Data structures are fundamental concepts in computer science used to store, organize, and manipulate data efficiently. Java provides built-in classes and interfaces to implement these structures, which are essential for solving real-world problems effectively.
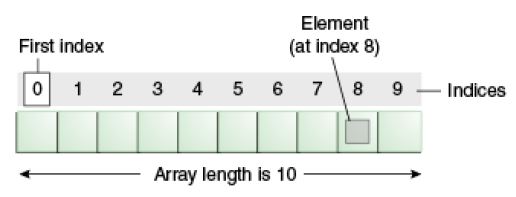
Arrays are fixed-size collections of elements of the same type stored sequentially in memory.
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.out.println(numbers[0]); // Output: 1- Fast Access to Elements
- Efficient Memory Usage
- Easy Iteration
A Linked List is a dynamic data structure where each element (node) contains data and a reference to the next node.
import java.util.LinkedList;
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("Java");
list.add("Python");
System.out.println(list); // Output: [Java, Python]- Dynamic size
- Efficient insertion/deletion
- Slower random access compared to arrays
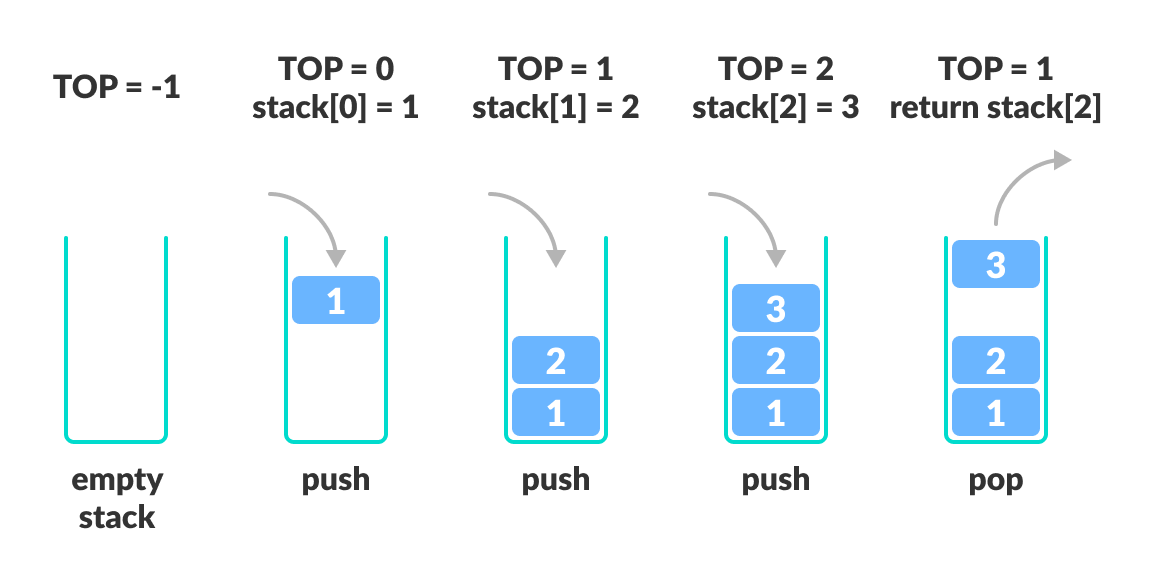
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the Last In, First Out (LIFO) principle. The most recently added element is the first to be removed. Common operations include push (add), pop (remove), and peek (view top element).
import java.util.Stack;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(10);
stack.push(20);
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // Output: 20- Simplicity in Function Calls
- Undo Mechanism
- Expression Evaluation
A queue is a linear data structure that follows the First In First Out (FIFO) principle. This means the element inserted first is the one removed first.
- Enqueue: Add an element to the rear of the queue.
- Dequeue: Remove an element from the front of the queue.
- Peek/Front: View the element at the front without removing it.
- IsEmpty: Check if the queue is empty.
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add("Task1");
queue.add("Task2");
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // Output: Task1- Orderly Processing
- Efficient Data Handling
- Fairness in Resource Allocation
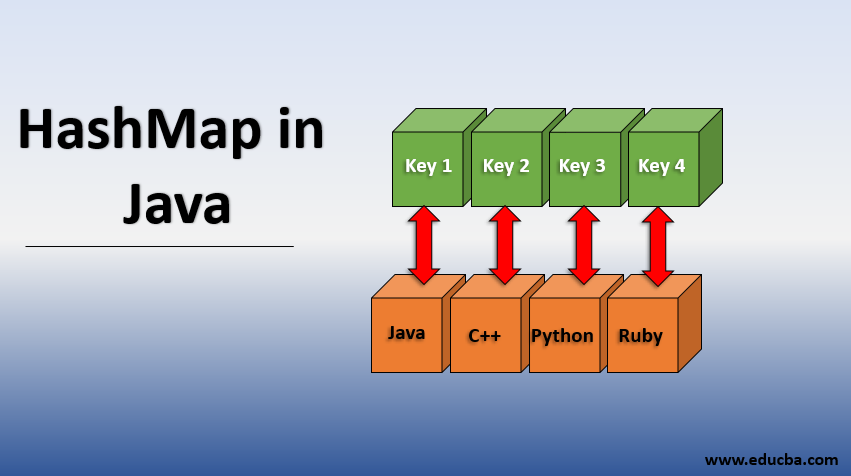
A Hash Map is a data structure that stores key-value pairs, allowing fast access to values based on their unique keys.
It uses a hash function to compute an index into an array of buckets, from which the desired value can be found.
import java.util.HashMap;
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("Apple", 10);
map.put("Banana", 5);
System.out.println(map.get("Apple")); // Output: 10- Fast lookup, insertion, and deletion (average-case O(1) time)
- Keys must be unique
- Commonly used in dictionaries, caches, and indexing
A tree is a hierarchical data structure made up of nodes, where each node has a value and links to child nodes.
It starts with a root node and branches out, forming a structure similar to a real tree.
- Each node has one parent (except the root) and zero or more children.
- Common types include binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL trees.
- Used in file systems, databases, and search algorithms.
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item) {
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
BinaryTree() { root = null; }
}- Efficient Searching and Sorting
- Hierarchical Representation
- Optimized Routing and Decision Making
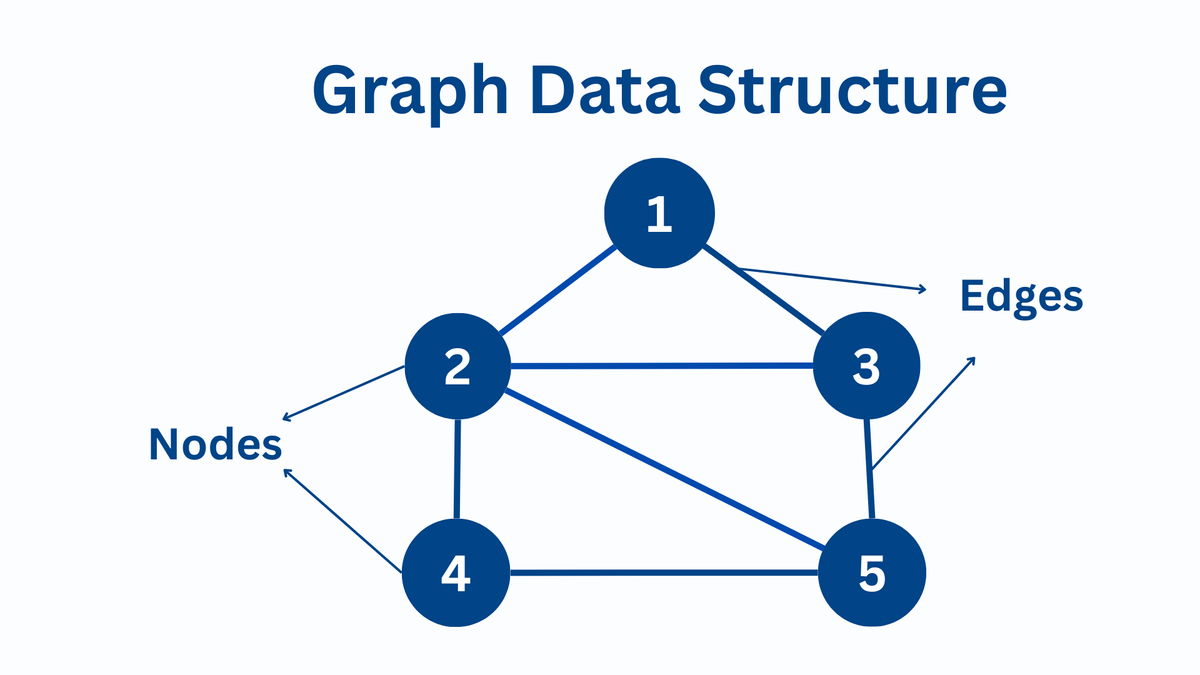
A graph is a data structure that consists of a set of nodes (also called vertices) and a set of edges that connect pairs of nodes. Graphs are used to represent relationships or connections between objects.
import java.util.*;
class Graph {
private int V;
private LinkedList<Integer> adj[];
Graph(int v) {
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for(int i=0; i<v; ++i)
adj[i] = new LinkedList();
}
void addEdge(int v, int w) {
adj[v].add(w);
}
}- Models Complex Relationships
- Flexible Structure
- Handles Cycles and Loops
Understanding fundamental data structures is essential for efficient problem-solving in computer science.
- Arrays provide fast access and are ideal for fixed-size collections.
- Linked Lists offer dynamic memory usage and flexible insertion/deletion.
- Stacks follow LIFO order and are useful in parsing and backtracking.
- Queues follow FIFO order and are great for scheduling and buffering.
- Hashmaps allow fast key-value access and are widely used in caching and indexing.
- Trees organize data hierarchically and support efficient searching.
- Graphs model complex relationships and support powerful algorithms.
Mastering these structures builds a strong foundation for algorithms, system design, and real-world applications.
- GeeksforGeeks: Data Structures
- Programiz: Data Structures Tutorials
- TutorialsPoint: Data Structures and Algorithms
- JavaTpoint: Data Structures
- Strivers a2Z: Data Structures and Algorithms