Live Demo: https://hackathon-starter.walcony.com
Jump to What's new?
A boilerplate for Node.js web applications.
If you have attended any hackathons in the past, then you know how much time it takes to get a project started: decide on what to build, pick a programming language, pick a web framework, pick a CSS framework. A while later, you might have an initial project up on GitHub and only then can other team members start contributing. Or how about doing something as simple as Sign in with Facebook authentication? You can spend hours on it if you are not familiar with how OAuth 2.0 works.
When I started this project, my primary focus was on simplicity and ease of use. I also tried to make it as generic and reusable as possible to cover most use cases of hackathon web apps, without being too specific. In the worst case, you can use this as a learning guide for your projects, if for example you are only interested in Sign in with Google authentication and nothing else.
“Nice! That README alone is already gold!”
— Adrian Le Bas
“Awesome. Simply awesome.”
— Steven Rueter
“I'm using it for a year now and many projects, it's an awesome boilerplate and the project is well maintained!”
— Kevin Granger
“Small world with Sahat's project. We were using his hackathon starter for our hackathon this past weekend and got some prizes. Really handy repo!”
— Interview candidate for one of the companies I used to work with.
- Features
- Prerequisites
- Getting Started
- Obtaining API Keys
- Project Structure
- List of Packages
- Useful Tools and Resources
- Recommended Design Resources
- Recommended Node.js Libraries
- Recommended Client-side Libraries
- Pro Tips
- FAQ
- How It Works
- Cheatsheets
- Deployment
- Docker
- Production
- Changelog
- Contributing
- License
- Local Authentication using Email and Password
- OAuth 1.0a Authentication via Twitter
- OAuth 2.0 Authentication via Facebook, Google, GitHub, LinkedIn, Instagram
- Flash notifications
- MVC Project Structure
- Node.js clusters support
- Sass stylesheets (auto-compiled via middleware)
- Bootstrap 4 + Extra Themes
- Contact Form (powered by Mailgun, Sendgrid or Mandrill)
- Account Management
- Gravatar
- Profile Details
- Change Password
- Forgot Password
- Reset Password
- Link multiple OAuth strategies to one account
- Delete Account
- CSRF protection
- API Examples: Facebook, Foursquare, Last.fm, Tumblr, Twitter, Stripe, LinkedIn and more.
- MongoDB
- Node.js 8.0+
- Command Line Tools
Mac OS X: Xcode (or OS X 10.9+:
xcode-select --install)Windows: Visual Studio OR Visual Studio Code + Windows Subsystem for Linux - Ubuntu
Ubuntu /
Linux Mint:
sudo apt-get install build-essentialFedora:
sudo dnf groupinstall "Development Tools"OpenSUSE:
sudo zypper install --type pattern devel_basis
Note: If you are new to Node or Express, I recommend to watch Node.js and Express 101 screencast by Alex Ford that teaches Node and Express from scratch. Alternatively, here is another great tutorial for complete beginners - Getting Started With Node.js, Express, MongoDB.
The easiest way to get started is to clone the repository:
# Get the latest snapshot
git clone https://github.com/sahat/hackathon-starter.git myproject
# Change directory
cd myproject
# Install NPM dependencies
npm install
# Then simply start your app
node app.jsWarning: If you want to use some API that need https to work (for example Pinterest or facebook), you will need to download ngrok. You must start ngrok after starting the project.
# start ngrok to intercept the data exchanged on port 8080
./ngrok http 8080Next, you must use the https URL defined by ngrok, for example, https://hackaton.ngrok.io
Note: I highly recommend installing Nodemon.
It watches for any changes in your node.js app and automatically restarts the
server. Once installed, instead of node app.js use nodemon app.js. It will
save you a lot of time in the long run, because you won't need to manually
restart the server each time you make a small change in code. To install, run
sudo npm install -g nodemon.
To use any of the included APIs or OAuth authentication methods, you will need to obtain appropriate credentials: Client ID, Client Secret, API Key, or Username & Password. You will need to go through each provider to generate new credentials.
Hackathon Starter 2.0 Update: I have included dummy keys and passwords for all API examples to get you up and running even faster. But don't forget to update them with your credentials when you are ready to deploy an app.
- Visit Google Cloud Console
- Click on the Create Project button
- Enter Project Name, then click on Create button
- Then click on APIs & auth in the sidebar and select API tab
- Click on Google+ API under Social APIs, then click Enable API
- Next, under APIs & auth in the sidebar click on Credentials tab
- Click on Create new Client ID button
- Select Web Application and click on Configure Consent Screen
- Fill out the required fields then click on Save
- In the Create Client ID modal dialog:
- Application Type: Web Application
- Authorized Javascript origins: http://localhost:8080
- Authorized redirect URI: http://localhost:8080/auth/google/callback
- Click on Create Client ID button
- Copy and paste Client ID and Client secret keys into
.env
Note: When you ready to deploy to production don't forget to
add your new URL to Authorized Javascript origins and Authorized redirect URI,
e.g. http://my-awesome-app.herokuapp.com and
http://my-awesome-app.herokuapp.com/auth/google/callback respectively.
The same goes for other providers.
- Visit Snap Kit Developer Portal
- Click on the + button to create an app
- Enter a name for your app
- Enable the scopes that you will want to use in your app
- Click on the Continue button
- Find the Kits section and make sure that Login Kit is enabled
- Find the Redirect URLs section, click the + Add button, and enter
http://localhost:8080/auth/snapchat/callback - Find the Development Environment section. Click the Generate button next to the Confidential OAuth2 Client heading within it.
- Copy and paste the generated Private Key and OAuth2 Client ID keys into
.env - Note: OAuth2 Client ID is SNAPCHAT_ID, Private Key is SNAPCHAT_SECRET in
.env - To prepare the app for submission, fill out the rest of the required fields: Category, Description, Privacy Policy Url, and App Icon
Note: For production use, don't forget to:
- generate a Confidential OAuth2 Client in the Production Environment and use the production Private Key and OAuth2 Client ID
- add the production URL to Redirect URLs section, e.g.
http://my-awesome-app.herokuapp.com/auth/snapchat/callback - submit the app for review and wait for approval
- Visit Facebook Developers
- Click My Apps, then select *Add a New App from the dropdown menu
- Enter a new name for your app
- Click on the Create App ID button
- Find the Facebook Login Product and click on Facebook Login
- Instead of going through their Quickstart, click on Settings for your app in the top left corner
- Copy and paste App ID and App Secret keys into
.env - Note: App ID is FACEBOOK_ID, App Secret is FACEBOOK_SECRET in
.env - Enter
localhostunder App Domains - Choose a Category that best describes your app
- Click on + Add Platform and select Website
- Enter
http://localhost:8080under Site URL - Click on the Settings tab in the left nav under Facebook Login
- Enter
http://localhost:8080/auth/facebook/callbackunder Valid OAuth redirect URIs
Note: After a successful sign in with Facebook, a user will be redirected back to the home page with appended hash #_=_ in the URL. It is not a bug. See this Stack Overflow discussion for ways to handle it.
- Go to Account Settings
- Select Developer settings from the sidebar
- Then inside click on Register new application
- Enter Application Name and Homepage URL
- For Authorization Callback URL: http://localhost:8080/auth/github/callback
- Click Register application
- Now copy and paste Client ID and Client Secret keys into
.envfile
- Sign in at https://apps.twitter.com
- Click Create a new application
- Enter your application name, website and description
- For Callback URL: http://127.0.0.1:8080/auth/twitter/callback
- Go to Settings tab
- Under Application Type select Read and Write access
- Check the box Allow this application to be used to Sign in with Twitter
- Click Update this Twitter's applications settings
- Copy and paste Consumer Key and Consumer Secret keys into
.envfile
- Sign in at LinkedIn Developer Network
- From the account name dropdown menu select API Keys
- It may ask you to sign in once again
- Click + Add New Application button
- Fill out all the required fields
- OAuth 2.0 Redirect URLs: http://localhost:8080/auth/linkedin/callback
- JavaScript API Domains: http://localhost:8080
- For Default Application Permissions make sure at least the following is checked:
r_basicprofile- Finish by clicking Add Application button
- Copy and paste API Key and Secret Key keys into
.envfile - API Key is your clientID
- Secret Key is your clientSecret
- Sign up or log into your dashboard
- Click on your profile and click on Account Settings
- Then click on API Keys
- Copy the Secret Key. and add this into
.envfile
- Visit PayPal Developer
- Log in to your PayPal account
- Click Applications > Create App in the navigation bar
- Enter Application Name, then click Create app
- Copy and paste Client ID and Secret keys into
.envfile - App ID is client_id, App Secret is client_secret
- Change host to api.paypal.com if you want to test against production and use the live credentials
- Go to Foursquare for Developers
- Click on My Apps in the top menu
- Click the Create A New App button
- Enter App Name, Welcome page url,
- For Redirect URI: http://localhost:8080/auth/foursquare/callback
- Click Save Changes
- Copy and paste Client ID and Client Secret keys into
.envfile
- Go to http://www.tumblr.com/oauth/apps
- Once signed in, click +Register application
- Fill in all the details
- For Default Callback URL:
http://localhost:8080/auth/tumblr/callback - Click ✔Register
- Copy and paste OAuth consumer key and OAuth consumer secret keys into
.envfile
- Go to http://steamcommunity.com/dev/apikey
- Sign in with your existing Steam account
- Enter your Domain Name, then and click Register
- Copy and paste Key into
.envfile
- Go to https://sendgrid.com/user/signup
- Sign up and confirm your account via the activation email
- Then enter your SendGrid Username and Password into
.envfile
- Go to http://www.mailgun.com
- Sign up and add your Domain Name
- From the domain overview, copy and paste the default SMTP Login and Password into
.envfile
- Go to https://www.twilio.com/try-twilio
- Sign up for an account.
- Once logged into the dashboard, expand the link 'show api credentials'
- Copy your Account Sid and Auth Token
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| config/passport.js | Passport Local and OAuth strategies, plus login middleware. |
| controllers/api.js | Controller for /api route and all api examples. |
| controllers/contact.js | Controller for contact form. |
| controllers/home.js | Controller for home page (index). |
| controllers/user.js | Controller for user account management. |
| models/User.js | Mongoose schema and model for User. |
| public/ | Static assets (fonts, css, js, img). |
| public/js/application.js | Specify client-side JavaScript dependencies. |
| public/js/main.js | Place your client-side JavaScript here. |
| public/css/main.scss | Main stylesheet for your app. |
| public/css/themes/default.scss | Some Bootstrap overrides to make it look prettier. |
| views/account/ | Templates for login, password reset, signup, profile. |
| views/api/ | Templates for API Examples. |
| views/partials/flash.pug | Error, info and success flash notifications. |
| views/partials/header.pug | Navbar partial template. |
| views/partials/footer.pug | Footer partial template. |
| views/layout.pug | Base template. |
| views/home.pug | Home page template. |
| .dockerignore | Folder and files ignored by docker usage. |
| .env.example | Your API keys, tokens, passwords and database URI. |
| .eslintrc | Rules for eslint linter. |
| .gitignore | Folder and files ignored by git. |
| .travis.yml | Configuration files for continue integration. |
| app.js | The main application file. |
| docker-compose.yml | Docker compose configuration file. |
| Dockerfile | Docker configuration file. |
| package.json | NPM dependencies. |
| package-lock.json | Contains exact versions of NPM dependencies in package.json. |
Note: There is no preference how you name or structure your views.
You could place all your templates in a top-level views directory without
having a nested folder structure, if that makes things easier for you.
Just don't forget to update extends ../layout and corresponding
res.render() paths in controllers.
| Package | Description |
|---|---|
| @octokit/rest | GitHub API library. |
| bcrypt | Library for hashing and salting user passwords. |
| body-parser | Node.js body parsing middleware. |
| chai | BDD/TDD assertion library. |
| chalk | Terminal string styling done right. |
| cheerio | Scrape web pages using jQuery-style syntax. |
| clockwork | Clockwork SMS API library. |
| compression | Node.js compression middleware. |
| connect-mongo | MongoDB session store for Express. |
| dotenv | Loads environment variables from .env file. |
| errorhandler | Development-only error handler middleware. |
| eslint | Linter JavaScript. |
| eslint-config-airbnb-base | Configuration eslint by airbnb. |
| eslint-plugin-chai-friendly | Makes eslint friendly towards Chai.js 'expect' and 'should' statements. |
| eslint-plugin-import | ESLint plugin with rules that help validate proper imports. |
| express | Node.js web framework. |
| express-flash | Provides flash messages for Express. |
| express-session | Simple session middleware for Express. |
| express-status-monitor | Reports real-time server metrics for Express. |
| express-validator | Easy form validation for Express. |
| fbgraph | Facebook Graph API library. |
| instagram-node | Instagram API library. |
| lastfm | Last.fm API library. |
| lob | Lob API library. |
| lodash | A utility library for working with arrays, numbers, objects, strings. |
| lusca | CSRF middleware. |
| mocha | Test framework. |
| mongoose | MongoDB ODM. |
| morgan | HTTP request logger middleware for node.js. |
| multer | Node.js middleware for handling multipart/form-data. |
| node-foursquare | Foursquare API library. |
| node-linkedin | LinkedIn API library. |
| node-sass | Node.js bindings to libsass. |
| node-sass-middleware | Sass middleware compiler. |
| nyc | Coverage test. |
| nodemailer | Node.js library for sending emails. |
| passport | Simple and elegant authentication library for node.js. |
| passport-facebook | Sign-in with Facebook plugin. |
| passport-github | Sign-in with GitHub plugin. |
| passport-google-oauth | Sign-in with Google plugin. |
| passport-instagram | Sign-in with Instagram plugin. |
| passport-linkedin-oauth2 | Sign-in with LinkedIn plugin. |
| passport-local | Sign-in with Username and Password plugin. |
| passport-openid | Sign-in with OpenId plugin. |
| passport-oauth | Allows you to set up your own OAuth 1.0a and OAuth 2.0 strategies. |
| passport-snapchat | Sign-in with Snapchat plugin. |
| passport-twitter | Sign-in with Twitter plugin. |
| paypal-rest-sdk | PayPal APIs library. |
| pug (jade) | Template engine for Express. |
| request | Simplified HTTP request library. |
| sinon | Test spies, stubs and mocks for JavaScript. |
| sinon-mongoose | Extend Sinon stubs for Mongoose methods to test chained methods easily. |
| stripe | Offical Stripe API library. |
| supertest | HTTP assertion library. |
| tumblr.js | Tumblr API library. |
| twilio | Twilio API library. |
| twit | Twitter API library. |
| validator | Used in conjunction with express-validator in controllers/api.js. |
- JavaScripting - The Database of JavaScript Libraries
- JS Recipes - JavaScript tutorials for backend and frontend development.
- HTML to Pug converter - HTML to PUG is a free online converter helping you to convert HTML files to pug syntax in real-time.
- JavascriptOO - A directory of JavaScript libraries with examples, CDN links, statistics, and videos.
- Favicon Generator - Generate favicons for PC, Android, iOS, Windows 8.
- Code Guide - Standards for developing flexible, durable, and sustainable HTML and CSS.
- Bootsnipp - Code snippets for Bootstrap.
- Bootstrap Zero - Free Bootstrap templates themes.
- Google Bootstrap - Google-styled theme for Bootstrap.
- Font Awesome Icons - It's already part of the Hackathon Starter, so use this page as a reference.
- Colors - A nicer color palette for the web.
- Creative Button Styles - awesome button styles.
- Creative Link Effects - Beautiful link effects in CSS.
- Medium Scroll Effect - Fade in/out header background image as you scroll.
- GeoPattern - SVG background pattern generator.
- Trianglify - SVG low-poly background pattern generator.
- Nodemon - Automatically restart Node.js server on code changes.
- geoip-lite - Geolocation coordinates from IP address.
- Filesize.js - Pretty file sizes, e.g.
filesize(265318); // "265.32 kB". - Numeral.js - Library for formatting and manipulating numbers.
- Node Inspector - Node.js debugger based on Chrome Developer Tools.
- node-taglib - Library for reading the meta-data of several popular audio formats.
- sharp - Node.js module for resizing JPEG, PNG, WebP and TIFF images.
- Framework7 - Full Featured HTML Framework For Building iOS7 Apps.
- InstantClick - Makes your pages load instantly by pre-loading them on mouse hover.
- NProgress.js - Slim progress bars like on YouTube and Medium.
- Hover - Awesome CSS3 animations on mouse hover.
- Magnific Popup - Responsive jQuery Lightbox Plugin.
- jQuery Raty - Star Rating Plugin.
- Headroom.js - Hide your header until you need it.
- X-editable - Edit form elements inline.
- Offline.js - Detect when user's internet connection goes offline.
- Alertify.js - Sweet looking alerts and browser dialogs.
- selectize.js - Styleable select elements and input tags.
- drop.js - Powerful Javascript and CSS library for creating dropdowns and other floating displays.
- scrollReveal.js - Declarative on-scroll reveal animations.
- When installing an NPM package, add a --save flag, and it will be automatically
added to
package.jsonas well. For example,npm install --save moment. - Use async.parallel() when you need to run multiple asynchronous tasks, and then render a page, but only when all tasks are completed. For example, you might want to scrape three different websites for some data and render the results in a template after all three websites have been scraped.
- Need to find a specific object inside an Array? Use _.find
function from Lodash. For example, this is how you would retrieve a
Twitter token from database:
var token = _.find(req.user.tokens, { kind: 'twitter' });, where 1st parameter is an array, and a 2nd parameter is an object to search for.
You need to add the following hidden input element to your form. This has been added in the pull request #40 as part of the CSRF protection.
input(type='hidden', name='_csrf', value=_csrf)
Note: It is now possible to whitelist certain URLs. In other words you can specify a list of routes that should bypass CSRF verification check.
Note 2: To whitelist dynamic URLs use regular expression tests inside the
CSRF middleware to see if req.originalUrl matches your desired pattern.
That's a custom error message defined in app.js to indicate that there was a
problem connecting to MongoDB:
mongoose.connection.on('error', (err) => {
console.error(err);
console.log('%s MongoDB connection error. Please make sure MongoDB is running.', chalk.red('✗'));
process.exit();
});You need to have a MongoDB server running before launching app.js. You can
download MongoDB here, or install it via a package manager.
Windows users, read Install MongoDB on Windows.
Tip: If you are always connected to the internet, you could just use
MongoDB Atlas or Compose instead
of downloading and installing MongoDB locally. You will only need to update database credentials
in .env file.
Chances are you haven't changed the Database URI in .env. If MONGODB is
set to localhost, it will only work on your machine as long as MongoDB is
running. When you deploy to Heroku, OpenShift or some other provider, you will not have MongoDB
running on localhost. You need to create an account with MongoDB Atlas
or Compose, then create a free tier database.
See Deployment for more information on how to setup an account
and a new database step-by-step with MongoDB Atlas.
When I first started this project I didn't have any experience with Handlebars. Since then I have worked on Ember.js apps and got myself familiar with the Handlebars syntax. While it is true Handlebars is easier, because it looks like good old HTML, I have no regrets picking Jade over Handlebars. First off, it's the default template engine in Express, so someone who has built Express apps in the past already knows it. Secondly, I find extends and block to be indispensable, which as far as I know, Handlebars does not have out of the box. And lastly, subjectively speaking, Jade looks much cleaner and shorter than Handlebars, or any non-HAML style for that matter.
For the sake of simplicity. While there might be a better approach,
such as passing app context to each controller as outlined in this
blog,
I find such style to be confusing for beginners.
It took me a long time to grasp the concept of exports and module.exports,
let alone having a global app reference in other files.
That to me is backward thinking.
The app.js is the "heart of the app", it should be the one referencing
models, routes, controllers, etc.
When working solo on small projects, I prefer to have everything inside app.js as is the case with this
REST API server.
Inside the nodemailer.createTransport method arguments, change the service from 'Sendgrid' to some other email service. Also, be sure to update both username and password below that. See the list of all supported services by Nodemailer.
This section is intended for giving you a detailed explanation of how a particular functionality works. Maybe you are just curious about how it works, or perhaps you are lost and confused while reading the code, I hope it provides some guidance to you.
HTML5 UP has many beautiful templates that you can download for free.
When you download the ZIP file, it will come with index.html, images, css and js folders. So, how do you integrate it with Hackathon Starter? Hackathon Starter uses Bootstrap CSS framework, but these templates do not. Trying to use both CSS files at the same time will likely result in undesired effects.
Note: Using the custom templates approach, you should understand that you cannot reuse any of the views I have created: layout, home page, api browser, login, signup, account management, contact. Those views were built using Bootstrap grid and styles. You will have to manually update the grid using a different syntax provided in the template. Having said that, you can mix and match if you want to do so: Use Bootstrap for main app interface, and a custom template for a landing page.
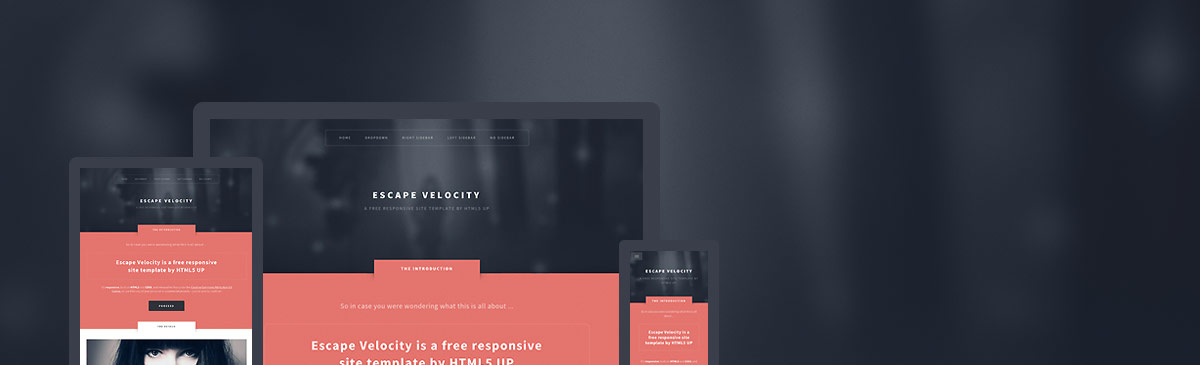
Let's start from the beginning. For this example I will use Escape Velocity template:
Note: For the sake of simplicity I will only consider index.html, and skip left-sidebar.html,
no-sidebar.html, right-sidebar.html.
Move all JavaScript files from html5up-escape-velocity/js to public/js. Then move all CSS files from html5up-escape-velocity/css to public/css. And finally, move all images from html5up-escape-velocity/images to public/images. You could move it to the existing img folder, but that would require manually changing every img reference. Grab the contents of index.html and paste it into HTML To Pug.
Note: Do not forget to update all the CSS and JS paths accordingly.
Create a new file escape-velocity.pug and paste the Pug markup in views folder.
Whenever you see the code res.render('account/login') - that means it will search for views/account/login.pug file.
Let's see how it looks. Create a new controller escapeVelocity inside controllers/home.js:
exports.escapeVelocity = (req, res) => {
res.render('escape-velocity', {
title: 'Landing Page'
});
};And then create a route in app.js. I placed it right after the index controller:
app.get('/escape-velocity', homeController.escapeVelocity);Restart the server (if you are not using nodemon); then you should see the new template at http://localhost:8080/escape-velocity.
I will stop right here, but if you would like to use this template as more than just a single page, take a look at how these Pug templates work: layout.pug - base template, index.pug - home page, partials/header.pug - Bootstrap navbar, partials/footer.pug - sticky footer. You will have to manually break it apart into smaller pieces. Figure out which part of the template you want to keep the same on all pages - that's your new layout.pug.
Then, each page that changes, be it index.pug, about.pug, contact.pug
will be embedded in your new layout.pug via block content. Use existing templates as a reference.
This is a rather lengthy process, and templates you get from elsewhere might have yet another grid system. That's why I chose Bootstrap for the Hackathon Starter. Many people are already familiar with Bootstrap, plus it's easy to get started with it if you have never used Bootstrap. You can also buy many beautifully designed Bootstrap themes at Themeforest, and use them as a drop-in replacement for Hackathon Starter. However, if you would like to go with a completely custom HTML/CSS design, this should help you to get started!
Flash messages allow you to display a message at the end of the request and access
it on next request and only next request. For instance, on a failed login attempt, you would
display an alert with some error message, but as soon as you refresh that page or visit a different
page and come back to the login page, that error message will be gone. It is only displayed once.
This project uses express-flash module for flash messages. And that
module is built on top of connect-flash, which is what I used in
this project initially. With express-flash you don't have to
explicitly send a flash message to every view inside res.render().
All flash messages are available in your views via messages object by default,
thanks to express-flash.
Flash messages have a two-step process. You use req.flash('errors', { msg: 'Error messages goes here' }
to create a flash message in your controllers, and then display them in your views:
if messages.errors
.alert.alert-danger.fade.in
for error in messages.errors
div= error.msgIn the first step, 'errors' is the name of a flash message, which should match the
name of the property on messages object in your views. You place alert messages
inside if message.errors because you don't want to show them flash messages are present.
The reason why you pass an error like { msg: 'Error message goes here' } instead
of just a string - 'Error message goes here', is for the sake of consistency.
To clarify that, express-validator module which is used for validating and sanitizing user's input,
returns all errors as an array of objects, where each object has a msg property with a message why an error has occurred. Here is a more general example of what express-validator returns when there are errors present:
[
{ param: "name", msg: "Name is required", value: "<received input>" },
{ param: "email", msg: "A valid email is required", value: "<received input>" }
]To keep consistent with that style, you should pass all flash messages
as { msg: 'My flash message' } instead of a string. Otherwise, you will see an alert box
without an error message. That is because in partials/flash.pug template it will try to output
error.msg (i.e. "My flash message".msg), in other words, it will try to call a msg method on a String object,
which will return undefined. Everything I just mentioned about errors, also applies
to "info" and "success" flash messages, and you could even create a new one yourself, such as:
Data Usage Controller (Example)
req.flash('warning', { msg: 'You have exceeded 90% of your data usage' });
User Account Page (Example)
if messages.warning
.alert.alert-warning.fade.in
for warning in messages.warning
div= warning.msgpartials/flash.pug is a partial template that contains how flash messages
are formatted. Previously, flash
messages were scattered throughout each view that used flash messages
(contact, login, signup, profile), but now, thankfully it uses a DRY approach.
The flash messages partial template is included in the layout.pug, along with footer and navigation.
body
include partials/header
.container
include partials/flash
block content
include partials/footerIf you have any further questions about flash messages, please feel free to open an issue, and I will update this mini-guide accordingly, or send a pull request if you would like to include something that I missed.
A more correct way to say this would be "How do I create a new route?" The main file app.js contains all the routes.
Each route has a callback function associated with it. Sometimes you will see three or more arguments for a route. In a case like that, the first argument is still a URL string, while middle arguments
are what's called middleware. Think of middleware as a door. If this door prevents you from
continuing forward, you won't get to your callback function. One such example is a route that requires authentication.
app.get('/account', passportConfig.isAuthenticated, userController.getAccount);It always goes from left to right. A user visits /account page. Then isAuthenticated middleware checks if you are authenticated:
exports.isAuthenticated = (req, res, next) => {
if (req.isAuthenticated()) {
return next();
}
res.redirect('/login');
};If you are authenticated, you let this visitor pass through your "door" by calling return next();. It then proceeds to the
next middleware until it reaches the last argument, which is a callback function that typically renders a template on GET requests or redirects on POST requests. In this case, if you are authenticated, you will be redirected to the Account Management page; otherwise, you will be redirected to the Login page.
exports.getAccount = (req, res) => {
res.render('account/profile', {
title: 'Account Management'
});
};Express.js has app.get, app.post, app.put, app.delete, but for the most part, you will only use the first two HTTP verbs, unless you are building a RESTful API.
If you just want to display a page, then use GET, if you are submitting a form, sending a file then use POST.
Here is a typical workflow for adding new routes to your application. Let's say we are building a page that lists all books from the database.
Step 1. Start by defining a route.
app.get('/books', bookController.getBooks);Note: As of Express 4.x you can define your routes like so:
app.route('/books')
.get(bookController.getBooks)
.post(bookController.createBooks)
.put(bookController.updateBooks)
.delete(bookController.deleteBooks)And here is how a route would look if it required an authentication and an authorization middleware:
app.route('/api/twitter')
.all(passportConfig.isAuthenticated)
.all(passportConfig.isAuthorized)
.get(apiController.getTwitter)
.post(apiController.postTwitter)Use whichever style that makes sense to you. Either one is acceptable. I think that chaining HTTP verbs on app.route is a very clean and elegant approach, but on the other hand, I can no longer see all my routes at a glance when you have one route per line.
Step 2. Create a new schema and a model Book.js inside the models directory.
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const bookSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String
});
const Book = mongoose.model('Book', bookSchema);
module.exports = Book;Step 3. Create a new controller file called book.js inside the controllers directory.
/**
* GET /books
* List all books.
*/
const Book = require('../models/Book.js');
exports.getBooks = (req, res) => {
Book.find((err, docs) => {
res.render('books', { books: docs });
});
};Step 4. Import that controller in app.js.
const bookController = require('./controllers/book');Step 5. Create books.pug template.
extends layout
block content
.page-header
h3 All Books
ul
for book in books
li= book.nameThat's it! I will say that you could have combined Step 1, 2, 3 as following:
app.get('/books',(req, res) => {
Book.find((err, docs) => {
res.render('books', { books: docs });
});
});Sure, it's simpler, but as soon as you pass 1000 lines of code in app.js it becomes a little challenging to navigate the file.
I mean, the whole point of this boilerplate project was to separate concerns, so you could
work with your teammates without running into MERGE CONFLICTS. Imagine you have four developers
working on a single app.js, I promise you it won't be fun resolving merge conflicts all the time.
If you are the only developer, then it's okay. But as I said, once it gets up to a certain LoC size, it becomes difficult to maintain everything in a single file.
That's all there is to it. Express.js is super simple to use. Most of the time you will be dealing with other APIs to do the real work: Mongoose for querying database, socket.io for sending and receiving messages over websockets, sending emails via Nodemailer, form validation using express-validator library, parsing websites using Cheerio, etc.
Dan Stroot submitted an excellent pull request that adds a real-time dashboard with socket.io. And as much as I'd like to add it to the project, I think it violates one of the main principles of the Hackathon Starter:
When I started this project, my primary focus was on simplicity and ease of use. I also tried to make it as generic and reusable as possible to cover most use cases of hackathon web apps, without being too specific.
When I need to use socket.io, I really need it, but most of the time - I don't. But more importantly, websockets support is still experimental on most hosting providers. As of October 2013, Heroku supports websockets, but not until you opt-in by running this command:
heroku labs:enable websockets -a myappAnd what if you are deploying to OpenShift? They do support websockets, but it is currently in a preview state. So, for OpenShift you would need to change the socket.io connect URI to the following:
const socket = io.connect('http://yoursite-namespace.rhcloud.com:8000');Wait, why is it on port 8000? Who knows, and if I didn't run across this blog post I wouldn't even know I had to use port 8000.
I am really glad that Heroku and OpenShift at least have a websockets support, because many other PaaS providers still do not support it. Due to the aforementioned issues with websockets, I cannot include socket.io as part of the Hackathon Starter. For now... If you need to use socket.io in your app, please continue reading.
First, you need to install socket.io:
npm install socket.io --saveReplace const app = express(); with the following code:
const app = express();
const server = require('http').Server(app);
const io = require('socket.io')(server);I like to have the following code organization in app.js (from top to bottom): module dependencies,
import controllers, import configs, connect to database, express configuration, routes,
start the server, socket.io stuff. That way I always know where to look for things.
Add the following code at the end of app.js:
io.on('connection', (socket) => {
socket.emit('greet', { hello: 'Hey there browser!' });
socket.on('respond', (data) => {
console.log(data);
});
socket.on('disconnect', () => {
console.log('Socket disconnected');
});
});One last thing left to change:
app.listen(app.get('port'), () => {to
server.listen(app.get('port'), () => {At this point, we are done with the back-end.
You now have a choice - to include your JavaScript code in Pug templates or have all your client-side
JavaScript in a separate file - in main.js. I admit, when I first started with Node.js and JavaScript in general,
I placed all JavaScript code inside templates because I have access to template variables passed in from Express
right then and there. It's the easiest thing you can do, but also the least efficient and harder to maintain. Since then I
almost never include inline JavaScript inside templates anymore.
But it's also understandable if you want to take the easier road. Most of the time you don't even care about performance during hackathons, you just want to "get shit done" before the time runs out. Well, either way, use whichever approach makes more sense to you. At the end of the day, it's what you build that matters, not how you build it.
If you want to stick all your JavaScript inside templates, then in layout.pug -
your main template file, add this to head block.
script(src='/socket.io/socket.io.js')
script.
let socket = io.connect(window.location.href);
socket.on('greet', function (data) {
console.log(data);
socket.emit('respond', { message: 'Hey there, server!' });
});Note: Notice the path of the socket.io.js, you don't actually
have to have socket.io.js file anywhere in your project; it will be generated
automatically at runtime.
If you want to have JavaScript code separate from templates, move that inline
script code into main.js, inside the $(document).ready() function:
$(document).ready(function() {
// Place JavaScript code here...
let socket = io.connect(window.location.href);
socket.on('greet', function (data) {
console.log(data);
socket.emit('respond', { message: 'Hello to you too, Mr.Server!' });
});
});Declares a read-only named constant.
const name = 'yourName';Declares a block scope local variable.
let index = 0;Using the `${}` syntax, strings can embed expressions.
const name = 'Oggy';
const age = 3;
console.log(`My cat is named ${name} and is ${age} years old.`);To import functions, objects or primitives exported from an external module. These are the most common types of importing.
const name = require('module-name');const { foo, bar } = require('module-name');To export functions, objects or primitives from a given file or module.
module.exports = { myFunction };module.exports.name = 'yourName';module.exports = myFunctionOrClass;The spread operator allows an expression to be expanded in places where multiple arguments (for function calls) or multiple elements (for array literals) are expected.
myFunction(...iterableObject);<ChildComponent {...this.props} />A Promise is used in asynchronous computations to represent an operation that hasn't completed yet, but is expected in the future.
var p = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) { });The catch() method returns a Promise and deals with rejected cases only.
p.catch(function(reason) { /* handle rejection */ });The then() method returns a Promise. It takes two arguments: callback for the success & failure cases.
p.then(function(value) { /* handle fulfillment */ }, function(reason) { /* handle rejection */ });The Promise.all(iterable) method returns a promise that resolves when all of the promises in the iterable argument have resolved or rejects with the reason of the first passed promise that rejects.
Promise.all([p1, p2, p3]).then(function(values) { console.log(values) });Arrow function expression. Shorter syntax & lexically binds the this value. Arrow functions are anonymous.
singleParam => { statements }() => { statements }(param1, param2) => expressionconst arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const squares = arr.map(x => x * x);The class declaration creates a new class using prototype-based inheritance.
class Person {
constructor(name, age, gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
}
incrementAge() {
this.age++;
}
}🎁 Credits: DuckDuckGo and @DrkSephy.
Math.floor(Date.now() / 1000);moment().unix();
var now = new Date();
now.setMinutes(now.getMinutes() + 30);moment().add(30, 'minutes');
// DD-MM-YYYY
var now = new Date();
var DD = now.getDate();
var MM = now.getMonth() + 1;
var YYYY = now.getFullYear();
if (DD < 10) {
DD = '0' + DD;
}
if (MM < 10) {
MM = '0' + MM;
}
console.log(MM + '-' + DD + '-' + YYYY); // 03-30-2016console.log(moment(new Date(), 'MM-DD-YYYY'));
// hh:mm (12 hour time with am/pm)
var now = new Date();
var hours = now.getHours();
var minutes = now.getMinutes();
var amPm = hours >= 12 ? 'pm' : 'am';
hours = hours % 12;
hours = hours ? hours : 12;
minutes = minutes < 10 ? '0' + minutes : minutes;
console.log(hours + ':' + minutes + ' ' + amPm); // 1:43 amconsole.log(moment(new Date(), 'hh:mm A'));
var today = new Date();
var nextWeek = new Date(today.getTime() + 7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000);moment().add(7, 'days');
var today = new Date();
var yesterday = date.setDate(date.getDate() - 1);moment().add(-1, 'days');
User.find((err, users) => {
console.log(users);
});let userEmail = 'example@gmail.com';
User.findOne({ email: userEmail }, (err, user) => {
console.log(user);
});User
.find()
.sort({ _id: -1 })
.limit(5)
.exec((err, users) => {
console.log(users);
});Let's suppose that each user has a votes field and you would like to count
the total number of votes in your database across all users. One very
inefficient way would be to loop through each document and manually accumulate
the count. Or you could use MongoDB Aggregation Framework instead:
User.aggregate({ $group: { _id: null, total: { $sum: '$votes' } } }, (err, votesCount) => {
console.log(votesCount.total);
});You will need docker and docker-compose installed to build the application.
After installing docker, start the application with the following commands :
# To build the project for the first time or when you add dependencies
docker-compose build web
# To start the application (or to restart after making changes to the source code)
docker-compose up web
To view the app, find your docker IP address + port 8080 ( this will typically be http://localhost:8080/ ). To use a port other than 8080, you would need to modify the port in app.js, Dockerfile, and docker-compose.yml.
Once you are ready to deploy your app, you will need to create an account with a cloud platform to host it. These are not the only choices, but they are my top picks. From my experience, the easiest way to get started is with Heroku. It will automatically restart your Node.js process when it crashes, has zero-downtime deployments and supports custom domains on free accounts. Additionally, you can create an account with MongoDB Atlas and then pick one of the 4 providers below. Again, there are plenty of other choices, and you are not limited to just the ones listed below.
- Download and install Heroku Toolbelt
- In a terminal, run
heroku loginand enter your Heroku credentials - From your app directory run
heroku create - Run
heroku addons:create mongolab. This will set up the mLab add-on and configure theMONGODB_URIenvironment variable in your Heroku app for you. - Lastly, do
git push heroku master. Done!
Note: To install Heroku add-ons your account must be verified.
- Go to https://www.mongodb.com/cloud/atlas
- Click the green Get started free button
- Fill in your information then hit Get started free
- You will be redirected to Create New Cluster page.
- Select a Cloud Provider and Region (such as AWS and a free tier region)
- Select cluster Tier to Free Shared Clusters
- Give Cluster a name (default: Cluster0)
- Click on green ⚡Create Cluster button
- Now, to access your database you need to create a DB user. To create a new MongoDB user, from the Clusters view, select the Security tab
- Under the MongoDB Users tab, click on +Add New User
- Fill in a username and password and give it either Atlas Admin User Privilege
- Next, you will need to create an IP address whitelist and obtain the connection URI. In the Clusters view, under the cluster details (i.e. SANDBOX - Cluster0), click on the CONNECT button.
- Under section (1) Check the IP Whitelist, click on ALLOW ACCESS FROM ANYWHERE. The form will add a field with
0.0.0.0/0. Click SAVE to save the0.0.0.0/0whitelist. - Under section (2) Choose a connection method, click on Connect Your Application
- In the new screen, select Node.js as Driver and version 2.2.12 or later. WARNING: Do not pick 3.0 or later since connect-mongo can't handle mongodb+srv:// connection strings.
- Finally, copy the URI connection string and replace the URI in MONGODB_URI of
.env.examplewith this URI string. Make sure to replace the with the db User password that you created under the Security tab. - Note that after some of the steps in the Atlas UI, you may see a banner stating
We are deploying your changes. You will need to wait for the deployment to finish before using the DB in your application.
Note: As an alternative to MongoDB Atlas, there is also Compose.
**NOTE** *These instructions might be out of date due to changes in OpenShift. Heroku is currently a good free alternative. If you the new process, please feel free to help us update this page*
- First, install this Ruby gem:
sudo gem install rhc💎 - Run
rhc loginand enter your OpenShift credentials - From your app directory run
rhc app create MyApp nodejs-0.10 - Note: MyApp is the name of your app (no spaces)
- Once that is done, you will be provided with URL, SSH and Git Remote links
- Visit provided URL, and you should see the Welcome to your Node.js application on OpenShift page
- Copy and paste Git Remote into
git remote add openshift YOUR_GIT_REMOTE - Before you push your app, you need to do a few modifications to your code
Add these two lines to app.js, just place them anywhere before app.listen():
var IP_ADDRESS = process.env.OPENSHIFT_NODEJS_IP || '127.0.0.1';
var PORT = process.env.OPENSHIFT_NODEJS_PORT || 8080;Then change app.listen() to:
app.listen(PORT, IP_ADDRESS,() => {
console.log(`Express server listening on port ${PORT} in ${app.settings.env} mode`);
});Add this to package.json, after name and version. This is necessary because, by default, OpenShift looks for server.js file. And by specifying supervisor app.js it will automatically restart the server when node.js process crashes.
"main": "app.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "supervisor app.js"
},- Finally, you can now push your code to OpenShift by running
git push -f openshift master - Note: The first time you run this command, you have to pass
-f(force) flag because OpenShift creates a dummy server with the welcome page when you create a new Node.js app. Passing-fflag will override everything with your Hackathon Starter project repository. Do not rungit pullas it will create unnecessary merge conflicts. - And you are done!
**NOTE** *Beyond the initial 12 month trial of Azure, the platform does not seem to offer a free tier for hosting NodeJS apps. If you are looking for a free tier service to host your app, Heroku might be a better choice at this point*
- Login to Windows Azure Management Portal
- Click the + NEW button on the bottom left of the portal
- Click COMPUTE, then WEB APP, then QUICK CREATE
- Enter a name for URL and select the datacenter REGION for your web site
- Click on CREATE WEB APP button
- Once the web site status changes to Running, click on the name of the web site to access the Dashboard
- At the bottom right of the Quickstart page, select Set up a deployment from source control
- Select Local Git repository from the list, and then click the arrow
- To enable Git publishing, Azure will ask you to create a user name and password
- Once the Git repository is ready, you will be presented with a GIT URL
- Inside your Hackathon Starter directory, run
git remote add azure [Azure Git URL] - To push your changes run
git push azure master - Note: You will be prompted for the password you created earlier
- On Deployments tab of your Windows Azure Web App, you will see the deployment history
NOTE At this point it appears that Bluemix's free tier to host NodeJS apps is limited to 30 days. If you are looking for a free tier service to host your app, Heroku might be a better choice at this point
-
Create a Bluemix Account
Sign up for Bluemix, or use an existing account.
-
Download and install the Cloud Foundry CLI to push your applications to Bluemix.
-
Create a
manifest.ymlfile in the root of your application.
applications:
- name: <your-app-name>
host: <your-app-host>
memory: 128M
services:
- myMongo-db-name
The host you use will determinate your application URL initially, e.g. <host>.mybluemix.net.
The service name 'myMongo-db-name' is a declaration of your MongoDB service. If you are using other services like Watson for example, then you would declare them the same way.
- Connect and login to Bluemix via the Cloud-foundry CLI
$ cf login -a https://api.ng.bluemix.net
- Create a MongoDB service
$ cf create-service mongodb 100 [your-service-name]
Note: this is a free and experiment verion of MongoDB instance. Use the MongoDB by Compose instance for production applications:
$ cf create-service compose-for-mongodb Standard [your-service-name]'
-
Push the application
$ cf push$ cf env <your-app-name > (To view the *environment variables* created for your application)
Done, now go to the staging domain(<host>.mybluemix.net.) and see your app running.
Cloud Foundry Commands More Bluemix samples Simple ToDo app in a programming language of your choice
Be sure to check out the full list of Watson services to forwarder enhance your application functionality with a little effort. Watson services are easy to get going; it is simply a RESTful API call. Here is an example of a Watson Toner Analyzer to understand the emotional context of a piece of text that you send to Watson.
Conversation - Quickly build and deploy chatbots and virtual agents across a variety of channels, including mobile devices, messaging platforms, and even robots.
Discovery - Unlock hidden value in data to find answers, monitor trends and surface patterns with the world’s most advanced cloud-native insight engine.
Language Translator - Translate text from one language to another.
Natural Language Classifier - Interpret and classify natural language with confidence.
Natural Language Understanding - Analyze text to extract meta-data from content such as concepts, entities, keywords and more.
Personality Insights - Predict personality characteristics, needs and values through written text.
Speech to Text - Convert audio and voice into written text for quick understanding of content.
Text to Speech - Convert written text into natural sounding audio in a variety of languages and voices.
Tone Analyzer - Understand emotions, social tendencies and perceived writing style.
Visual Recognition - Tag, classify and search visual content using machine learning.
Click here for live demos of each Watson service.
-
Select or create a Google Cloud Platform Console project
-
Enable billing for your project (there's a $300 free trial)
-
Install and initialize the Google Cloud SDK
-
Create an
app.yamlfile at the root of yourhackathon-starterfolder with the following contents:runtime: nodejs env: flex manual_scaling: instances: 1
-
Make sure you've set
MONGODB_URIin.env.example -
Run the following command to deploy the
hackathon-starterapp:gcloud app deploy
-
Monitor your deployed app in the Cloud Console
-
View the logs for your app in the Cloud Console
If you are starting with this boilerplate to build an application for prod deployment, or if after your hackathon you would like to get your project hardened for production use, see prod-checklist.md.
You can find the changelog for the project in: CHANGELOG.md
If something is unclear, confusing, or needs to be refactored, please let me know. Pull requests are always welcome, but due to the opinionated nature of this project, I cannot accept every pull request. Please open an issue before submitting a pull request. This project uses Airbnb JavaScript Style Guide with a few minor exceptions. If you are submitting a pull request that involves Pug templates, please make sure you are using spaces, not tabs.
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2014-2019 Sahat Yalkabov
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.