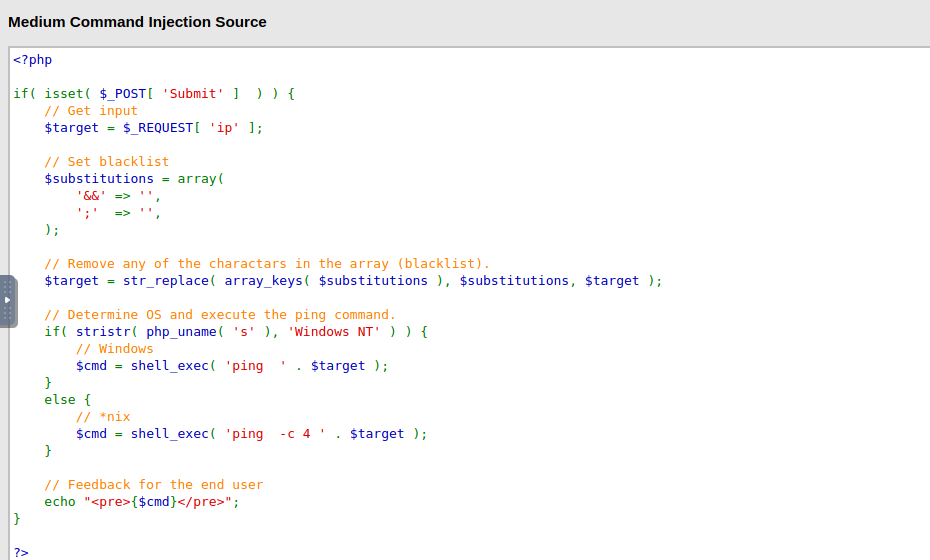
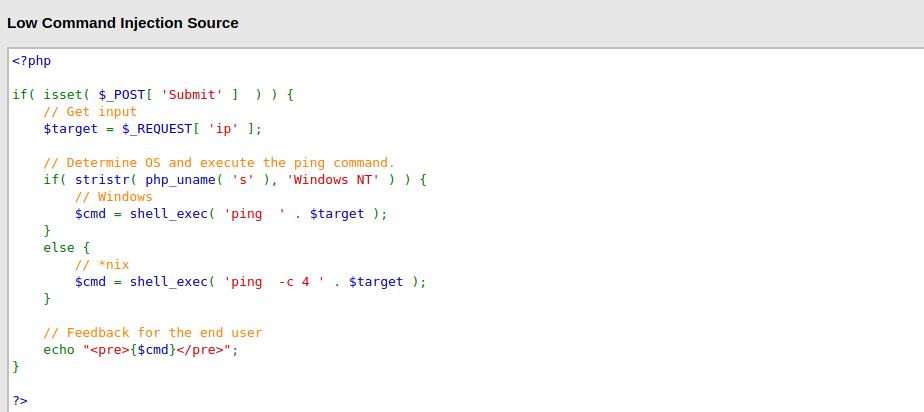
Command injection is an attack in which the goal is execution of arbitrary commands on the host operating system via a vulnerable application. Command injection attacks are possible when an application passes unsafe user supplied data (forms, cookies, HTTP headers etc.) to a system shell. In this attack, the attacker-supplied operating system commands are usually executed with the privileges of the vulnerable application. Command injection attacks are possible largely due to insufficient input validation.
This attack differs from Code Injection, in that code injection allows the attacker to add their own code that is then executed by the application. In Command Injection, the attacker extends the default functionality of the application, which execute system commands, without the necessity of injecting code.
i use this tool Commix-testbed is a collection of real-world scenarios, vulnerable to command injection flaws, used to evaluate the detection and exploitation abilities of commix:
- Regular injection scenarios.
- Cookie injection scenarios.
- User-Agent injection scenarios.
- Referer injection scenarios.
- Weak filters scenarios. (Hints)
While there are various versions of DVWA around, the only supported version is the latest source from the official GitHub repository. You can either clone it from the repo:
- git clone https://github.com/digininja/DVWA.git Or download a ZIP of the files
- you could use TryHackMe from this link https://tryhackme.com/room/dvwa and no need for installation
- for the Commix-testbed https://github.com/commixproject/commix-testbed everyting will be in this link and no need need for installation it's already download in kali linux
Installation Videos Installing DVWA on Kali running in VirtualBox Installing Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA) on Windows 10 [12:39 minutes] Windows + XAMPP The easiest way to install DVWA is to download and install XAMPP if you do not already have a web server setup.
XAMPP is a very easy to install Apache Distribution for Linux, Solaris, Windows and Mac OS X. The package includes the Apache web server, MySQL, PHP, Perl, a FTP server and phpMyAdmin.
XAMPP can be downloaded from: https://www.apachefriends.org/
A variety of shell metacharacters can be used to perform OS command injection attacks.
A number of characters function as command separators, allowing commands to be chained together. The following command separators work on both Windows and Unix-based systems:
& && | || The following command separators work only on Unix-based systems:
; Newline (0x0a or \n) On Unix-based systems, you can also use backticks or the dollar character to perform inline execution of an injected command within the original command:
injected command
$(
injected command )
Note that the different shell metacharacters have subtly different behaviors that might affect whether they work in certain situations, and whether they allow in-band retrieval of command output or are useful only for blind exploitation.
Sometimes, the input that you control appears within quotation marks in the original command. In this situation, you need to terminate the quoted context (using " or ') before using suitable shell metacharacters to inject a new command.
By far the most effective way to prevent OS command injection vulnerabilities is to never call out to OS commands from application-layer code. In virtually every case, there are alternate ways of implementing the required functionality using safer platform APIs.
If it is considered unavoidable to call out to OS commands with user-supplied input, then strong input validation must be performed. Some examples of effective validation include:
Validating against a whitelist of permitted values. Validating that the input is a number. Validating that the input contains only alphanumeric characters, no other syntax or whitespace.