A practical educational example showing how file encryption and decryption logic works in a ransomware-like application using C# and .NET 6 Windows Forms.
⚠️ Educational use only. This code is designed for security learning and malware analysis training. Run only inside an isolated virtual machine with disposable test files.
Full explanation:
How a Ransomware Works in C#
Below is a short demonstration of the encryption process running inside a safe virtual machine:
This project simulates how ransomware encrypts files using hybrid cryptography (AES + RSA).
It provides a simple Windows Forms interface that lists affected files and includes a button to decrypt them once the private key is provided.
There is no real payload, networking, or persistence.
The focus is understanding how file encryption and key handling work at a low level.
Program.Main()initializes application configuration and starts the main form (Form1).- When the form loads (
Form1_Load), encryption starts automatically, then the UI updates to show affected files.
- The public RSA key is loaded from embedded project resources (
Properties.Resources.publickey). - AES (256-bit) is used for symmetric encryption of each file in the local
./testfolder. - Each file gets:
- A random AES key and IV.
- Both encrypted with the RSA public key (2048-bit) and written as the first 512 bytes of the output.
- File contents streamed through a
CryptoStreamusing AES. - The original file deleted after successful encryption.
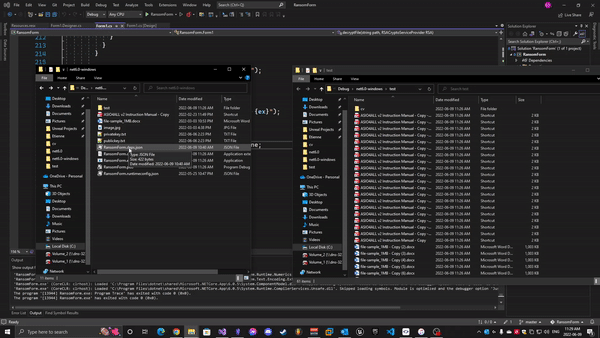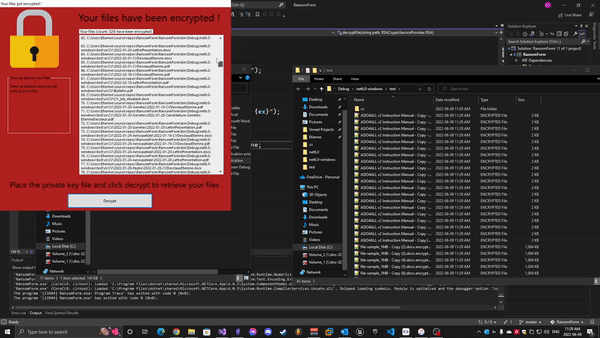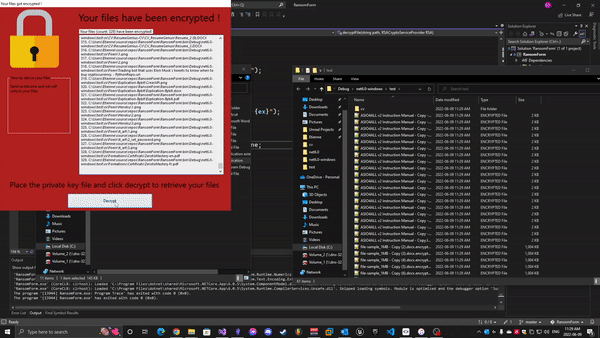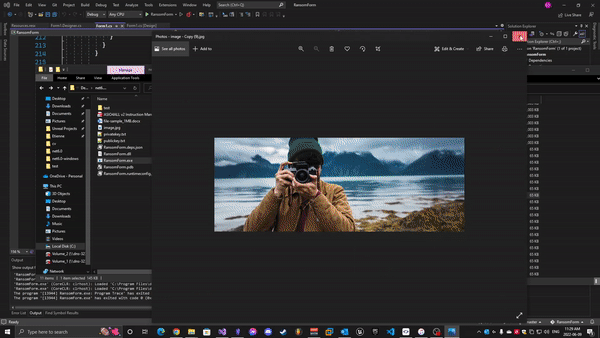
- The process recurses through subfolders, skipping files already ending in
.encrypted.
- When the user clicks Decrypt, the app:
- Loads
privatekey.pemfrom the working directory. - Imports it using
RSA.ImportPkcs8PrivateKey(...). - Decrypts AES key and IV from each
.encryptedfile. - Reconstructs the original file and deletes the encrypted one.
- Loads
- Displays a padlock image, a counter of encrypted files, and a fake ransom note text.
- A Decrypt button triggers the recovery process.
- Implemented via standard Windows Forms controls (
Label,TextBox,Button,PictureBox).
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Language | C# (.NET 6, Windows Forms) |
| Crypto | AES-256 for file data, RSA-2048 for key encapsulation |
| Resources | Embedded public key (publickey.pem), padlock icon |
| UI Framework | System.Windows.Forms |
| I/O | FileStream + CryptoStream for efficient block encryption |
| Target | Windows (x64) |
- Create a
testfolder next to the executable. - Copy dummy text files only.
- Run the program in a virtual machine (e.g., VirtualBox, VMware, Hyper-V).
- Observe new files with the
.encryptedextension. - To decrypt, place
privatekey.pembeside the executable and click Decrypt.
- Understand AES/RSA hybrid encryption in real-world malware.
- Learn proper key management and stream-based encryption.
- Explore resource embedding and UI feedback loops.
- Reinforce the ethics of cybersecurity research.
MIT License © 2025 Etienne Desclaux
For educational and defensive security research only.