Easy Bbox is a Python package designed to simplify bounding box operations. It provides a comprehensive set of tools for manipulating bounding boxes in various coordinate formats, including Pascal VOC, COCO, YOLO and Albumentations. The package supports transformations, geometric operations, and conversions, making it a versatile tool for computer vision tasks.
- Pydantic model: Bbox objects are Pydantic models.
- Multiple Coordinate Formats: Supports Pascal VOC, COCO, YOLO and Albumentation formats.
- Transformations: Shift, scale, expand, and pad bounding boxes.
- Geometric Operations: Calculate intersections, unions, and IoU (Intersection over Union).
- Conversions: Convert between different coordinate formats.
- Utility Functions: Includes Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) for filtering overlapping bounding boxes.
Easy Bbox is published as a python package and can be pip installed.
pip install easy-bboxYou can create a bounding box using the Bbox class. The bounding box is stored in Pascal VOC format, which is top-left, bottom-right with a top-left origin (PIL coordinate system), but can be instantiated from different formats.
from easy_bbox import Bbox
# All of the following Bbox are equal
# Create a bounding box using top-left and bottom-right coordinates
bbox = Bbox(left=10, top=20, right=30, bottom=40)
# Instantiate from a sequence in Pascal VOC format
bbox = Bbox.from_pascal_voc([10, 20, 30, 40])
bbox = Bbox.from_tlbr([10, 20, 30, 40])
bbox = Bbox.from_xyxy([10, 20, 30, 40])
bbox = Bbox.from_list([10, 20, 30, 40])
# Create a bounding box using top-left and width-height coordinates (COCO format)
bbox = Bbox.from_tlwh((10, 20, 20, 20))
bbox = Bbox.from_coco((10, 20, 20, 20))
# Create a bounding box using center and width-height coordinates
bbox = Bbox.from_cwh((20, 30, 20, 20))Easy Bbox provides several methods for transforming bounding boxes:
Easy Bbox provides methods for converting between different coordinate formats:
# Convert to Top-Left, Bottom-Right format
tlbr = bbox.to_tlbr() # Same as `.to_pascal_voc()`, `.to_xyxy()`
# Convert to Top-Left, Width-Height format
tlwh = bbox.to_tlwh() # Same as `.to_coco()`
# Convert to Center, Width-Height format
cwh = bbox.to_cwh()
# Convert to normalized Top-Left, Bottom-Right format
norm_tlbr = bbox.to_norm_tlbr(img_w=100, img_h=100) # Same as `.to_albu(...)`
# Convert to normalized Top-Left, Width-Height format
norm_tlwh = bbox.to_norm_tlwh(img_w=100, img_h=100)
# Convert to normalized Center, Width-Height format
norm_cwh = bbox.to_norm_cwh(img_w=100, img_h=100) # Same as `.to_yolo(...)`
# Convert to polygon format
polygon = bbox.to_polygon()Easy Bbox includes utility functions for common tasks:
from easy_bbox import nms
# Get the minimal englobing bbox
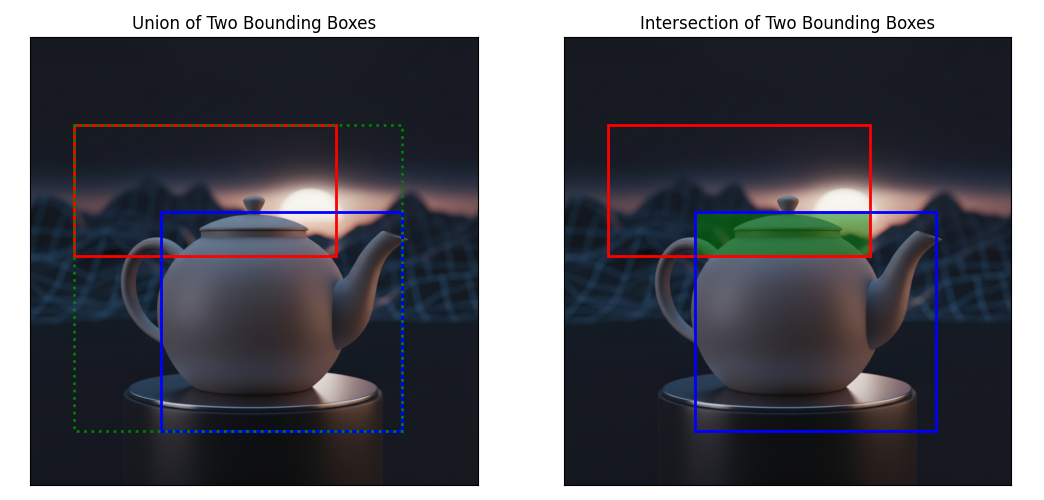
union = bbox1.union(bbox2) # same as bbox1 | bbox2
# Get the intersection
inter = bbox1.intersection(bbox2) # same as bbox1 & bbox2
# Calculate the IoU of two bboxes
iou = bbox1.iou(bbox2)
# Check if two bboxes are overlapping
overlap = bbox1.overlaps(bbox2)
# Check if a bbox contains a point
is_inside = bbox1.contains_point((5, 10))
# Calculate the distance from a point to a bbox
dist = bbox1.distance_to_point((5, 10))
# Perform Non-Maximum Suppression
selected_bboxes = nms(bboxes, scores, iou_threshold=0.5)