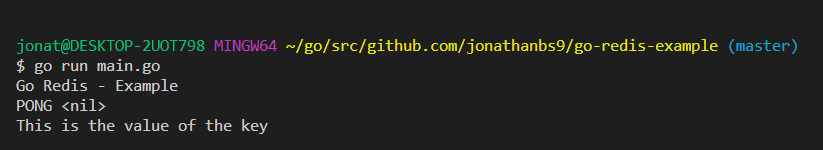
We took a look at the basics of working with Redis in Go. We looked at how we can connect to Redis databases using the github.com/go-redis/redis package and we looked at how you can interact with that database using some of the methods that the package provides for us. (ping and pong as an example)
Redis is a fantastic open-source in-memory data structure store which can be used for various purposes such a database for your app, or a caching service or even a message broker.
It supports a wide variety of different data structures and is incredibly versatile and fast. If you are concerned with things like resiliency then you’ll be pleased to hear that it has built-in replication and can be run in a cluster setup to ensure that your applications are not reliant on a single instance.
For the purpose of this example, we are going to be keeping it nice and simple with a single, locally running instance of redis which we’ll be running with Docker.
1 - ✔️ It’s super fast. Faster than any other cashing out there.
2 - ✔️ Due to easy setup, Redis is Simple and easy to use.
3 - ✔️ Redis has flexible data structures, it supports almost all data structures.
4 - ✔️ Redis allows storing key and value pairs as large as 512 MB.
5 - ✔️ Redis uses its own hashing mechanism called Redis Hashing.
6 - ✔️ Zero downtime or performance impact while scaling up or down.
7 - ✔️ It is open source and stable
Once we have docker installed.
docker run --name redisdb -p 6379:6379 redis
docker exec -it redisdb redis-cli
1- Clone the repo
2- Run file
go run main.go