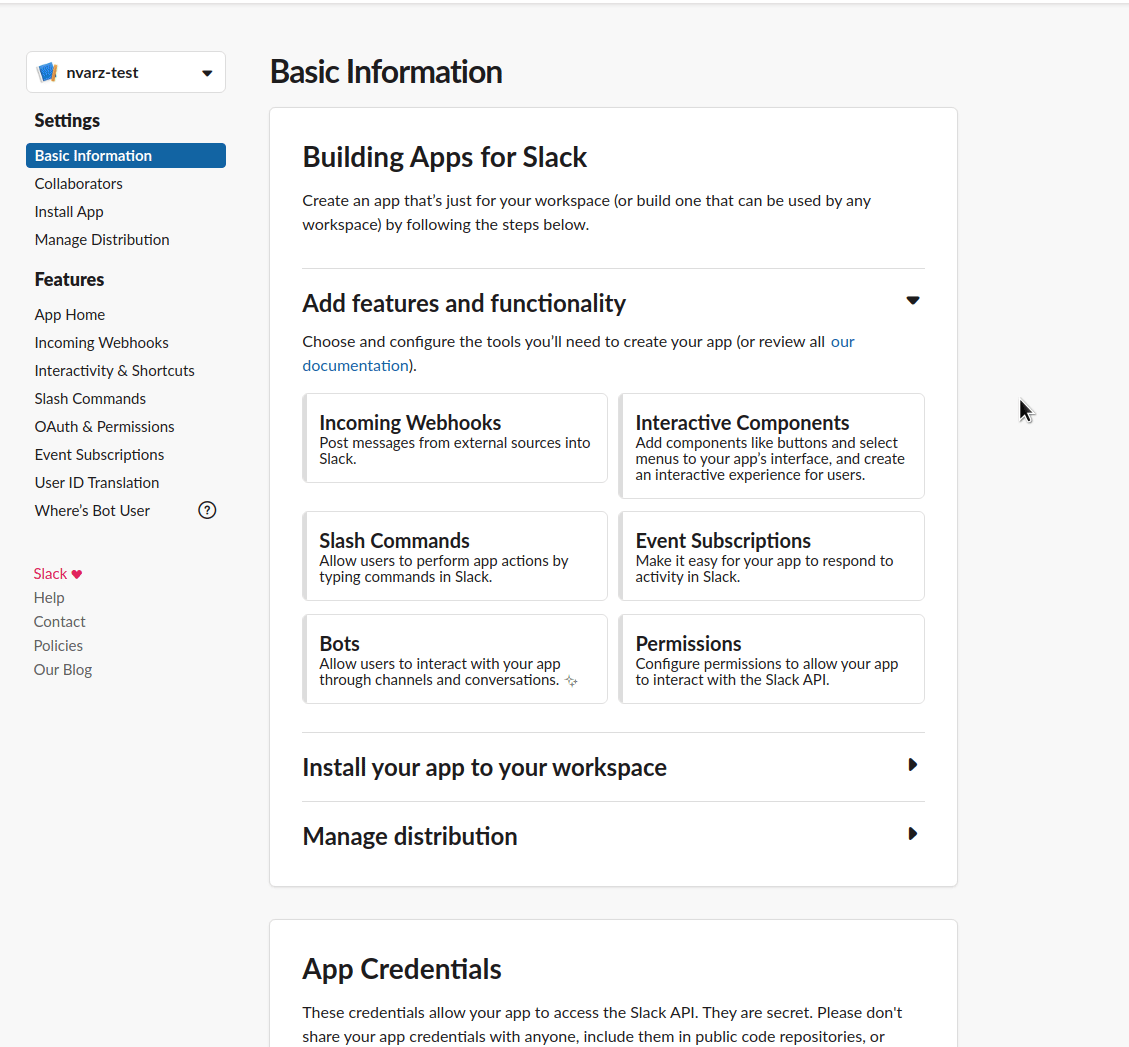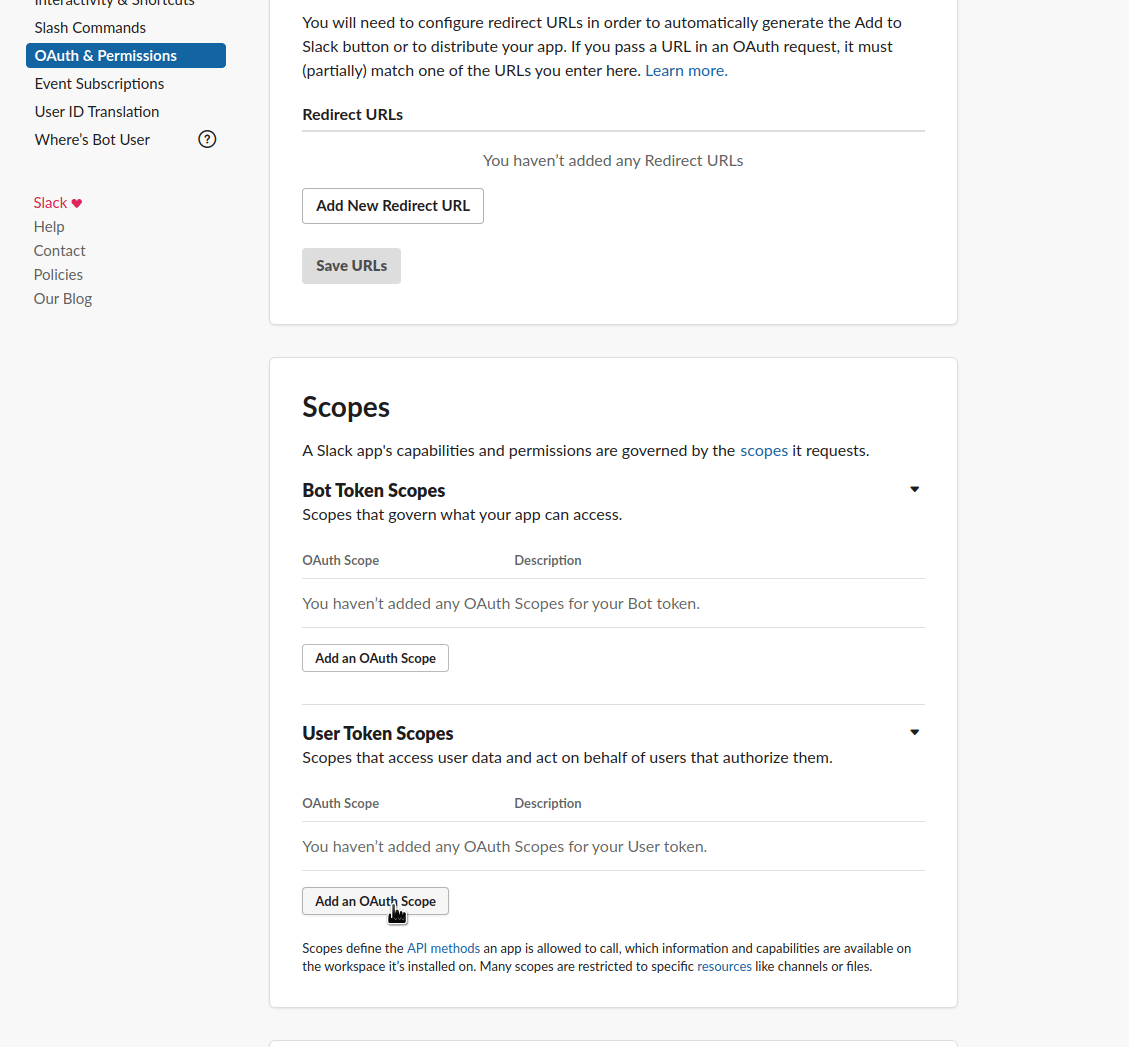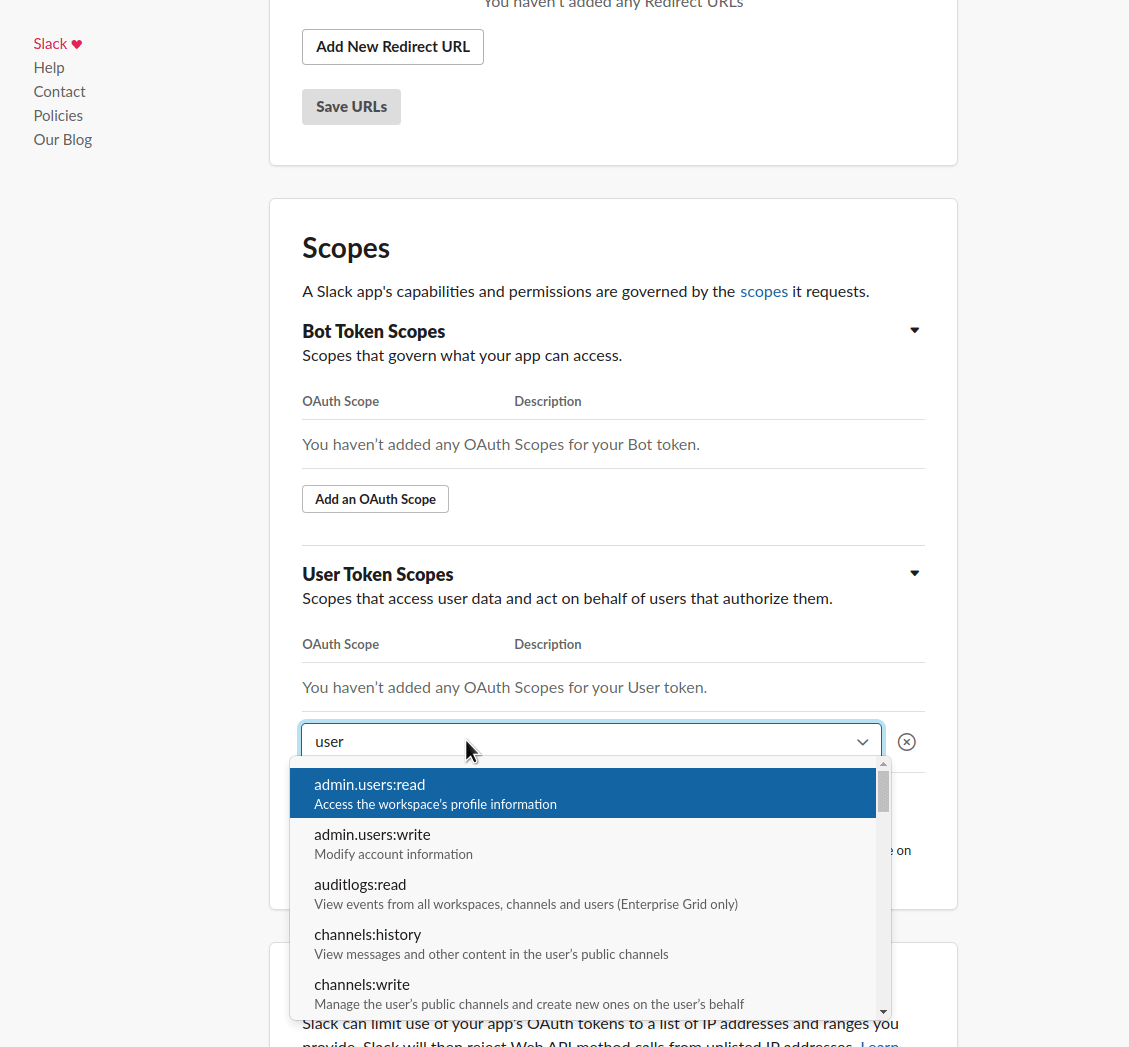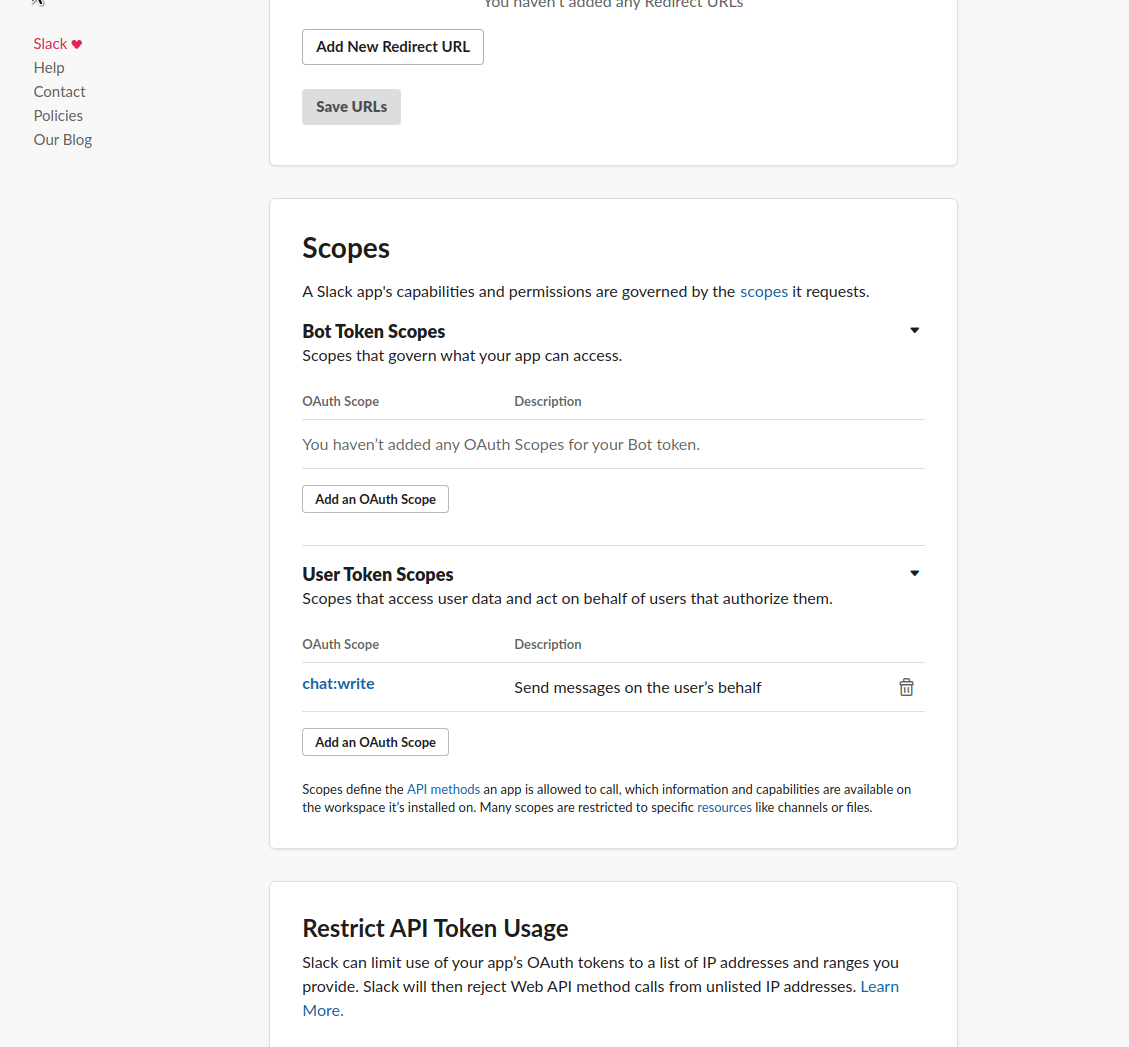
To generate a token, create a new Slack App and add it to your workspace.
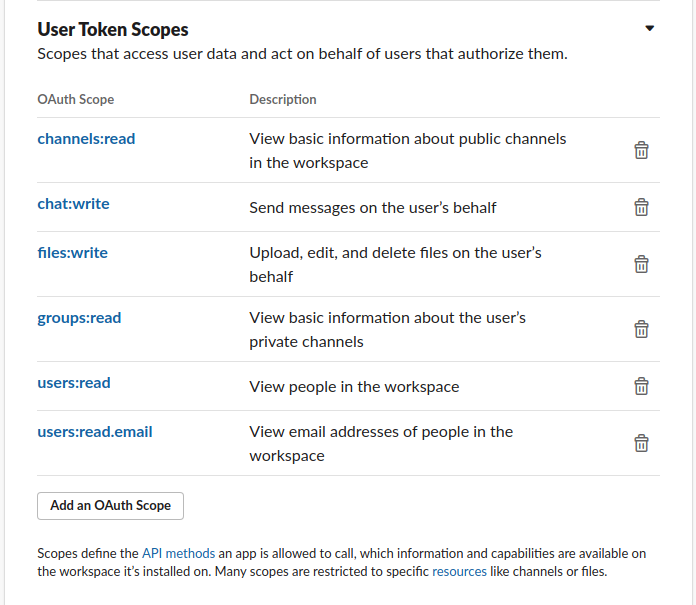
Grant API Permissions to your App, select all that apply (you probably want "chat:write"):
This is an example of how it could look like:
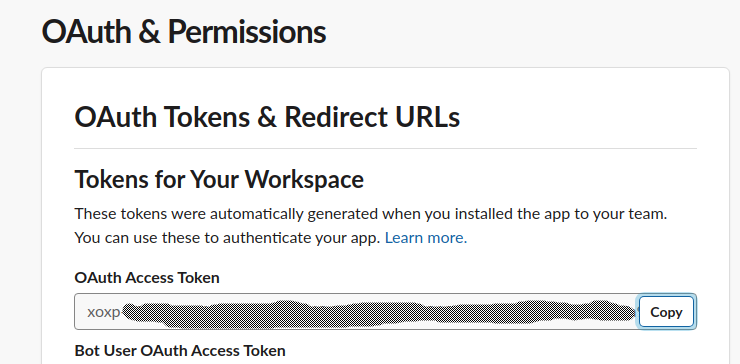
Now hit the green Install App to workspace button, and you will be presented with a token you can use for authentication.
I am very much open to comments! Please don't be afraid to raise issues or open pull requests.
This work is licensed under the terms of the MIT License
Note that this project was initially a fork of slacker-cli but the two projects have now considerably diverged.
Install the development requirements:
pip install -e .[development]
Run all tests:
make test
Format your code with black:
make format
python -c "from slackcli.emoji import Emojis; Emojis.download()"