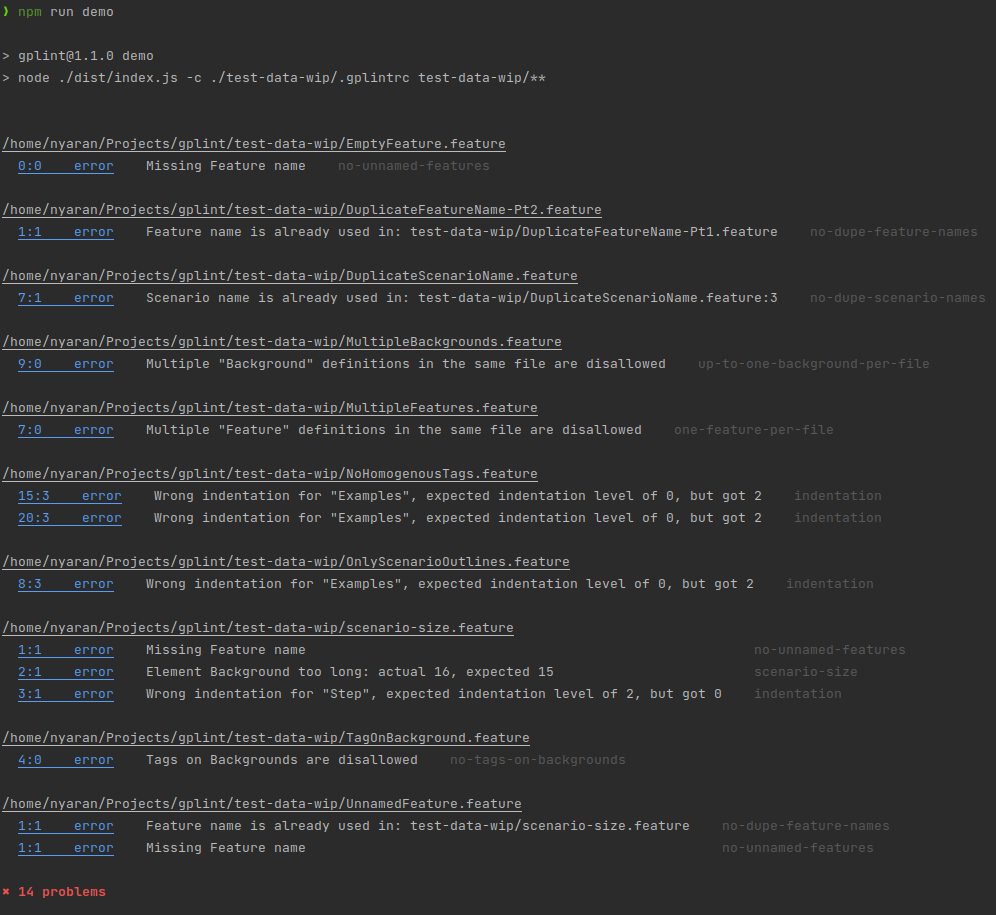
Uses Gherkin to parse feature files and runs linting against the default rules, and the optional rules you specified in your .gplintrc file.
Forked from gherkin-lint
npm install gplintTo see the output for all the errors that the linter can detect run:
git clone https://github.com/Nyaran/gplint.git
npm run demoRules with ⚙️ means that allows auto-fix with
--fixargument.
| Name | Functionality |
|---|---|
no-tags-on-backgrounds * |
Disallows tags on Background |
one-feature-per-file * |
Disallows multiple Feature definitions in the same file |
up-to-one-background-per-file * |
Disallows multiple Background definition in the same file |
no-multiline-steps * |
Disallows multiline Steps |
allowed-tags |
Just the listed tags are allowed |
allow-all-caps |
Allows the user to specify if some nodes allows texts completely in uppercase. |
allow-all-lowercase |
Allows the user to specify if some nodes allows texts completely in lowercase. |
file-name |
Restrict feature file names to a common style |
⚙️ indentation |
Allows the user to specify indentation rules |
keywords-in-logical-order |
Requires that Given, When and Then appear in logical sequence |
max-scenarios-per-file |
Allows the user to specify the max number of scenarios per feature file |
max-tags-lines |
Allows the user to specify the max number of lines for tags in each level. |
name-length |
Allows restricting length of Feature/Scenario/Step names |
new-line-at-eof |
Disallows/enforces new line at EOF |
no-background-only-scenario |
Disallows background when there is just one scenario |
no-dupe-feature-names |
Disallows duplicate Feature names |
no-dupe-scenario-names |
Disallows duplicate Scenario names |
no-duplicate-tags |
Disallows duplicate tags on the same Feature or Scenario |
no-empty-background |
Disallows features with backgrounds without steps |
no-empty-file |
Disallows empty feature files |
no-examples-in-scenarios |
Disallow the use of "Examples" in Scenarios, only allowed in Scenario Outlines |
no-files-without-scenarios |
Disallows files with no scenarios |
no-homogenous-tags |
Disallows tags present on every Scenario/Rule in a Feature or Rule, rather than on the Feature/Rule itself. Skips if contains a single scenario |
no-multiple-empty-lines |
Disallows multiple empty lines |
no-partially-commented-tag-lines |
Disallows partially commented tag lines |
no-restricted-patterns |
A list of patterns to disallow globally, or specifically in features, rules, backgrounds, scenarios, or scenario outlines, Steps |
no-restricted-tags |
Disallow use of particular @tags |
no-scenario-outlines-without-examples |
Disallows scenario outlines without examples |
no-superfluous-tags |
Disallows tags present on a Node, its parents (E.g. Same tags in a Scenario and/or Example, and also on the Feature or Rule that contains it |
⚙️ no-trailing-spaces |
Disallows trailing spaces |
no-unnamed-features |
Disallows empty Feature name |
no-unnamed-scenarios |
Disallows empty Scenario name |
no-unused-variables |
Disallows unused variables in scenario outlines |
one-space-between-tags |
Tags on the same line must be separated by a single space |
required-tags |
Require tags/patterns of tags |
related-tags |
Tags that requires other tags. |
scenario-size |
Allows restricting the maximum number of steps in a scenario, scenario outline and background |
table-align |
Allows to force table alignment on steps and/or examples. |
use-and |
Disallows repeated step names requiring use of And instead |
* These rules cannot be turned off because they detect undocumented cucumber functionality that causes the gherkin parser to crash.
The not-configurable rules are turned on by default and cannot be turned off. Configurable rules can be customized using a file.
The configurable rules are off by default. To turn them on, you will need to create a json file, where you specify the name of each rule and its desired level (which can be "error" or "warn" or "off"). Eg:
{
"no-unnamed-features": "error"
}will turn on the no-unnamed-features rule.
allowed-tags should be configured with the list of allowed tags and patterns:
{
"allowed-tags": ["error", {"tags": ["@watch", "@wip"], "patterns": ["^@todo$"]}]
}Any tag not included in this list won't be allowed.
allow-all-caps / allow-all-lowercase should be configured with the list of allowed tags and patterns:
{
"allow-all-caps": ["error", {
"Global": false,
"Description": true,
"ExampleHeader": true,
"ExampleBody": true
}] ,
"allow-all-lowercase": ["error", {
"Global": false,
"Description": true,
"ExampleHeader": true,
"ExampleBody": true
}]
}- Global: If a node is not specified, "Global" is applied. Default value is
false. - Description: Apply to all descriptions for any node.
- Feature: Apply to Feature title.
- Rule: Apply to Rule title.
- Background: Apply to Background title.
- Scenario: Apply to Scenario title.
- Step: Apply to Step value.
- Example: Apply to Example title.
- ExampleHeader: Apply to each header of Example tables.
- ExampleBody: Apply to each value of Example tables.
file-name is configured with a style to enforce. The default is PascalCase:
{
"file-name": ["error", {"style": "PascalCase"}]
}The list of supported styles is:
PascalCase- first letter of each word capitalized (no spaces) e.g. "MyFancyFeature.feature"Title Case- first letter of each word capitalized (with spaces) e.g. "My Fancy Feature.feature"camelCase- first letter of each word capitalized, except first e.g. "myFancyFeature.feature"kebab-case- all lowercase, hyphen-delimited e.g. "my-fancy-feature.feature"snake_case- all lowercase, underscore-delimited e.g. "my_fancy_feature.feature"
If you are using acronyms with the style camelCase and you want to preserve them capitalized, you can set the
allowAcronyms property to true:
{
"file-name": ["error", {"style": "camelCase", "allowAcronyms": true}]
}camelCase- first letter of each word capitalized, except first e.g. "myFancyFeatureACRON.feature"
Disallows partially commented tag lines. You can configure if a comment is allowed if is separated with a space or not allowed at all:
{
"no-partially-commented-tag-lines": ["error", {"allowSeparated": true}]
}The following table illustrates how it works:
| Example | Description | Result |
|---|---|---|
@foo |
Without a comment | Valid |
@foo #comment |
With a comment separated with space | Valid |
@foo#comment |
With a comment non-separated | Invalid |
{
"no-partially-commented-tag-lines": ["error", {"allowSeparated": false}]
}The following table illustrates how it works:
| Example | Description | Result |
|---|---|---|
@foo |
Without a comment | Valid |
@foo #comment |
With a comment separated with space | Invalid |
@foo#comment |
With a comment non-separated | Invalid |
no-restricted-patterns is a list of exact or partial patterns whose matches are disallowed in feature name and description, and in background, scenario and scenario outline name, description and steps.
All patterns are treated as case-insensitive.
The rule can be configured like this:
{
"no-restricted-patterns": ["error", {
"Global": [
"^globally restricted pattern"
],
"Feature": [
"poor description",
"validate",
"verify"
],
"Background": [
"show last response",
"a debugging step"
],
"Scenario": [
"show last response",
"a debugging step"
],
"Examples": [
"poor examples name",
"really bad examples description"
],
"ExampleHeader": [
"^.*disallowed.*$"
],
"ExampleBody": [
"^.*invalid.*$"
],
"Step": [
"bad step"
],
"Given": [
"bad step given",
"a debugging step given"
],
"When": [
"bad step when",
"a debugging step when"
],
"Then": [
"bad step then",
"a debugging step then"
],
"DocString": [
"^.*disallowed.*$"
],
"DataTable": [
"^.*invalid.*$",
"wrong value"
]
}]
}Notes:
- Description violations always get reported in the Feature/Scenario/etc. definition line. This is due to the parsed gherkin tree not having information about which line the description appears.
indentation can be configured in a more granular level and uses following rules by default:
- Expected indentation for Feature, Background, Scenario, Examples heading: 0 spaces
- Expected indentation for Steps and each example: 2 spaces
You can override the defaults for indentation like this:
{
"indentation" : [
"error", {
"Feature": 0,
"Background": 0,
"Scenario": 0,
"Step": 2,
"Examples": 0,
"example": 2,
"given": 2,
"when": 2,
"then": 2,
"and": 2,
"but": 2,
"feature tag": 0,
"scenario tag": 0,
"examples tag": 0
}
]
}There is no need to override all the defaults, as is done above, instead they can be overridden only where required. Step will be used as a fallback if the keyword of the step, e.g. 'given', is not specified. If feature tag is not set then Feature is used as a fallback, and if scenario tag is not set then Scenario is used as a fallback.
This feature is able to handle all localizations of the gherkin steps.
The max-scenarios-per-file supports some configuration options:
maxScenarios(number) the maximum scenarios per file after which the rule fails - defaults to10countOutlineExamples(boolean) whether to count every example row for a Scenario Outline, as opposed to just 1 for the whole block - defaults totrue
The configuration looks like this (showing the defaults):
{
"max-scenarios-per-file": ["error", {"maxScenarios": 10, "countOutlineExamples": true}]
}max-tags-lines lets the user specify the maximum allowed lines for tags per level type. Each level type can be configured separately.
Example configuration wth default values:
{
"max-tags-lines": [
"error",
{
"feature": 1,
"scenario": 5,
"example": 5
}
]
}name-length can be configured separately for Feature, Scenario and Step names.
The default is 70 characters for each of these:
{
"name-length" : ["error", { "Feature": 70, "Scenario": 70, "Step": 70 }]
}new-line-at-eof can be configured to enforce or disallow new lines at EOF.
- To enforce new lines at EOF:
{
"new-line-at-eof": ["error", "yes"]
}- To disallow new lines at EOF:
{
"new-line-at-eof": ["error", "no"]
}no-dupe-scenario-names can be configured to search for duplicates in each individual feature or amongst all feature
files. The default case is testing against all the features (same scenario name in different features will raise an
error). To get that behavior use the following configuration:
{
"no-dupe-scenario-names": "error"
}You can specify the scope, by using different configuration options:
Same as the default behaviour, find duplicates along all files.
{
"no-dupe-scenario-names": ["error", "anywhere"]
}To enable searching for duplicates in each individual feature (same scenario name in different features won't raise an error) you need to configure the rule like this:
{
"no-dupe-scenario-names": ["error", "in-feature"]
}To enable searching for duplicates in each individual rule (same scenario name in different rules won't raise an error) you need to configure the rule like this:
{
"no-dupe-scenario-names": ["error", "in-rule"]
}Additionally, you can also look for duplicated on Outline Scenarios with variables on the title, just adding -compile
suffix to the rule configuration (If you use this option, you need to have a variable on the title of all your Outlines):
Same as the default behaviour, find duplicates along all files, including compiling Outlines:
{
"no-dupe-scenario-names": ["error", "anywhere-compile"]
}Same as in-feature, but including compiling Outlines:
{
"no-dupe-scenario-names": ["error", "in-feature-compile"]
}Same as in-rule, but including compiling Outlines:
{
"no-dupe-scenario-names": ["error", "in-rule-compile"]
}no-restricted-tags should be configured with the list of restricted tags and patterns:
{
"no-restricted-tags": ["error", {"tags": ["@watch", "@wip"], "patterns": ["^@todo$"]}]
}keywords-in-logical-order Allows the user to maintain the wording order by using the scenario keywords, following the Given, When, Then sequence.
detectMissingKeywords(boolean): whether to ignore the lack of some keyword that violates the structure - defaults tofalse. Example configuration with default values:
{
"keywords-in-logical-order": [
"error",
{
"detectMissingKeywords": false
}
]
}required-tags supports some configuration options:
ignoreUntagged(boolean): whether to ignore scenarios that have no tag - defaults totrue.global(array): the array of tag patterns that must match - defaults to[]feature(array): the array of tag patterns that must match - defaults to[]rule(array): the array of tag patterns that must match - defaults to[]scenario(array): the array of tag patterns that must match - defaults to[]example(array): the array of tag patterns that must match - defaults to[]extendRule(boolean): When Scenario is not contained inside Rule, extends requiredruletags toscenario- defaults tofalseextendExample(boolean): When Scenario is not a Scenario Outline, extends requiredexampletags toscenario- defaults tofalse
* All levels allows to define a sub-array to mark only one of the members of array as required.
{
"required-tags": [
"error",
{
"global": ["/^@ID\\.APP-[0-9]+$/"],
"feature": ["/@feature\\..+/"],
"rule": ["/^@user-case\\..+$/"],
"scenario": [["@ready", "@manual", "@wip"]],
"example": ["/^@type\\..+$/"],
"extendRule": true,
"extendExample": true,
"ignoreUntagged": false
}
]
}related-tags allow to define a list of tags with a list of related tags that should be present too. The related tags can be an string or a regular expression (represented as a string between slashes /)
{
"related-tags": ["error", {
"tags": {
"@disable": ["/^@TICKET.PROJ-[0-9]+$/"],
"@a-tag": ["@otherTag", "@otherTagBis"]
}
}]
}scenario-size lets you specify a maximum step length for scenarios and backgrounds. The Scenario configuration applies to both scenarios and scenario outlines:
{
"scenario-size": ["error", { "steps-length": { "Background": 15, "Scenario": 15 }}]
}table-align lets you specify if tables must be aligned or not. This can be activated for steps and for examples (by default both are activated):
{
"table-align": ["error", { "steps": true, "examples": true }]
}The default name for the configuration file is .gplintrc and it's expected to be in your working directory.
The file contents must be valid JSON, though it does allow comments.
If you are using a file with a different name or a file in a different folder, you will need to specify the -c or --config option and pass in the relative path to your configuration file. Eg: gplint -c path/to/configuration/file.extension
You can find an example configuration file, that turns on all the rules in the root of this repo (.gplintrc).
Each should have a rule level configured, there are 3 available levels
- "off" or "0": Turn the rule off.
- "warn" or "1" or 1: Turn the rule on, without affection exit code.
- "error" or "2" or 2: Turn the rule on, setting exit code to 1 when triggered.
Note: "warn" can provoke an exit code 1 if --max-warnings is provided with 0 or greater value.
There are 2 ways you can specify files that the linter should ignore:
- Add a
.gplintignorefile in your working directory and specify one glob pattern per file line - Use the command line option
-ior--ignore, pass in a comma separated list of glob patterns. If specified, the command line option will override the.gplintignorefile.
You can specify one more custom rules directories by using the -r or --rulesdir command line option. Rules in the given directories will be available additionally to the default rules.
Example:
gplint --rulesdir "/path/to/my/rulesdir" --rulesdir "from/cwd/rulesdir"Paths can either be absolute or relative to the current working directory.
Have a look at the src/rules/ directory for examples; The no-empty-file rule is a good example to start with.