-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 17.7k
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
runtime: mark assist blocks GC microbenchmark for 7ms #27732
Comments
|
#16528 (now closed) I think might have been cited in discussion of a previous incarnation of this GC benchmark. Also probably related is this prior blog post: And also cited in that blog is this mailing list conversation from 2016: |
|
Expanding my comment slightly: The benchmark code appearing within the text of that 2016 blog: seems to match the benchmark code that @dr2chase says he used as his starting point above: Both are from the same original author. That 2016 blog reported ~7 ms pause time for Go 1.7.3, and at the time #16528 was theorized as the root cause as why the results weren't better (e.g., see the "Why Are the Go Results Not Better?" section there). In any event, mainly just wanted to mention the older investigation in case that is useful (and apologies if not useful). |
|
A bit more info: it turns out that in the original, the 4800000 byte circular buffer was allocated on the stack, and large stack frames are not handled incrementally in the same way that large objects are. Modifying the benchmark to allocate the circular buffer and store the pointer in a global, the latency falls to 2ms, which is better, though still far worse than expected. In the snapshot from the trace, you can see that the GC work is now shared among several threads, but the worker thread is 100% running mark assist during that interval. A different modification, to move the declaration of var c circularBuffer to a global, also shortens the worst case latency in the same way, also with the same 100% mark assist for about 2ms. Still to investigate:
Once mark assist is dealt with, this microbenchmark is likely to have problems with long sweeps, a different, known bug ( #18155 ) that I've also seen in some of these traces. That looks like: |
|
New summary of apparent subissues:
Remaining mystery: For reliable measurement of steady-state latencies, benchmark ought to do a warmup run first, because rapid heap growth around startup is more likely to provoke mysterious OS interference with progress. |
|
Change https://golang.org/cl/136555 mentions this issue: |
|
Lack of credit for mark assist of roots is a contributor to long pauses. |
|
Change https://golang.org/cl/146817 mentions this issue: |
|
Turns out it is in fact policy to allocate up to 10M-sized things on the stack, if they are plain vars and not explicit allocations. See |
…C or traceReader This repairs one of the several causes of pauses uncovered by a GC microbenchmark. A pause can occur when a goroutine's quantum expires "at the same time" a GC is needed. The current M switches to running a GC worker, which means that the amount of available work has expanded by one. The GC worker, however, does not call ready, and does not itself conditionally wake a P (a "normal" thread would do this). This is also true if M switches to a traceReader. This is problem 4 in this list: #27732 (comment) Updates #27732. Change-Id: I6905365cac8504cde6faab2420f4421536551f0b Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/146817 Run-TryBot: David Chase <drchase@google.com> TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org> Reviewed-by: Austin Clements <austin@google.com>
* cmd/compile: add unsigned divisibility rules
"Division by invariant integers using multiplication" paper
by Granlund and Montgomery contains a method for directly computing
divisibility (x%c == 0 for c constant) by means of the modular inverse.
The method is further elaborated in "Hacker's Delight" by Warren Section 10-17
This general rule can compute divisibilty by one multiplication and a compare
for odd divisors and an additional rotate for even divisors.
To apply the divisibility rule, we must take into account
the rules to rewrite x%c = x-((x/c)*c) and (x/c) for c constant on the first
optimization pass "opt". This complicates the matching as we want to match
only in the cases where the result of (x/c) is not also available.
So, we must match on the expanded form of (x/c) in the expression x == c*(x/c)
in the "late opt" pass after common subexpresion elimination.
Note, that if there is an intermediate opt pass introduced in the future we
could simplify these rules by delaying the magic division rewrite to "late opt"
and matching directly on (x/c) in the intermediate opt pass.
Additional rules to lower the generic RotateLeft* ops were also applied.
On amd64, the divisibility check is 25-50% faster.
name old time/op new time/op delta
DivconstI64-4 2.08ns ± 0% 2.08ns ± 1% ~ (p=0.881 n=5+5)
DivisibleconstI64-4 2.67ns ± 0% 2.67ns ± 1% ~ (p=1.000 n=5+5)
DivisibleWDivconstI64-4 2.67ns ± 0% 2.67ns ± 0% ~ (p=0.683 n=5+5)
DivconstU64-4 2.08ns ± 1% 2.08ns ± 1% ~ (p=1.000 n=5+5)
DivisibleconstU64-4 2.77ns ± 1% 1.55ns ± 2% -43.90% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
DivisibleWDivconstU64-4 2.99ns ± 1% 2.99ns ± 1% ~ (p=1.000 n=5+5)
DivconstI32-4 1.53ns ± 2% 1.53ns ± 0% ~ (p=1.000 n=5+5)
DivisibleconstI32-4 2.23ns ± 0% 2.25ns ± 3% ~ (p=0.167 n=5+5)
DivisibleWDivconstI32-4 2.27ns ± 1% 2.27ns ± 1% ~ (p=0.429 n=5+5)
DivconstU32-4 1.78ns ± 0% 1.78ns ± 1% ~ (p=1.000 n=4+5)
DivisibleconstU32-4 2.52ns ± 2% 1.26ns ± 0% -49.96% (p=0.000 n=5+4)
DivisibleWDivconstU32-4 2.63ns ± 0% 2.85ns ±10% +8.29% (p=0.016 n=4+5)
DivconstI16-4 1.54ns ± 0% 1.54ns ± 0% ~ (p=0.333 n=4+5)
DivisibleconstI16-4 2.10ns ± 0% 2.10ns ± 1% ~ (p=0.571 n=4+5)
DivisibleWDivconstI16-4 2.22ns ± 0% 2.23ns ± 1% ~ (p=0.556 n=4+5)
DivconstU16-4 1.09ns ± 0% 1.01ns ± 1% -7.74% (p=0.000 n=4+5)
DivisibleconstU16-4 1.83ns ± 0% 1.26ns ± 0% -31.52% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
DivisibleWDivconstU16-4 1.88ns ± 0% 1.89ns ± 1% ~ (p=0.365 n=5+5)
DivconstI8-4 1.54ns ± 1% 1.54ns ± 1% ~ (p=1.000 n=5+5)
DivisibleconstI8-4 2.10ns ± 0% 2.11ns ± 0% ~ (p=0.238 n=5+4)
DivisibleWDivconstI8-4 2.22ns ± 0% 2.23ns ± 2% ~ (p=0.762 n=5+5)
DivconstU8-4 0.92ns ± 1% 0.94ns ± 1% +2.65% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
DivisibleconstU8-4 1.66ns ± 0% 1.26ns ± 1% -24.28% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
DivisibleWDivconstU8-4 1.79ns ± 0% 1.80ns ± 1% ~ (p=0.079 n=4+5)
A follow-up change will address the signed division case.
Updates #30282
Change-Id: I7e995f167179aa5c76bb10fbcbeb49c520943403
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/168037
Run-TryBot: Brian Kessler <brian.m.kessler@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
* cmd/link/internal/ld: consolidate macho platform setup
Determine the macho platform once and use that the two places that
need it. This makes it easier to add a third platform check for a
follow-up change.
Updates #31447
Change-Id: I522a5fface647ab8e608f816c5832d531534df7a
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174198
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
* cmd/link/internal/ld,syscall: drop $INODE64 suffixes on simulators
Some libc functions are suffixed with "$INODE64" on macOS.
Unfortunately, the iOS simulator doesn't have the suffixes, so we can't
use GOARCH to distinguish the two platform.
Add linker support for adding the suffix, using the macho platform
to determine whether it is needed.
While here, add the correct suffix for fdopendir on 386. It's
"$INODE64$UNIX2003", believe it or not. Without the suffix,
GOARCH=386 go test -short syscall
crashes on my Mojave machine.
Fixes #31447
Change-Id: I9bd3de40ece7df62f744bc24cd00909e56b00b78
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174199
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
* cmd/link/internal/ld,syscall: replace getfsstat64 with getfsstat
getfsstat64 is deprecated but not yet caught by the App Store checks.
Use the supported getfsstat$INODE64 form instead to ensure forward
compatibility.
Change-Id: I0d97e8a8b254debb3de1cfcb3778dbed3702c249
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174200
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
* cmd/go/internal/renameio: use ERROR_ACCESS_DENIED to check for errors
CL 172418 added code to check for "Access is denied" error.
But "Access is denied" error will be spelled differently on
non-English version of Windows.
Check if error is ERROR_ACCESS_DENIED instead.
Updates #31247
Change-Id: I7b1633013d563f7c06c1f12a9be75122106834f9
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174123
Reviewed-by: Emmanuel Odeke <emm.odeke@gmail.com>
* syscall: allow setting security attributes on processes
This allows creating processes that can only be debugged/accessed by
certain tokens, according to a particular security descriptor. We
already had everything ready for this but just neglected to pass through
the value from the user-accessible SysProcAttr.
Change-Id: I4a3fcc9f5078aa0058b26c103355c984093ae03f
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174197
Run-TryBot: Jason Donenfeld <Jason@zx2c4.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Alex Brainman <alex.brainman@gmail.com>
* runtime: remove spurious register loads for openbsd/amd64 kqueue
The kqueue system call takes no arguments, hence there should be no need
to zero the registers used for the first syscall arguments.
Change-Id: Ia79b2d4f4d568bb6795cb885e1464cf1fc2bf7c7
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174128
Run-TryBot: Benny Siegert <bsiegert@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Benny Siegert <bsiegert@gmail.com>
* cmd/compile: intrinsify math/bits.Add64 for ppc64x
This change creates an intrinsic for Add64 for ppc64x and adds a
testcase for it.
name old time/op new time/op delta
Add64-160 1.90ns ±40% 2.29ns ± 0% ~ (p=0.119 n=5+5)
Add64multiple-160 6.69ns ± 2% 2.45ns ± 4% -63.47% (p=0.016 n=4+5)
Change-Id: I9abe6fb023fdf62eea3c9b46a1820f60bb0a7f97
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/173758
Reviewed-by: Lynn Boger <laboger@linux.vnet.ibm.com>
Run-TryBot: Carlos Eduardo Seo <cseo@linux.vnet.ibm.com>
* runtime: whitelist debugCall32..debugCall65536 in debugCallCheck
Whitelists functions debugCall32 through debugCall65536 in
runtime.debugCallCheck so that any instruction inside those functions
is considered a safe point.
This is useful for implementing nested function calls.
For example when evaluating:
f(g(x))
The debugger should:
1. initiate the call to 'f' until the entry point of 'f',
2. complete the call to 'g(x)'
3. copy the return value of 'g(x)' in the arguments of 'f'
4. complete the call to 'f'
Similarly for:
f().amethod()
The debugger should initiate the call to '.amethod()', then initiate
and complete the call to f(), copy the return value to the arguments
of '.amethod()' and finish its call.
However in this example, unlike the other example, it may be
impossible to determine the entry point of '.amethod()' until after
'f()' is evaluated, which means that the call to 'f()' needs to be
initiated while stopped inside a debugCall... function.
Change-Id: I575c23542709cedb1a171d63576f7e11069c7674
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/161137
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Heschi Kreinick <heschi@google.com>
* strconv: Document ParseFloat's special cases
Updates #30990
Change-Id: I968fb13251ab3796328089046a3f0fc5c7eb9df9
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174204
Reviewed-by: Benny Siegert <bsiegert@gmail.com>
Run-TryBot: Benny Siegert <bsiegert@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/go: implement Go checksum database support
This CL adds support for consulting the Go checksum database
when downloading a module that is not already listed in go.sum.
The overall system is described at golang.org/design/25530-sumdb,
and this CL implements the functionality described specifically in
golang.org/design/25530-sumdb#command-client.
Although the eventual plan is to set GOPROXY and GOSUMDB to
default to a Google-run proxy serving the public Go ecosystem,
this CL leaves them off by default.
Fixes #30601.
Change-Id: Ie46140f93c6cc2d85573fbce0878a258819ff44d
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/173951
Run-TryBot: Russ Cox <rsc@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Emmanuel Odeke <emm.odeke@gmail.com>
Reviewed-by: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* encoding/json: add a Fuzz function
Adds a sample Fuzz test function to package encoding/json following the
guidelines defined in #31309, based on
https://github.com/dvyukov/go-fuzz-corpus/blob/master/json/json.go
Fixes #31309
Updates #19109
Change-Id: I5fe04d9a5f41c0de339f8518dae30896ec14e356
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174058
Reviewed-by: Dmitry Vyukov <dvyukov@google.com>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
Run-TryBot: Dmitry Vyukov <dvyukov@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* all: remove a few unused parameters
I recently modified tabwriter to reduce the number of defers due to
flush calls. However, I forgot to notice that the new function
flushNoDefers can no longer return an error, due to the lack of the
defer.
In crypto/tls, hashForServerKeyExchange never returned a non-nil error,
so simplify the code.
Finally, in go/types and net we can find a few trivially unused
parameters, so remove them.
Change-Id: I54c8de83fbc944df432453b55c93008d7e810e61
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174131
Run-TryBot: Daniel Martí <mvdan@mvdan.cc>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Benny Siegert <bsiegert@gmail.com>
* net/http: remove "number:" from Response.Status string
The behavior of Value.String method on non-string JavaScript types has
changed after CL 169757.
Update the implementation of Transport.RoundTrip method to construct the
Response.Status string without relying on result.Get("status").String(),
since that now returns strings like "<number: 200>" instead of "200".
Fixes #31736
Change-Id: I27b3e6cc95aa65fd1918b1400e88478a154aad12
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174218
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Richard Musiol <neelance@gmail.com>
* cmd/link/internal/s390x: fix s390x build
Fix breakage from CL 173437
Change-Id: If218ffaa1259fbdee641143ffbe4b38030c373b9
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174278
Reviewed-by: Michael Munday <mike.munday@ibm.com>
Reviewed-by: Cherry Zhang <cherryyz@google.com>
* net: correct docs of KeepAlive field in Dialer type
KeepAlive field used to report the wording "keep-alive period"
which may be misleading. This field does not represent the whole
TCP keepalive time, that is the inactivity period upon which one
endpoint starts probing the other end. But it acctually specifies
the keepalive interval, that is the time between two keepalive
probes.
Fixes #29089
Change-Id: If99b38ba108830d0e5fe527171a2f5c96a3bcde7
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/155960
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* misc/wasm: fix command line arguments containing multi-byte characters
Command line arguments containing multi-byte characters were causing
go_js_wasm_exec to crash (RangeError: Source is too large), because
their byte length was not handled correctly. This change fixes the bug.
Fixes #31645.
Change-Id: I7860ebf5b12da37d9d0f43d4b6a22d326a90edaf
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/173877
Run-TryBot: Richard Musiol <neelance@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Emmanuel Odeke <emm.odeke@gmail.com>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* runtime: initialise cpu.HWCap on openbsd/arm64
OpenBSD does not provide auxv, however we still need to initialise cpu.HWCap.
For now initialise it to the bare minimum, until some form of CPU capability
detection is implemented or becomes available - see issue #31746.
Updates #31656
Change-Id: I68c3c069319fe60dc873f46def2a67c9f3d937d5
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174129
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* runtime: support all as parameter in gdb goroutine commands.
For example, can use `goroutine all bt` to dump all goroutines'
information.
Change-Id: I51b547c2b837913e4bdabf0f45b28f09250a3e34
GitHub-Last-Rev: d04dcd4f581f97e35ee45969a864f1270d79e49b
GitHub-Pull-Request: golang/go#26283
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/122589
Run-TryBot: Emmanuel Odeke <emm.odeke@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Emmanuel Odeke <emm.odeke@gmail.com>
Reviewed-by: David Chase <drchase@google.com>
* os/exec: always set SYSTEMROOT on Windows if not listed in Cmd.Env
Fixes #25210
Change-Id: If27b61776154dae9b9b67bf4e4f5faa785d98105
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174318
Reviewed-by: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
* runtime/cgo: ignore missing Info.plist files on iOS
When running Go programs on Corellium virtual iPhones, the Info.plist
files might not exist. Ignore the error.
Updates #31722
Change-Id: Id2e315c09346b69dda9e10cf29fb5dba6743aac4
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174202
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* syscall: don't return EINVAL on zero Chmod mode on Windows
Fixes #20858
Change-Id: I45c397795426aaa276b20f5cbeb80270c95b920c
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174320
Reviewed-by: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
Run-TryBot: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* testing: delay flag registration; move to an Init function
Any code that imports the testing package forces the testing flags to be
defined, even in non-test binaries. People work around this today by
defining a copy of the testing.TB interface just to avoid importing
testing.
Fix this by moving flag registration into a new function, testing.Init.
Delay calling Init until the testing binary begins to run, in
testing.MainStart.
Init is exported for cases where users need the testing flags to be
defined outside of a "go test" context. In particular, this may be
needed where testing.Benchmark is called outside of a test.
Fixes #21051
Change-Id: Ib7e02459e693c26ae1ba71bbae7d455a91118ee3
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/173722
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* runtime: make mmap return 0 instead of -1 on aix/ppc64
Most of the platforms are returning 0 instead of -1 when mmap syscalls
is failing. This patch corrects it for AIX in order to fix
TestMmapErrorSign and to improve AIX compatibility.
Change-Id: I1dad88d0e69163ad55c504b2b4a997892fd876cd
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174297
Run-TryBot: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
* cmd/go: add XCOFF format handler for go version
Change-Id: Ib102ae95acfd89fc3c9942a4ec82c74362f62045
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174299
Run-TryBot: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
* runtime: account for callbacks in checkdead on Windows
When a callback runs on a different thread in Windows, as in the
runtime package test TestCallbackInAnotherThread, it will use the
extra M. That can cause the test in checkdead to fail incorrectly.
Check whether there actually is an extra M before expecting it.
I think this is a general problem unrelated to timers. I think the test
was passing previously because the timer goroutine was using an M.
But I haven't proved that. This change seems correct, and it avoids
the test failure when using the new timers on Windows.
Updates #27707
Change-Id: Ieb31c04ff0354d6fae7e173b59bcfadb8b0464cd
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174037
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
* cmd,runtime: enable cgo for openbsd/arm64
Updates #31656.
Change-Id: Ide6f829282fcdf20c67998b766a201a6a92c3035
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174132
Run-TryBot: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
* cmd/compile: evaluate map initializers incrementally
For the code:
m := map[int]int {
a(): b(),
c(): d(),
e(): f(),
}
We used to do:
t1 := a()
t2 := b()
t3 := c()
t4 := d()
t5 := e()
t6 := f()
m := map[int]int{}
m[t1] = t2
m[t3] = t4
m[t5] = t6
After this CL we do:
m := map[int]int{}
t1 := a()
t2 := b()
m[t1] = t2
t3 := c()
t4 := d()
m[t3] = t4
t5 := e()
t6 := f()
m[t5] = t6
Ordering the initialization this way limits the lifetime of the
temporaries involved. In particular, for large maps the number of
simultaneously live temporaries goes from ~2*len(m) to ~2. This change
makes the compiler (regalloc, mostly) a lot happier. The compiler runs
faster and uses a lot less memory.
For #26546, changes compile time of a big map from 8 sec to 0.5 sec.
Fixes #26552
Update #26546
Change-Id: Ib7d202dead3feaf493a464779fd9611c63fcc25f
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174417
Run-TryBot: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Matthew Dempsky <mdempsky@google.com>
* cmd/go: add test of $GONOPROXY, $GONOSUMDB behavior
Change-Id: I8a4917ce14ea22d5991226e485d43a9c9312950e
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174219
Run-TryBot: Russ Cox <rsc@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
* encoding/json: fix Unmarshal hang on recursive pointers
indirect walks down v until it gets to a non-pointer. But it does not
handle the case when v is a pointer to itself, like in:
var v interface{}
v = &v
Unmarshal(b, v)
So just stop immediately if we see v is a pointer to itself.
Fixes #31740
Change-Id: Ie396264119e24d70284cd9bf76dcb2050babb069
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174337
Run-TryBot: Daniel Martí <mvdan@mvdan.cc>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Daniel Martí <mvdan@mvdan.cc>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* runtime: do not use heap arena hints on wasm
The address space of WebAssembly's linear memory is contiguous, so
requesting specific addresses is not supported. Do not use heap arena
hints so we do not have unused memory ranges.
This fixes go1 benchmarks on wasm which ran out of memory since
https://golang.org/cl/170950.
Change-Id: I70115b18dbe43abe16dd5f57996343d97bf94760
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174203
Run-TryBot: Richard Musiol <neelance@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Cherry Zhang <cherryyz@google.com>
* cmd/internal/obj/wasm: cache SP in a local
We use Wasm global variables extensively for simulating
registers, especially SP. V8 does not handle global variables
efficiently.
This CL reduces global variable accesses by caching the global SP
in a local variable in each function. The local cache is set on
function entry and updated after each call (where the stack could
have moved). Within a function, the SP access will use the local
variable.
Supersedes https://golang.org/cl/173979.
Running on Chrome Version 73.0.3683.103 on darwin/amd64:
name old time/op new time/op delta
BinaryTree17 15.3s ± 2% 14.5s ± 3% -5.20% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
Fannkuch11 8.91s ± 2% 9.48s ± 2% +6.41% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
FmtFprintfEmpty 197ns ± 5% 165ns ± 3% -16.09% (p=0.000 n=9+8)
FmtFprintfString 354ns ± 8% 325ns ± 7% -8.33% (p=0.001 n=10+10)
FmtFprintfInt 400ns ± 4% 368ns ± 6% -8.01% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
FmtFprintfIntInt 618ns ± 3% 587ns ± 6% -4.97% (p=0.001 n=10+10)
FmtFprintfPrefixedInt 637ns ± 4% 606ns ± 4% -4.88% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
FmtFprintfFloat 965ns ± 7% 898ns ± 4% -6.97% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
FmtManyArgs 2.34µs ± 1% 2.24µs ± 3% -4.40% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
GobDecode 29.8ms ± 3% 28.8ms ± 6% -3.60% (p=0.006 n=9+10)
GobEncode 20.5ms ± 8% 17.6ms ± 3% -14.32% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
Gzip 714ms ± 3% 718ms ± 8% ~ (p=0.971 n=10+10)
Gunzip 148ms ± 3% 136ms ± 3% -7.99% (p=0.000 n=10+9)
HTTPClientServer 219µs ± 3% 215µs ± 4% ~ (p=0.190 n=10+10)
JSONEncode 35.1ms ± 2% 31.8ms ±13% -9.52% (p=0.002 n=10+10)
JSONDecode 220ms ± 3% 207ms ± 5% -5.87% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
Mandelbrot200 5.22ms ± 1% 5.11ms ± 4% -2.11% (p=0.027 n=8+10)
GoParse 17.2ms ± 6% 16.1ms ± 5% -6.63% (p=0.000 n=10+9)
RegexpMatchEasy0_32 375ns ± 3% 340ns ± 3% -9.25% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
RegexpMatchEasy0_1K 2.70µs ± 3% 2.65µs ± 4% ~ (p=0.118 n=10+10)
RegexpMatchEasy1_32 341ns ± 2% 305ns ± 4% -10.62% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
RegexpMatchEasy1_1K 3.20µs ± 3% 2.99µs ± 3% -6.35% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
RegexpMatchMedium_32 520ns ± 3% 501ns ± 4% -3.64% (p=0.002 n=9+10)
RegexpMatchMedium_1K 145µs ± 7% 128µs ± 3% -11.57% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
RegexpMatchHard_32 7.88µs ± 3% 7.01µs ± 5% -10.97% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
RegexpMatchHard_1K 237µs ± 5% 207µs ± 4% -12.71% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
Revcomp 2.34s ± 1% 2.31s ± 5% ~ (p=0.230 n=7+10)
Template 261ms ± 7% 246ms ± 5% -5.93% (p=0.007 n=10+10)
TimeParse 1.47µs ± 3% 1.39µs ± 5% -5.75% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
TimeFormat 1.52µs ± 3% 1.43µs ± 4% -6.42% (p=0.000 n=8+10)
name old speed new speed delta
GobDecode 25.7MB/s ± 3% 26.7MB/s ± 5% +3.77% (p=0.006 n=9+10)
GobEncode 37.5MB/s ± 8% 43.7MB/s ± 3% +16.61% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
Gzip 27.2MB/s ± 3% 27.0MB/s ± 7% ~ (p=0.971 n=10+10)
Gunzip 131MB/s ± 3% 142MB/s ± 5% +8.07% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
JSONEncode 55.2MB/s ± 2% 61.2MB/s ±12% +10.80% (p=0.002 n=10+10)
JSONDecode 8.84MB/s ± 3% 9.39MB/s ± 5% +6.28% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
GoParse 3.37MB/s ± 6% 3.61MB/s ± 5% +7.09% (p=0.000 n=10+9)
RegexpMatchEasy0_32 85.3MB/s ± 3% 94.0MB/s ± 3% +10.20% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
RegexpMatchEasy0_1K 379MB/s ± 3% 387MB/s ± 4% ~ (p=0.123 n=10+10)
RegexpMatchEasy1_32 93.9MB/s ± 2% 105.1MB/s ± 4% +11.96% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
RegexpMatchEasy1_1K 320MB/s ± 3% 342MB/s ± 3% +6.79% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
RegexpMatchMedium_32 1.92MB/s ± 2% 2.00MB/s ± 3% +3.94% (p=0.001 n=9+10)
RegexpMatchMedium_1K 7.09MB/s ± 6% 8.01MB/s ± 3% +13.00% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
RegexpMatchHard_32 4.06MB/s ± 3% 4.56MB/s ± 5% +12.38% (p=0.000 n=10+10)
RegexpMatchHard_1K 4.32MB/s ± 4% 4.96MB/s ± 4% +14.60% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
Revcomp 109MB/s ± 1% 110MB/s ± 5% ~ (p=0.219 n=7+10)
Template 7.44MB/s ± 8% 7.91MB/s ± 5% +6.30% (p=0.007 n=10+10)
Change-Id: I5828cf6b23ce104c02addc2642aba48dd6c48aab
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174062
Run-TryBot: Richard Musiol <neelance@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Cherry Zhang <cherryyz@google.com>
* cmd/go/internal/modfetch: fix concurrent read/write race in modfetch
On Windows systems, the failure rate for cmd/go's TestScript/mod_concurrent
is somewhere around 3-10% without this change. With the change, I have yet
to see a failure.
Fixes #31744.
Change-Id: Ib321ebb9556dd8438086cf329dfa083a9e051732
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174439
Run-TryBot: Russ Cox <rsc@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* encoding/csv: add a Fuzz function
Adds a sample Fuzz test function to package encoding/csv based on
https://github.com/dvyukov/go-fuzz-corpus/blob/master/csv/main.go
Updates #19109
Updates #31309
Change-Id: Ieb0cb6caa1df72dbb7e29df4bdeed0bfa91187d3
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174302
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
Run-TryBot: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/go: say to confirm import path when it's not found
Fixes #31366.
Change-Id: Ief26f53e7fe94bedb7db79d3d7130c4cdcec4281
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174179
Run-TryBot: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
Reviewed-by: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* html: add a Fuzz function
Adds a sample Fuzz test function to package html based on
https://github.com/dvyukov/go-fuzz-corpus/blob/master/stdhtml/main.go
Updates #19109
Updates #31309
Change-Id: I8c49fff8f70fc8a8813daf1abf0044752003adbb
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174301
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
Run-TryBot: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/dist: disable cgo for darwin/386
Fixes #31751
Change-Id: Id002f14557a34accc3597cb1b9a42e838a027da4
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174497
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
Run-TryBot: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* runtime: implement pthread functions for darwin/arm64
They were not needed when Go only produced binaries with cgo suppport.
Now that Go is about to run self-hosted on iOS we do need these.
Updates #31722
Change-Id: If233aa2b31edc7b1c2dcac68974f9fba0604f9a3
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174300
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
* cmd/link: add .go.buildinfo in XCOFF symbol table
.go.buildinfo must be added to the symbol table on AIX. Otherwise, ld
won't be able to handle its relocations.
This patch also make ".data" the default section for all symbols inside
the data segment.
Change-Id: I83ac2bf1050e0ef6ef9c96ff793efd4ddc8e98d7
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174298
Run-TryBot: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* all: add new GOOS=illumos, split out of GOOS=solaris
Like GOOS=android which implies the "linux" build tag, GOOS=illumos
implies the "solaris" build tag. This lets the existing ecosystem of
packages still work on illumos, but still permits packages to start
differentiating between solaris and illumos.
Fixes #20603
Change-Id: I8f4eabf1a66060538dca15d7658c1fbc6c826622
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174457
Run-TryBot: Benny Siegert <bsiegert@gmail.com>
Reviewed-by: Benny Siegert <bsiegert@gmail.com>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* runtime: fix data sizes for res_search results
The return values are 32 bit, not 64 bit.
I don't think this would be the cause of any problems, but
it can't hurt to fix it.
Change-Id: Icdd50606360ab9d74070271f9d1721d5fe640bc7
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174518
Run-TryBot: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/go/internal/modcmd: allow mod download without go.mod
Fixes #29522
Change-Id: I48f3a945d24c23c7c7ef5c7f1fe5046b6b2898e9
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/157937
Run-TryBot: Bryan C. Mills <bcmills@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Bryan C. Mills <bcmills@google.com>
* all: refer to map elements as elements instead of values
The spec carefully and consistently uses "key" and "element"
as map terminology. The implementation, not so much.
This change attempts to make the implementation consistently
hew to the spec's terminology. Beyond consistency, this has
the advantage of avoid some confusion and naming collisions,
since v and value are very generic and commonly used terms.
I believe that I found all everything, but there are a lot of
non-obvious places for these to hide, and grepping for them is hard.
Hopefully this change changes enough of them that we will start using
elem going forward. Any remaining hidden cases can be removed ad hoc
as they are discovered.
The only externally-facing part of this change is in package reflect,
where there is a minor doc change and a function parameter name change.
Updates #27167
Change-Id: I2f2d78f16c360dc39007b9966d5c2046a29d3701
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174523
Run-TryBot: Josh Bleecher Snyder <josharian@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* encoding/gob: adding missing fuzz skip to one of the fuzz tests
It's slow & often times out randomly on longtest builders. Not useful.
Fixes #31517
Change-Id: Icedbb0c94fbe43d04e8b47d5785ac61c5e2d8750
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174522
Run-TryBot: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Bryan C. Mills <bcmills@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/dist: set the default external linker on platforms without gcc
The go tool already sets -extld to the appropriate compiler. This
CL changes cmd/dist to do the same, to fix bootstrapping on platforms
that only have clang (Android and iOS).
Updates #31722
Change-Id: I8a4fd227f85a768053a8946198eab68bbbdf9ae5
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174305
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/dist: detect GOHOSTARCH on iOS
cmd/dist defaults to GOHOSTARCH=amd64 on darwin because no other
darwin host could build Go. With the upcoming self-hosted iOS
builders, GOHOSTARCH=arm64 is also possible.
Updates #31722
Change-Id: I9af47d9f8c57ea45475ce498acefbfe6bf4815b9
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174306
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/go: derive executable name from package path in 'go run'
Change name of temporary executable on go run . to directory name.
Fixes #31571
Change-Id: I0a0ce74154e76205bb43805c95bd7fb8fd2dfd01
GitHub-Last-Rev: e0964983e18a1d45b55f7098c7489059708c7e5e
GitHub-Pull-Request: golang/go#31614
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/173297
Run-TryBot: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
* time: look for zoneinfo.zip in GOROOT
The zoneinfo.zip file will be in the $GOROOT in self-hsoted builds
on iOS.
Updates #31722
Change-Id: I991fae92e3dc50581b099a2d8901aed36ecc7cef
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174310
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* cmd/go: query modules in parallel
Refactor modload.QueryPackage and modload.QueryPattern to share code.
Fine-tune error reporting and make it consistent between QueryPackage and QueryPattern.
Expand tests for pattern errors.
Update a TODO in modget/get.go and add a test case that demonstrates it.
Updates #26232
Change-Id: I900ca8de338ef9a51b7f85ed93d8bcf837621646
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/173017
Run-TryBot: Bryan C. Mills <bcmills@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
* net/http: make Server return 501 for unsupported transfer-encodings
Ensures that our HTTP/1.X Server properly responds
with a 501 Unimplemented as mandated by the spec at
RFC 7230 Section 3.3.1, which says:
A server that receives a request message with a
transfer coding it does not understand SHOULD
respond with 501 (Unimplemented).
Fixes #30710
Change-Id: I096904e6df053cd1e4b551774cc27523ff3d09f6
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/167017
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
Run-TryBot: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/go,cmd/internal/sys,cmd/link: skip Go build ids for externally linked tools
cmd/go already skips build ids on Android where buildmode=pie is
forced. Expand the check to all externally linked tools.
Necessary for self-hosted iOS builds where PIE is not forced but
external linking is.
Updates #31722
Change-Id: Iad796a9411a37eb0c44d365b70a3c5907537e461
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174307
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
* cmd/go/internal/modfetch/codehost: disable fetch of server-resolved commit hash
We cannot rely on the server to filter out the refs we don't want
(we only want refs/heads/* and refs/tags/*), so do not give it
the full hash.
Fixes #31191.
Change-Id: If1208c35954228aa6e8734f8d5f1725d0ec79c87
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174517
Run-TryBot: Russ Cox <rsc@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Bryan C. Mills <bcmills@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/compile: remove dynamic entry handling from sinit/maplit
The order pass now handles all the dynamic entries.
Update #26552
Followup to CL 174417
Change-Id: Ie924cadb0e0ba36c423868f654f13040100b44c6
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174498
Run-TryBot: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Matthew Dempsky <mdempsky@google.com>
* os: fix tests on self-hosted Go builds
Updates #31722
Change-Id: I467bb2539f993fad642abf96388a58a263fbe007
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174311
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
Reviewed-by: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/asm: reject BSWAPW on amd64
Since BSWAP operation on 16-bit registers is undefined,
forbid the usage of BSWAPW. Users should rely on XCHGB instead.
This behavior is consistent with what GAS does.
Fixes #29167
Change-Id: I3b31e3dd2acfd039f7564a1c17e6068617bcde8d
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174312
Run-TryBot: Iskander Sharipov <quasilyte@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* cmd/compile: fix line numbers for index panics
In the statement x = a[i], the index panic should appear to come from
the line number of the '['. Previous to this CL we sometimes used the
line number of the '=' instead.
Fixes #29504
Change-Id: Ie718fd303c1ac2aee33e88d52c9ba9bcf220dea1
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174617
Run-TryBot: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/compile: add signed divisibility rules
"Division by invariant integers using multiplication" paper
by Granlund and Montgomery contains a method for directly computing
divisibility (x%c == 0 for c constant) by means of the modular inverse.
The method is further elaborated in "Hacker's Delight" by Warren Section 10-17
This general rule can compute divisibilty by one multiplication, and add
and a compare for odd divisors and an additional rotate for even divisors.
To apply the divisibility rule, we must take into account
the rules to rewrite x%c = x-((x/c)*c) and (x/c) for c constant on the first
optimization pass "opt". This complicates the matching as we want to match
only in the cases where the result of (x/c) is not also needed.
So, we must match on the expanded form of (x/c) in the expression x == c*(x/c)
in the "late opt" pass after common subexpresion elimination.
Note, that if there is an intermediate opt pass introduced in the future we
could simplify these rules by delaying the magic division rewrite to "late opt"
and matching directly on (x/c) in the intermediate opt pass.
On amd64, the divisibility check is 30-45% faster.
name old time/op new time/op delta`
DivisiblePow2constI64-4 0.83ns ± 1% 0.82ns ± 0% ~ (p=0.079 n=5+4)
DivisibleconstI64-4 2.68ns ± 1% 1.87ns ± 0% -30.33% (p=0.000 n=5+4)
DivisibleWDivconstI64-4 2.69ns ± 1% 2.71ns ± 3% ~ (p=1.000 n=5+5)
DivisiblePow2constI32-4 1.15ns ± 1% 1.15ns ± 0% ~ (p=0.238 n=5+4)
DivisibleconstI32-4 2.24ns ± 1% 1.20ns ± 0% -46.48% (p=0.016 n=5+4)
DivisibleWDivconstI32-4 2.27ns ± 1% 2.27ns ± 1% ~ (p=0.683 n=5+5)
DivisiblePow2constI16-4 0.81ns ± 1% 0.82ns ± 1% ~ (p=0.135 n=5+5)
DivisibleconstI16-4 2.11ns ± 2% 1.20ns ± 1% -42.99% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
DivisibleWDivconstI16-4 2.23ns ± 0% 2.27ns ± 2% +1.79% (p=0.029 n=4+4)
DivisiblePow2constI8-4 0.81ns ± 1% 0.81ns ± 1% ~ (p=0.286 n=5+5)
DivisibleconstI8-4 2.13ns ± 3% 1.19ns ± 1% -43.84% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
DivisibleWDivconstI8-4 2.23ns ± 1% 2.25ns ± 1% ~ (p=0.183 n=5+5)
Fixes #30282
Fixes #15806
Change-Id: Id20d78263a4fdfe0509229ae4dfa2fede83fc1d0
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/173998
Run-TryBot: Brian Kessler <brian.m.kessler@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
* cmd/go: make get -u upgrade only modules providing packages
Currently, 'go get -u' upgrades modules matching command line
arguments and any modules they transitively require. 'go get -u' with
no positional arguments upgrades all modules transitively required by
the main module. This usually adds a large number of indirect
requirements, which is surprising to users.
With this change, 'go get' will load packages specified by
its arguments using a similar process to other commands
('go build', etc). Only modules providing packages will be upgraded.
'go get -u' now upgrades modules providing packages transitively
imported by the command-line arguments. 'go get -u' without arguments
will only upgrade modules needed by the package in the current
directory.
'go get -m' will load all packages within a module. 'go get -m -u'
without arguments will upgrade modules needed by the main module. It
is equivalent to 'go get -u all'. Neither command will upgrade modules
that are required but not used.
Note that 'go get -m' and 'go get -d' both download modules in order
to load packages.
Fixes #26902
Change-Id: I2bad686b3ca8c9de985a81fb42b16a36bb4cc3ea
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174099
Run-TryBot: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Russ Cox <rsc@golang.org>
* syscall: on wasm, do not use typed array asynchronously
The underlying buffer of a typed array becomes invalid as soon as we
grow the WebAssembly memory, which can happen at any time while Go code
runs. This is a known limitation, see https://golang.org/cl/155778.
As a consequence, using a typed array with one of the asynchronous
read/write operations of Node.js' fs module is dangerous, since it may
become invalid while the asynchronous operation has not finished yet.
The result of this situation is most likely undefined.
I am not aware of any nice solution to this issue, so this change adds
a workaround of using an additional typed array which is not backed by
WebAssembly memory and copying the bytes between the two typed arrays.
Maybe WebAssembly will come up with a better solution in the future.
Fixes #31702.
Change-Id: Iafc2a0fa03c81db414520bd45a1a17c00080b61e
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174304
Run-TryBot: Richard Musiol <neelance@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Cherry Zhang <cherryyz@google.com>
* net/http: add Transport.ReadBufferSize and WriteBufferSize
Previously transport was using the hardcoded bufio.defaultBufSize
(4096), limiting throughput and increasing cpu usage when uploading or
downloading large files.
Add options to allow users to configure the buffer sizes as needed.
I tested the maximum benefit of this change by uploading data from
/dev/zero to a server discarding the bytes. Here is an example upload
using the default buffer size:
$ time ./upload 10 https://localhost:8000/
Uploaded 10.00g in 25.13 seconds (407.49m/s)
real 0m25.135s
user 0m5.167s
sys 0m11.643s
With this change, using 128k buffer size:
$ time ./upload 10 https://localhost:8000/
Uploaded 10.00g in 7.93 seconds (1291.51m/s)
real 0m7.935s
user 0m4.517s
sys 0m2.603s
In real world usage the difference will be smaller, depending on the
local and remote storage and the network.
See https://github.com/nirs/http-bench for more info.
Fixes #22618
Change-Id: Iac99ed839c7b95d6dc66602ba8fe1fc5b500c47c
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/76410
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* net/http: make Transport.MaxConnsPerHost work for HTTP/2
Treat HTTP/2 connections as an ongoing persistent connection. When we
are told there is no cached connections, cleanup the associated
connection and host connection count.
Fixes #27753
Change-Id: I6b7bd915fc7819617cb5d3b35e46e225c75eda29
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/140357
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* internal/cpu: add detection for the new ECDSA and EDDSA capabilities on s390x
This CL will check for the Message-Security-Assist Extension 9 facility
which enables the KDSA instruction.
Change-Id: I659aac09726e0999ec652ef1f5983072c8131a48
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174529
Run-TryBot: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* net: set DNSError.IsTemporary from addrinfoErrno errors
Today it is not possible (AFAICT) to detect if a DNSError if of type EAI_AGAIN, i.e. if it is something temporary that should be retried. This information is available inside addrinfoErrno but when the DNSError is created this information is lost.
This PR fixes this so that the addinfoErrno.Temporary information is added to DNSError as well. With that a user who gets a DNSError can check now is its a temporary error (for errors that resulted from a addrinfoErrno this is EAI_AGAIN).
Change-Id: I64badb2ebd904e41fc2e0755416f7f32560534d8
GitHub-Last-Rev: ced7238a6597039fb23f36f372bd1cf33d60d4a6
GitHub-Pull-Request: golang/go#31676
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174557
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* os,time: fix tests on iOS
When fixing tests for for self-hosted iOS builds, I
broke hosted builds.
Updates #31722
Change-Id: Id4e7d234fbd86cb2d29d320d75f4441efd663d12
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174698
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* test: enable more memcombine tests for ppc64le
This enables more of the testcases in memcombine for ppc64le,
and adds more detail to some existing.
Change-Id: Ic522a1175bed682b546909c96f9ea758f8db247c
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174737
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
Run-TryBot: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* runtime: change the span allocation policy to first-fit
This change modifies the treap implementation to be address-ordered
instead of size-ordered, and further augments it so it may be used for
allocation. It then modifies the find method to implement a first-fit
allocation policy.
This change to the treap implementation consequently makes it so that
spans are scavenged in highest-address-first order without any
additional changes to the scavenging code. Because the treap itself is
now address ordered, and the scavenging code iterates over it in
reverse, the highest address is now chosen instead of the largest span.
This change also renames the now wrongly-named "scavengeLargest" method
on mheap to just "scavengeLocked" and also fixes up logic in that method
which made assumptions about size.
For #30333.
Change-Id: I94b6f3209211cc1bfdc8cdaea04152a232cfbbb4
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/164101
Run-TryBot: Michael Knyszek <mknyszek@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Austin Clements <austin@google.com>
* go/internal/gccgoimporter: skip new test with aliases with old gccgo
Add the issue31540 test to the list of tests that needs to be skipped
with old copies of gccgo. Along the way, add an explicit field to the
importer test struct that can be used to tag the test (as opposed to
having special cases by name in the test routine), so as to make it
easier to remember to tag testcases correctly.
Fixes #31764.
Change-Id: Ib9d98fea2df8ce0b51e5a886fb2c4acd6db490ff
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174738
Reviewed-by: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
Run-TryBot: Ian Lance Taylor <iant@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/compile/internal/ppc64: improve naming for ginsnop2
This is a follow up from a review comment at the end of the last
Go release, to provide a more meaningful name for ginsnop2.
Updates #30475
Change-Id: Ice9efd763bf2204a9e8c55ae230d3e8a80210108
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174757
Run-TryBot: Lynn Boger <laboger@linux.vnet.ibm.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
* index/suffixarray: add 32-bit implementation
The original index/suffixarray used 32-bit ints on 64-bit machines,
because that's what 'int' meant in Go at the time. When we changed
the meaning of int, that doubled the space overhead of suffix arrays
for all uses, even though the vast majority of them describe less
than 2 GB of text.
The space overhead of a suffix array compared to the text is not
insignificant: there's a big difference for many uses between 4X and 8X.
This CL adjusts names in qsufsort.go so that a global search and
replace s/32/64/g produces a working 64-bit implementation,
and then it modifies suffixarray.go to choose between the 32-bit
and 64-bit implementation as appropriate depending on the input size.
The 64-bit implementation is generated by 'go generate'.
This CL also restructures the benchmarks, to test different
input sizes, different input texts, and 32-bit vs 64-bit.
The serialized form uses varint-encoded numbers and is unchanged,
so on-disk suffix arrays written by older versions of Go will be
readable by this version, and vice versa.
The 32-bit version runs a up to 17% faster than the 64-bit version
on real inputs, but more importantly it uses 50% less memory.
I have a followup CL that also implements a faster algorithm
on top of these improvements, but these are a good first step.
name 64-bit speed 32-bit speed delta
New/text=opticks/size=100K/bits=*-12 4.44MB/s ± 0% 4.64MB/s ± 0% +4.41% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=opticks/size=500K/bits=*-12 3.70MB/s ± 1% 3.82MB/s ± 0% +3.30% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=go/size=100K/bits=*-12 4.40MB/s ± 0% 4.61MB/s ± 0% +4.82% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=go/size=500K/bits=*-12 3.66MB/s ± 0% 3.77MB/s ± 0% +3.01% (p=0.016 n=4+5)
New/text=go/size=1M/bits=*-12 3.29MB/s ± 0% 3.55MB/s ± 0% +7.90% (p=0.016 n=5+4)
New/text=go/size=5M/bits=*-12 2.25MB/s ± 1% 2.65MB/s ± 0% +17.81% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=go/size=10M/bits=*-12 1.82MB/s ± 0% 2.09MB/s ± 1% +14.36% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=go/size=50M/bits=*-12 1.35MB/s ± 0% 1.51MB/s ± 1% +12.33% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=zero/size=100K/bits=*-12 3.42MB/s ± 0% 3.32MB/s ± 0% -2.74% (p=0.000 n=5+4)
New/text=zero/size=500K/bits=*-12 3.00MB/s ± 1% 2.97MB/s ± 0% -1.13% (p=0.016 n=5+4)
New/text=zero/size=1M/bits=*-12 2.81MB/s ± 0% 2.78MB/s ± 2% ~ (p=0.167 n=5+5)
New/text=zero/size=5M/bits=*-12 2.46MB/s ± 0% 2.53MB/s ± 0% +3.18% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=zero/size=10M/bits=*-12 2.35MB/s ± 0% 2.42MB/s ± 0% +2.98% (p=0.016 n=4+5)
New/text=zero/size=50M/bits=*-12 2.12MB/s ± 0% 2.18MB/s ± 0% +3.02% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=rand/size=100K/bits=*-12 6.98MB/s ± 0% 7.22MB/s ± 0% +3.38% (p=0.016 n=4+5)
New/text=rand/size=500K/bits=*-12 5.53MB/s ± 0% 5.64MB/s ± 0% +1.92% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=rand/size=1M/bits=*-12 4.62MB/s ± 1% 5.06MB/s ± 0% +9.61% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=rand/size=5M/bits=*-12 3.09MB/s ± 0% 3.43MB/s ± 0% +10.94% (p=0.016 n=4+5)
New/text=rand/size=10M/bits=*-12 2.68MB/s ± 0% 2.95MB/s ± 0% +10.39% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=rand/size=50M/bits=*-12 1.92MB/s ± 0% 2.06MB/s ± 1% +7.41% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
SaveRestore/bits=*-12 243MB/s ± 1% 259MB/s ± 0% +6.68% (p=0.000 n=9+10)
name 64-bit alloc/op 32-bit alloc/op delta
New/text=opticks/size=100K/bits=*-12 1.62MB ± 0% 0.81MB ± 0% -50.00% (p=0.000 n=5+4)
New/text=opticks/size=500K/bits=*-12 8.07MB ± 0% 4.04MB ± 0% -49.89% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=go/size=100K/bits=*-12 1.62MB ± 0% 0.81MB ± 0% -50.00% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=go/size=500K/bits=*-12 8.07MB ± 0% 4.04MB ± 0% -49.89% (p=0.029 n=4+4)
New/text=go/size=1M/bits=*-12 16.1MB ± 0% 8.1MB ± 0% -49.95% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=go/size=5M/bits=*-12 80.3MB ± 0% 40.2MB ± 0% ~ (p=0.079 n=4+5)
New/text=go/size=10M/bits=*-12 160MB ± 0% 80MB ± 0% -50.00% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=go/size=50M/bits=*-12 805MB ± 0% 402MB ± 0% -50.06% (p=0.029 n=4+4)
New/text=zero/size=100K/bits=*-12 3.02MB ± 0% 1.46MB ± 0% ~ (p=0.079 n=4+5)
New/text=zero/size=500K/bits=*-12 19.7MB ± 0% 8.7MB ± 0% -55.98% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=zero/size=1M/bits=*-12 39.0MB ± 0% 19.7MB ± 0% -49.60% (p=0.000 n=5+4)
New/text=zero/size=5M/bits=*-12 169MB ± 0% 85MB ± 0% -49.46% (p=0.029 n=4+4)
New/text=zero/size=10M/bits=*-12 333MB ± 0% 169MB ± 0% -49.43% (p=0.000 n=5+4)
New/text=zero/size=50M/bits=*-12 1.63GB ± 0% 0.74GB ± 0% -54.61% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=rand/size=100K/bits=*-12 1.61MB ± 0% 0.81MB ± 0% -50.00% (p=0.000 n=5+4)
New/text=rand/size=500K/bits=*-12 8.07MB ± 0% 4.04MB ± 0% -49.89% (p=0.000 n=5+4)
New/text=rand/size=1M/bits=*-12 16.1MB ± 0% 8.1MB ± 0% -49.95% (p=0.029 n=4+4)
New/text=rand/size=5M/bits=*-12 80.7MB ± 0% 40.3MB ± 0% -50.06% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=rand/size=10M/bits=*-12 161MB ± 0% 81MB ± 0% -50.03% (p=0.008 n=5+5)
New/text=rand/size=50M/bits=*-12 806MB ± 0% 403MB ± 0% -50.00% (p=0.016 n=4+5)
SaveRestore/bits=*-12 9.47MB ± 0% 5.28MB ± 0% -44.29% (p=0.000 n=9+8)
https://perf.golang.org/search?q=upload:20190126.1+|+bits:64+vs+bits:32
Fixes #6816.
Change-Id: Ied2fbea519a202ecc43719debcd233344ce38847
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174097
Run-TryBot: Russ Cox <rsc@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* runtime: look for idle p to run current goroutine when switching to GC or traceReader
This repairs one of the several causes of pauses uncovered
by a GC microbenchmark. A pause can occur when a goroutine's
quantum expires "at the same time" a GC is needed. The
current M switches to running a GC worker, which means that
the amount of available work has expanded by one. The GC
worker, however, does not call ready, and does not itself
conditionally wake a P (a "normal" thread would do this).
This is also true if M switches to a traceReader.
This is problem 4 in this list:
https://github.com/golang/go/issues/27732#issuecomment-423301252
Updates #27732.
Change-Id: I6905365cac8504cde6faab2420f4421536551f0b
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/146817
Run-TryBot: David Chase <drchase@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Austin Clements <austin@google.com>
* cmd/go/internal/modfetch/codehost: fix pseudoversions for non-semver tags and tags on other branches
Pseudoversion determination depends in part on the results from gitRepo.RecentTag, which currently invokes:
git describe --first-parent --always --abbrev=0 --match <prefix>v[0-9]*.[0-9]*.[0-9]* --tags <rev>
The comment at https://github.com/golang/go/issues/27171#issuecomment-470134255 describes some problems with the current approach.
One problem is Docker and other repos can have tags that are not valid semver tags but that still match a glob pattern of v[0-9]*.[0-9]*.[0-9]* which are found by 'git describe' but then rejected by cmd/go, and hence those repos currently can end up with v0.0.0 pseudoversions instead of finding a proper semver tag to use as input to building a pseudoversion (when then causes problems when the v0.0.0 pseudoversion is fed into MVS). An example problematic tag is a date-based tag such as 'v18.06.16', which matches the glob pattern, but is not a valid semver tag (due to the leading 0 in '06').
Issues #31673, #31287, and #27171 also describe problems where the '--first-parent' argument to 'git describe' cause the current approach to miss relevant semver tags that were created on a separate branch and then subsequently merged to master.
In #27171, Bryan described the base tag that is supposed to be used for pseudoversions as:
"It is intended to be the semantically-latest tag that appears on any commit that is a (transitive) parent of the commit with the given hash, regardless of branches. (The pseudo-version is supposed to sort after every version — tagged or otherwise — that came before it, but before the next tag that a human might plausibly want to apply to the branch.)"
This CL solves the glob problem and tags-on-other-branches problem more directly than the current approach: this CL gets the full list of tags that have been merged into the specific revision of interest, and then sorts and filters the results in cmd/go to select the semantically-latest valid semver tag.
Fixes #31673
Fixes #31287
Updates #27171
Change-Id: I7c3e6b46b2b21dd60562cf2893b6bd2afaae61d5
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174061
Run-TryBot: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
* cmd/go/internal/get: fix strayed verbose output on stdout
Fixes #31768
Change-Id: I3cc0ebc4be34d7c2d2d4fd655bfd0c2515ff3021
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174739
Reviewed-by: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
Run-TryBot: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/dist: only build exec wrappers when cross compiling
Updates #31722
Change-Id: Ib44b46e628e364fff6eacda2b26541db2f0a4261
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174701
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* misc/cgo/testcarchive: skip TestExtar on self-hosted iOS
iOS cannot (directly) run shell scripts.
Updates #31722
Change-Id: I69473e9339c50a77338d391c73b4e146bce3fa89
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174700
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* strings, bytes: add ToValidUTF8
The newly added functions create a copy of their input with all bytes in
invalid UTF-8 byte sequences mapped to the UTF-8 byte sequence
given as replacement parameter.
Fixes #25805
Change-Id: Iaf65f65b40c0581c6bb000f1590408d6628321d0
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/142003
Run-TryBot: Martin Möhrmann <moehrmann@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* cmd/go: sort vendor/modules.txt package lists
Right now they are in a deterministic order
but one that depends on the shape of the import graph.
Sort them instead.
Change-Id: Ia0c076a0d6677a511e52acf01f38353e9895dec2
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174527
Run-TryBot: Russ Cox <rsc@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/compile: fix maplit init panics for dynamic entry
golang.org/cl/174498 removes dynamic map entry handling in maplit, by
filtering the static entry only. It panics if it see a dynamic entry.
It relies on order to remove all dynamic entries.
But after recursively call order on the statics, some static entries
become dynamic, e.g OCONVIFACE node:
type i interface {
j()
}
type s struct{}
func (s) j() {}
type foo map[string]i
var f = foo{
"1": s{},
}
To fix it, we recursively call order on each static entry, if it changed
to dynamic, put entry to dynamic then.
Fixes #31777
Change-Id: I1004190ac8f2d1eaa4beb6beab989db74099b025
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174777
Run-TryBot: Matthew Dempsky <mdempsky@google.com>
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
* cmd/go/internal/web: fix log message
The web package is now used for proxy fetches, so its logs shouldn't
start with "Parsing meta tags".
Change-Id: I22a7dce09e3a681544ee4b860f93c63336e547ca
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174740
Run-TryBot: Heschi Kreinick <heschi@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* cmd/compile: disable Go1.13 language features for -lang=go1.12 and below
Fixes #31747.
Updates #19308.
Updates #12711.
Updates #29008.
Updates #28493.
Updates #19113.
Change-Id: I76d2fdbc7698cc4e0f31b7ae24cbb4d28afbb6a3
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174897
Run-TryBot: Robert Griesemer <gri@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Matthew Dempsky <mdempsky@google.com>
* errors: fix comment referencing the Wrapper interface
The Unwrap function performs a type assertion looking for the Wrapper
interface. The method of that interface is called Unwrap but the
interface itself is called Wrapper.
Change-Id: Ie3bf296f93b773d36015bcab2a0e6585d39783c7
GitHub-Last-Rev: 32b1a0c2f8bf8f3eaebf6de252571d82313e86e0
GitHub-Pull-Request: golang/go#31794
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174917
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* doc/go1.13: start doc, note macOS, FreeBSD deprecations
For #23011.
For #27619.
Change-Id: Id1f280993ecdfb07a7420926ca1c0f5b7872afbb
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174521
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* cmd/compile: remove outdate TODO in inl.go
Mid-stack inlining is enable now, see #19348, but we still can not
remove the special case for runtime.heapBits.nextArena, because
runtime.heapBits.next is too complex to be inlined
(cost 96 exceeds budget 80).
Change-Id: I04ea86509074afdc83a3f70d68b8a1a8829763d1
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174839
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* cmd/go: make modconv test more robust
Change-Id: I3e75201c56779eda1bcd725691c72d384da56f73
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174840
Run-TryBot: Baokun Lee <nototon@gmail.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
* cmd/go/internal/modload: make 'list -u' consider current pseudoversion
As pointed out by thepudds in #30634, the 'list -u' documentation states that the current version should be considered for upgrade:
The -u flag adds information about available upgrades. When the latest version of a given module is newer than the current one, list -u sets the Module's Update field to information about the newer module.
In go 1.12.4 (and current tip), an older version will be suggested as upgrade to a newer pseudo version.
Updates: #30634
Change-Id: If2c8887198884b8e7ccb3a604908065aa1f1878a
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174206
Run-TryBot: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Jay Conrod <jayconrod@google.com>
* cmd/dist: don't generate exec wrappers for compatible cross compiles
This change will allow android/arm64 hosts to build for android/arm,
and likewise for iOS.
Updates #31722
Change-Id: Id410bd112abbab585ebb13b61fe4d3a38a1a81fb
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/174705
Run-TryBot: Elias Naur <mail@eliasnaur.com>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
Reviewed-by: Brad Fitzpatrick <bradfitz@golang.org>
* cmd/link: support PIE mode with internal link on linux arm64
This CL improves internal link to provide basic support for cgo and PIE:
1, add support for GOT, PLT and GOTPLT.
2, add support for following ELF relocation types which have been used by std
packages:
R_AARCH64_ADR_GOT_PAGE
R_AARCH64_LD64_GOT_LO12_NC
R_AARCH64_ADR_PREL_PG_HI21
R_AARCH64_ADD_ABS_LO12_NC
R_AARCH64_LDST8_ABS_LO12_NC
R_AARCH64_LDST32_ABS_LO12_NC
R_AARCH64_LDST64_ABS_LO12_NC
R_AARCH64_JUMP26
R_AARCH64_ABS64
R_AARCH64_PREL32
R_AARCH64_PREL64
With this change, Go toolchain can be built in internal linking mode, and
pure Go programs can be built with PIE mode in internal linking mode on arm64.
Updates #10373
The prototype of this CL is contributed by Wei Xiao <wei.xiao@arm.com>
Change-Id: I2253923c69e855fd1524d54def309a961dce6247
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/163579
Reviewed-by: Cherry Zhang <cherryyz@google.com>
Run-TryBot: Cherry Zhang <cherryyz@google.com>
* sort: simplify bootstrap
We compile package sort as part of the compiler bootstrap,
to make sure the compiler uses a consistent sort algorithm
no matter what version of Go it is compiled against.
(This matters for elements that compare "equal" but are distinguishab…
|
I didn't find better fit issue to describe my problem, please let me know if I should open another issue. |
|
@dr2chase @aclements please let me know if I could help with debug or if you have any ideas what allocation patterns could cause that. |
|
Sorry not to reply earlier, I haven't looked at this for a little while. In terms of bugs-we've-got, that matches the above subproblems
I don't know of an automated way to check for that, but if you think that's happening, you can force things to the heap by assigning their address to a global (I just looked at the "Run Vitess Locally" instructions, that's a lot, I would probably need that GOEXPERIMENT anyway myself. How do you feel about lighting this up with 1.13 for testing purposes?) |
|
@dr2chase our project isn't exactly vitess, it's using only |
|
Change https://golang.org/cl/180817 mentions this issue: |
Shrinks the size of things that can be stack allocated from
10M to 128k for declared variables and from 64k to 16k for
implicit allocations (new(T), &T{}, etc).
Usage: "go build -gcflags -smallframes hello.go"
An earlier GOEXPERIMENT version of this caused only one
problem, when a gc-should-detect-oversize-stack test no
longer had an oversized stack to detect. The change was
converted to a flag to make it easier to access (for
diagnosing "long" GC-related single-thread pauses) and to
remove interference with the test.
Includes test to verify behavior.
Updates #27732.
Change-Id: I1255d484331e77185e07c78389a8b594041204c2
Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/180817
Run-TryBot: David Chase <drchase@google.com>
Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org>
|
@LK4D4 I just submitted a change to 1.13 tip that might help you diagnose this (depending on the complexity of your build process). Crudely, You can look for differences by comparing output of Austin's unproven-but-plausible theory for this is that between 1.10 and 1.12 one of the incremental improvements in escape analysis let something large be allocated on the stack. |
|
Change https://golang.org/cl/180958 mentions this issue: |
Tool refactoring smallStacks into smallFrames helpfully "corrected" the capitalization in a string, this undoes the help. This is necessary to ensure correct (re)building when the flag is used to research stack-marking GC latency bugs. Updates #27732. Change-Id: Ib7c8d4a36c9e4f9612559be68bd481f9d9cc69f1 Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/go/+/180958 Run-TryBot: David Chase <drchase@google.com> TryBot-Result: Gobot Gobot <gobot@golang.org> Reviewed-by: Keith Randall <khr@golang.org>
|
Further info: besides incremental changes to escape analysis, incremental changes to inlining could also cause new things to not escape and become stack-allocated. I also did a quick round of diffs building the compiler this way and building a collection of benchmarks this way, and large frames are exceedingly rare. This might motivate some other approach to the indivisible-no-credit stack-scanning problem, that is, make small frames the default, and when large objects are stack eligible, the compiler will explicitly heap allocate and deallocate them instead. |
At a high level, the runtime garbage collector can impact user goroutine latency in two ways. The first is that it pauses all goroutines during its stop-the-world sweep termination and mark termination phases. The second is that it backpressures memory allocations by instructing user goroutines to assist with scanning and marking in response to a high allocation rate. There is plenty of observability into the first of these sources of user-visible latency. There is significantly less observability into the second. As a result, it is often more difficult to diagnose latency problems due to over-assist (e.g. golang#14812, golang#27732, golang#40225). To this point, the ways to determine that GC assist was a problem were to use execution tracing or to use GODEBUG=gctrace=1 tracing, neither of which is easy to access programmatically in a running system. CPU profiles also give some insight, but are rarely as instructive as one might expect because heavy GC assist time is scattered across a profile. Notice even in https://tip.golang.org/doc/gc-guide, the guidance on recognizing and remedying performance problems due to GC assist is sparse. This commit adds a counter to the MemStats and GCStats structs called AssistTotalNs, which tracks the cumulative nanoseconds in GC assist since the program started. This provides a new form of observability into GC assist delays, and one that can be manipulated programmatically. There's more work to be done in this area. This feels like a reasonable first step.
|
Change https://go.dev/cl/431877 mentions this issue: |
…ncy issues Gc_latency is a modified version of a program that tickled multiple latency glitches in the Go GC/runtime. This version reports the time of the worst observed glitches so that they can be easily located in a trace file and debugged. This program can also be run as a benchmark to allow easier automated performance monitoring; by default the benchmark doesn't report worst case times because those are too noisy. Updates golang/go#27732. Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6 Reviewed-on: https://go-review.googlesource.com/c/benchmarks/+/372256 TryBot-Result: Gopher Robot <gobot@golang.org> Reviewed-by: Austin Clements <austin@google.com> Run-TryBot: David Chase <drchase@google.com>
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues This emits statistical latency measurements, not the worst case, because as a benchmark, worst-case is too noisy. This retains latency debugging features. Updates golang/go#27732. Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues Gc_latency is a modified version of a program that tickled multiple latency glitches in the Go GC/runtime. This version reports the time of the worst observed glitches so that they can be easily located in a trace file and debugged. This program can also be run as a benchmark to allow easier automated performance monitoring; by default the benchmark doesn't report worst case times because those are too noisy. Updates golang/go#27732. Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
-OR-
runs as a go benchmark:
go test -bench=B -count=10 . -- -fluff -how=stack
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
pkg: golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-1038NG7 CPU @ 2.00GHz
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 3722432744 ns/op 560.0 avg-ns 400.0 median-ns 1461 p29-ns 25774 p39-ns 38630 p49-ns 110696 p59-ns 4753393 p69-ns 5538766 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4067024228 ns/op 622.0 avg-ns 407.0 median-ns 1648 p29-ns 29543 p39-ns 49744 p49-ns 122664 p59-ns 6239471 p69-ns 6593770 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 5113548640 ns/op 670.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 2028 p29-ns 28188 p39-ns 66678 p49-ns 1448743 p59-ns 7695377 p69-ns 12281974 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 3975527414 ns/op 606.0 avg-ns 406.0 median-ns 1578 p29-ns 28443 p39-ns 43476 p49-ns 113114 p59-ns 6413033 p69-ns 7211445 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4174308310 ns/op 633.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1720 p29-ns 29063 p39-ns 54298 p49-ns 373535 p59-ns 6489633 p69-ns 8041030 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 3980984757 ns/op 609.0 avg-ns 406.0 median-ns 1555 p29-ns 28855 p39-ns 45865 p49-ns 120082 p59-ns 6046351 p69-ns 6346751 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4138732421 ns/op 601.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1550 p29-ns 27874 p39-ns 40879 p49-ns 155143 p59-ns 5705793 p69-ns 8028793 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 5552645990 ns/op 849.0 avg-ns 411.0 median-ns 1962 p29-ns 29602 p39-ns 185457 p49-ns 6228738 p59-ns 19579494 p69-ns 43328862 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4339053770 ns/op 637.0 avg-ns 405.0 median-ns 1674 p29-ns 27410 p39-ns 50768 p49-ns 505246 p59-ns 6891708 p69-ns 88489177 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4715056872 ns/op 719.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1827 p29-ns 28776 p39-ns 70652 p49-ns 3236747 p59-ns 14152105 p69-ns 20386545 worst-ns
PASS
ok golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency 52.349s
as a fake main package benchmark:
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues.
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
-OR-
runs as a go benchmark:
go test -bench=. .
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
pkg: golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-1038NG7 CPU @ 2.00GHz
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack/fluff=false-8 1 561.0 ns/op 411.0 p50-ns 1273 p99-ns 26096 p99.9-ns 41346 p99.99-ns 119637 p99.999-ns 4654801 p99.9999-ns 6614854 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack/fluff=true-8 1 568.0 ns/op 412.0 p50-ns 1282 p99-ns 14150 p99.9-ns 36183 p99.99-ns 114340 p99.999-ns 5826293 p99.9999-ns 6325730 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap/fluff=false-8 1 561.0 ns/op 412.0 p50-ns 1346 p99-ns 25910 p99.9-ns 42044 p99.99-ns 134310 p99.999-ns 508977 p99.9999-ns 673312 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap/fluff=true-8 1 552.0 ns/op 412.0 p50-ns 1376 p99-ns 12748 p99.9-ns 36589 p99.99-ns 102647 p99.999-ns 194319 p99.9999-ns 325812 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global/fluff=false-8 1 564.0 ns/op 411.0 p50-ns 1313 p99-ns 27417 p99.9-ns 42880 p99.99-ns 102889 p99.999-ns 415022 p99.9999-ns 810535 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global/fluff=true-8 1 555.0 ns/op 412.0 p50-ns 1315 p99-ns 15738 p99.9-ns 36374 p99.99-ns 131995 p99.999-ns 556023 p99.9999-ns 2372839 worst-ns
PASS
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues.
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
-OR-
runs as a go benchmark:
go test -bench=B -count=2 .
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
pkg: golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-1038NG7 CPU @ 2.00GHz
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=false-8 1 3746777895 ns/op 564.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1266 p29-ns 21452 p39-ns 40774 p49-ns 122054 p59-ns 4629961 p69-ns 5152588 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=false-8 1 3960773922 ns/op 607.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1386 p29-ns 30254 p39-ns 48302 p49-ns 117086 p59-ns 6043114 p69-ns 8353592 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=false-8 1 3832759983 ns/op 582.0 avg-ns 411.0 median-ns 1519 p29-ns 26273 p39-ns 47897 p49-ns 114378 p59-ns 216399 p69-ns 484183 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=false-8 1 4079520582 ns/op 618.0 avg-ns 417.0 median-ns 2263 p29-ns 29662 p39-ns 60282 p49-ns 147765 p59-ns 344228 p69-ns 638498 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=false-8 1 3688413511 ns/op 562.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1351 p29-ns 28113 p39-ns 40730 p49-ns 104352 p59-ns 202013 p69-ns 468936 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=false-8 1 3590957128 ns/op 544.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1397 p29-ns 25142 p39-ns 40059 p49-ns 101923 p59-ns 431897 p69-ns 658914 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=true-8 1 3645081827 ns/op 552.0 avg-ns 408.0 median-ns 1387 p29-ns 14013 p39-ns 39086 p49-ns 81027 p59-ns 5174202 p69-ns 5994034 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=true-8 1 3761717212 ns/op 573.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1648 p29-ns 20665 p39-ns 39151 p49-ns 92594 p59-ns 5747097 p69-ns 6512030 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=true-8 1 3686269094 ns/op 559.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1441 p29-ns 14351 p39-ns 39182 p49-ns 96212 p59-ns 334248 p69-ns 1308733 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=true-8 1 3642812482 ns/op 549.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1363 p29-ns 14274 p39-ns 38962 p49-ns 97677 p59-ns 267289 p69-ns 662851 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=true-8 1 3618725949 ns/op 549.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1369 p29-ns 13421 p39-ns 39061 p49-ns 103189 p59-ns 227176 p69-ns 541692 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=true-8 1 3634821717 ns/op 550.0 avg-ns 408.0 median-ns 1350 p29-ns 15195 p39-ns 39664 p49-ns 90323 p59-ns 529328 p69-ns 590649 worst-ns
PASS
ok golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency 55.136s
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues.
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
-OR-
runs as a go benchmark:
go test -bench=. .
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
pkg: golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-1038NG7 CPU @ 2.00GHz
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=false-8 1 565.0 ns/op 415.0 p.50-ns 1656 p.99-ns 11869 p.999-ns 44211 p.9999-ns 257396 p.99999-ns 4696488 p.999999-ns 6604076 p1.00-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=false-8 1 545.0 ns/op 415.0 p.50-ns 1393 p.99-ns 9876 p.999-ns 43237 p.9999-ns 76236 p.99999-ns 428879 p.999999-ns 662239 p1.00-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=false-8 1 557.0 ns/op 416.0 p.50-ns 1577 p.99-ns 11138 p.999-ns 43720 p.9999-ns 78440 p.99999-ns 424166 p.999999-ns 4096860 p1.00-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=true-8 1 549.0 ns/op 416.0 p.50-ns 1448 p.99-ns 9264 p.999-ns 40628 p.9999-ns 72465 p.99999-ns 4872942 p.999999-ns 5791115 p1.00-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=true-8 1 552.0 ns/op 415.0 p.50-ns 1365 p.99-ns 12163 p.999-ns 40034 p.9999-ns 71399 p.99999-ns 404900 p.999999-ns 538348 p1.00-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=true-8 1 553.0 ns/op 415.0 p.50-ns 1410 p.99-ns 11901 p.999-ns 37628 p.9999-ns 124533 p.99999-ns 453355 p.999999-ns 787258 p1.00-ns
PASS
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
-OR-
runs as a go benchmark:
go test -bench=B -count=10 . -- -fluff -how=stack
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
pkg: golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-1038NG7 CPU @ 2.00GHz
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 3722432744 ns/op 560.0 avg-ns 400.0 median-ns 1461 p29-ns 25774 p39-ns 38630 p49-ns 110696 p59-ns 4753393 p69-ns 5538766 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4067024228 ns/op 622.0 avg-ns 407.0 median-ns 1648 p29-ns 29543 p39-ns 49744 p49-ns 122664 p59-ns 6239471 p69-ns 6593770 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 5113548640 ns/op 670.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 2028 p29-ns 28188 p39-ns 66678 p49-ns 1448743 p59-ns 7695377 p69-ns 12281974 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 3975527414 ns/op 606.0 avg-ns 406.0 median-ns 1578 p29-ns 28443 p39-ns 43476 p49-ns 113114 p59-ns 6413033 p69-ns 7211445 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4174308310 ns/op 633.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1720 p29-ns 29063 p39-ns 54298 p49-ns 373535 p59-ns 6489633 p69-ns 8041030 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 3980984757 ns/op 609.0 avg-ns 406.0 median-ns 1555 p29-ns 28855 p39-ns 45865 p49-ns 120082 p59-ns 6046351 p69-ns 6346751 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4138732421 ns/op 601.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1550 p29-ns 27874 p39-ns 40879 p49-ns 155143 p59-ns 5705793 p69-ns 8028793 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 5552645990 ns/op 849.0 avg-ns 411.0 median-ns 1962 p29-ns 29602 p39-ns 185457 p49-ns 6228738 p59-ns 19579494 p69-ns 43328862 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4339053770 ns/op 637.0 avg-ns 405.0 median-ns 1674 p29-ns 27410 p39-ns 50768 p49-ns 505246 p59-ns 6891708 p69-ns 88489177 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4715056872 ns/op 719.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1827 p29-ns 28776 p39-ns 70652 p49-ns 3236747 p59-ns 14152105 p69-ns 20386545 worst-ns
PASS
ok golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency 52.349s
as a fake main package benchmark:
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues.
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
-OR-
runs as a go benchmark:
go test -bench=. .
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
pkg: golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-1038NG7 CPU @ 2.00GHz
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack/fluff=false-8 1 561.0 ns/op 411.0 p50-ns 1273 p99-ns 26096 p99.9-ns 41346 p99.99-ns 119637 p99.999-ns 4654801 p99.9999-ns 6614854 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack/fluff=true-8 1 568.0 ns/op 412.0 p50-ns 1282 p99-ns 14150 p99.9-ns 36183 p99.99-ns 114340 p99.999-ns 5826293 p99.9999-ns 6325730 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap/fluff=false-8 1 561.0 ns/op 412.0 p50-ns 1346 p99-ns 25910 p99.9-ns 42044 p99.99-ns 134310 p99.999-ns 508977 p99.9999-ns 673312 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap/fluff=true-8 1 552.0 ns/op 412.0 p50-ns 1376 p99-ns 12748 p99.9-ns 36589 p99.99-ns 102647 p99.999-ns 194319 p99.9999-ns 325812 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global/fluff=false-8 1 564.0 ns/op 411.0 p50-ns 1313 p99-ns 27417 p99.9-ns 42880 p99.99-ns 102889 p99.999-ns 415022 p99.9999-ns 810535 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global/fluff=true-8 1 555.0 ns/op 412.0 p50-ns 1315 p99-ns 15738 p99.9-ns 36374 p99.99-ns 131995 p99.999-ns 556023 p99.9999-ns 2372839 worst-ns
PASS
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues.
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
-OR-
runs as a go benchmark:
go test -bench=B -count=2 .
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
pkg: golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-1038NG7 CPU @ 2.00GHz
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=false-8 1 3746777895 ns/op 564.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1266 p29-ns 21452 p39-ns 40774 p49-ns 122054 p59-ns 4629961 p69-ns 5152588 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=false-8 1 3960773922 ns/op 607.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1386 p29-ns 30254 p39-ns 48302 p49-ns 117086 p59-ns 6043114 p69-ns 8353592 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=false-8 1 3832759983 ns/op 582.0 avg-ns 411.0 median-ns 1519 p29-ns 26273 p39-ns 47897 p49-ns 114378 p59-ns 216399 p69-ns 484183 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=false-8 1 4079520582 ns/op 618.0 avg-ns 417.0 median-ns 2263 p29-ns 29662 p39-ns 60282 p49-ns 147765 p59-ns 344228 p69-ns 638498 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=false-8 1 3688413511 ns/op 562.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1351 p29-ns 28113 p39-ns 40730 p49-ns 104352 p59-ns 202013 p69-ns 468936 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=false-8 1 3590957128 ns/op 544.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1397 p29-ns 25142 p39-ns 40059 p49-ns 101923 p59-ns 431897 p69-ns 658914 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=true-8 1 3645081827 ns/op 552.0 avg-ns 408.0 median-ns 1387 p29-ns 14013 p39-ns 39086 p49-ns 81027 p59-ns 5174202 p69-ns 5994034 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=true-8 1 3761717212 ns/op 573.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1648 p29-ns 20665 p39-ns 39151 p49-ns 92594 p59-ns 5747097 p69-ns 6512030 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=true-8 1 3686269094 ns/op 559.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1441 p29-ns 14351 p39-ns 39182 p49-ns 96212 p59-ns 334248 p69-ns 1308733 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=true-8 1 3642812482 ns/op 549.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1363 p29-ns 14274 p39-ns 38962 p49-ns 97677 p59-ns 267289 p69-ns 662851 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=true-8 1 3618725949 ns/op 549.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1369 p29-ns 13421 p39-ns 39061 p49-ns 103189 p59-ns 227176 p69-ns 541692 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=true-8 1 3634821717 ns/op 550.0 avg-ns 408.0 median-ns 1350 p29-ns 15195 p39-ns 39664 p49-ns 90323 p59-ns 529328 p69-ns 590649 worst-ns
PASS
ok golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency 55.136s
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues Gc_latency is a modified version of a program that tickled multiple latency glitches in the Go GC/runtime. This version reports the time of the worst observed glitches so that they can be easily located in a trace file and debugged. This program can also be run as a benchmark to allow easier automated performance monitoring; by default the benchmark doesn't report worst case times because those are too noisy. Updates golang/go#27732. Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues.
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
-OR-
runs as a go benchmark:
go test -bench=B -count=2 .
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
pkg: golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-1038NG7 CPU @ 2.00GHz
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=false-8 1 3746777895 ns/op 564.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1266 p29-ns 21452 p39-ns 40774 p49-ns 122054 p59-ns 4629961 p69-ns 5152588 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=false-8 1 3960773922 ns/op 607.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1386 p29-ns 30254 p39-ns 48302 p49-ns 117086 p59-ns 6043114 p69-ns 8353592 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=false-8 1 3832759983 ns/op 582.0 avg-ns 411.0 median-ns 1519 p29-ns 26273 p39-ns 47897 p49-ns 114378 p59-ns 216399 p69-ns 484183 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=false-8 1 4079520582 ns/op 618.0 avg-ns 417.0 median-ns 2263 p29-ns 29662 p39-ns 60282 p49-ns 147765 p59-ns 344228 p69-ns 638498 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=false-8 1 3688413511 ns/op 562.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1351 p29-ns 28113 p39-ns 40730 p49-ns 104352 p59-ns 202013 p69-ns 468936 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=false-8 1 3590957128 ns/op 544.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1397 p29-ns 25142 p39-ns 40059 p49-ns 101923 p59-ns 431897 p69-ns 658914 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=true-8 1 3645081827 ns/op 552.0 avg-ns 408.0 median-ns 1387 p29-ns 14013 p39-ns 39086 p49-ns 81027 p59-ns 5174202 p69-ns 5994034 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=stack-fluff=true-8 1 3761717212 ns/op 573.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1648 p29-ns 20665 p39-ns 39151 p49-ns 92594 p59-ns 5747097 p69-ns 6512030 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=true-8 1 3686269094 ns/op 559.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1441 p29-ns 14351 p39-ns 39182 p49-ns 96212 p59-ns 334248 p69-ns 1308733 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=heap-fluff=true-8 1 3642812482 ns/op 549.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1363 p29-ns 14274 p39-ns 38962 p49-ns 97677 p59-ns 267289 p69-ns 662851 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=true-8 1 3618725949 ns/op 549.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1369 p29-ns 13421 p39-ns 39061 p49-ns 103189 p59-ns 227176 p69-ns 541692 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency/how=global-fluff=true-8 1 3634821717 ns/op 550.0 avg-ns 408.0 median-ns 1350 p29-ns 15195 p39-ns 39664 p49-ns 90323 p59-ns 529328 p69-ns 590649 worst-ns
PASS
ok golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency 55.136s
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6
…ncy issues
When run with -bench, emits latency measurements in benchmark
format. Includes -trace option for debugging latency issues
(omit -bench for location of worst delay).
go run . -help
Usage of /<yuck>/gc_latency:
-bench
output in Go benchmark format
-fluff
insert 'fluff' into allocation runs to break up sweeps
-how string
how the buffer is allocated = {stack,heap,global} (default "stack")
-trace string
name of trace file to create
-OR-
runs as a go benchmark:
go test -bench=B -count=10 . -- -fluff -how=stack
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
pkg: golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-1038NG7 CPU @ 2.00GHz
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 3722432744 ns/op 560.0 avg-ns 400.0 median-ns 1461 p29-ns 25774 p39-ns 38630 p49-ns 110696 p59-ns 4753393 p69-ns 5538766 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4067024228 ns/op 622.0 avg-ns 407.0 median-ns 1648 p29-ns 29543 p39-ns 49744 p49-ns 122664 p59-ns 6239471 p69-ns 6593770 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 5113548640 ns/op 670.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 2028 p29-ns 28188 p39-ns 66678 p49-ns 1448743 p59-ns 7695377 p69-ns 12281974 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 3975527414 ns/op 606.0 avg-ns 406.0 median-ns 1578 p29-ns 28443 p39-ns 43476 p49-ns 113114 p59-ns 6413033 p69-ns 7211445 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4174308310 ns/op 633.0 avg-ns 409.0 median-ns 1720 p29-ns 29063 p39-ns 54298 p49-ns 373535 p59-ns 6489633 p69-ns 8041030 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 3980984757 ns/op 609.0 avg-ns 406.0 median-ns 1555 p29-ns 28855 p39-ns 45865 p49-ns 120082 p59-ns 6046351 p69-ns 6346751 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4138732421 ns/op 601.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1550 p29-ns 27874 p39-ns 40879 p49-ns 155143 p59-ns 5705793 p69-ns 8028793 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 5552645990 ns/op 849.0 avg-ns 411.0 median-ns 1962 p29-ns 29602 p39-ns 185457 p49-ns 6228738 p59-ns 19579494 p69-ns 43328862 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4339053770 ns/op 637.0 avg-ns 405.0 median-ns 1674 p29-ns 27410 p39-ns 50768 p49-ns 505246 p59-ns 6891708 p69-ns 88489177 worst-ns
BenchmarkGCLatency-8 1 4715056872 ns/op 719.0 avg-ns 410.0 median-ns 1827 p29-ns 28776 p39-ns 70652 p49-ns 3236747 p59-ns 14152105 p69-ns 20386545 worst-ns
PASS
ok golang.org/x/benchmarks/gc_latency 52.349s
as a fake main package benchmark:
go run . -bench
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkAverageLatency 1 574ns
BenchmarkMedianLatency 1 412ns
Benchmark99Latency 1 1791ns
Benchmark999Latency 1 25843ns
Benchmark9999Latency 1 35585ns
Benchmark99999Latency 1 109314ns
BenchmarkWorstLatency 1 6169500ns
Updates golang/go#27732.
Change-Id: I19b9060f24cda1547b8d75f762316dd5271e32c6



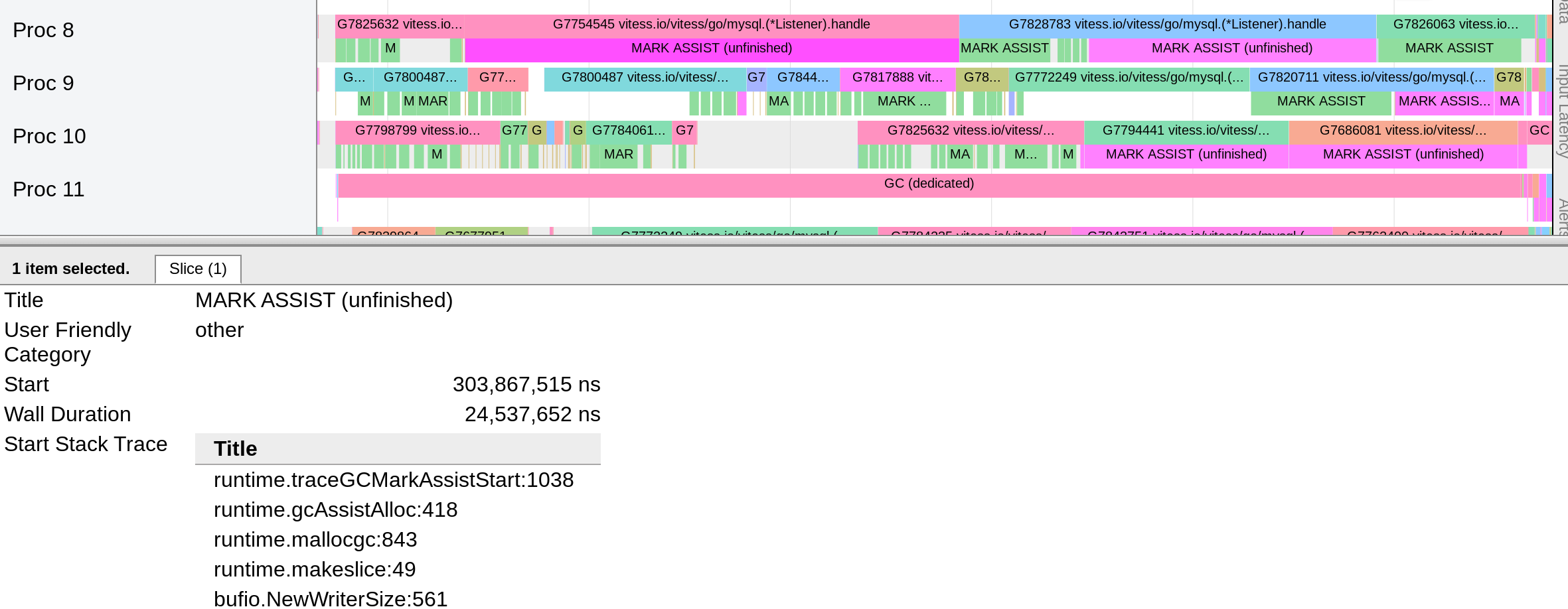
Please answer these questions before submitting your issue. Thanks!
What version of Go are you using (
go version)?1.11
Does this issue reproduce with the latest release?
Yes
What operating system and processor architecture are you using (
go env)?OSX (also observed on Linux), both AMD64.
What did you do?
This singlethreaded microbenchmark measures GC latency to allocate a byte slice and store it in a big circular buffer, repeating the operation 5 times the size of the big circular buffer (i.e. one initialization and four reuses). Live memory is about 210MB, in the form of the circular buffer
(200,000 slice elements) and 200,000 pointer-free buffers of size 1k.
This version of the benchmark is instrumented to collect a trace, because that's how we figured out that it was mark assist.
The original benchmark source is https://github.com/WillSewell/gc-latency-experiment, adapted here to be more instrumented and more plain-spoken about what it is doing.
What did you expect to see?
I expected to see a sub-millisecond worst-case latency; the average time without GC to initialize a new slice is less about a microsecond (on a 2017 Mac laptop).
What did you see instead?
Worst-case latencies on the order of 4-10ms.
I'v attached the trace file for the following run:
The worst case latency ends at 995ms, corresponding to a single 5ms mark assist.
A zoom of the trace displaying this is also attached.
trace2.out.gz
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: