GitHub Action
index-digest
GitHub Action for running index-digest that analyses your MySQL queries and schema and suggests indices and schema improvements.
With this Action you can easily implement database performance regression testing in your continuos integration pipeline.
Take a look at what does index-digest check.
We assume that you have a MySQL up and running in your CI pipeline. Your tests suite runs using this database and SQL queries log is collected.
Given your MySQL test instance (and the optional SQL queries log) you can simply add this Action to your pipeline:
- name: Install and run index-digest
id: run-index-digest
uses: macbre/actions-index-digest@0.9.0
with:
index-digest-version: "1.5.0" # or "latest" if you wish use the master version
index-digest-dsn: "mysql://test_user:test_password@127.0.0.1:3306/test_db"
index-digest-report-file: "./report.yml"Here we assume that MySQL uses
test_userwithtest_passwordcredential fortest_dbdatabase. And that the MySQL server runs locally listening on a default port (3306).
index-digest image will be fetched and run with the provided options. The YAML report file will be stored in the location specified by index-digest-report-file. You can use it for additional assertions and to raise an error in your CI pipeline if there's something wrong.
Read more on medium.com - Using Continuous Integration pipeline to guard against database performance regressions
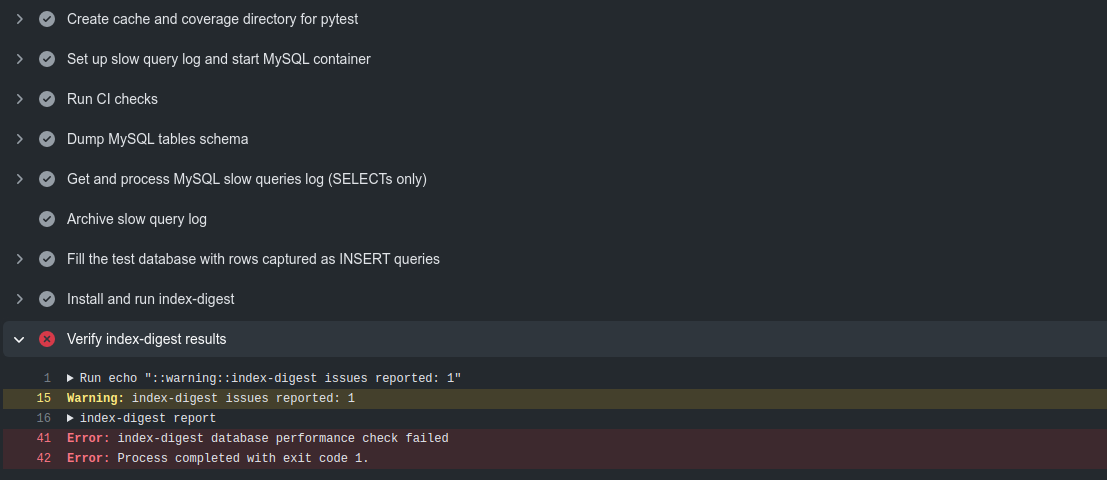
You can make the action fail if there are issues reported by index-digest. Simply add fail-on-issues: true option to with context when calling the action.
with:
# ...
fail-on-issues: trueAnd you'll get something similar to:
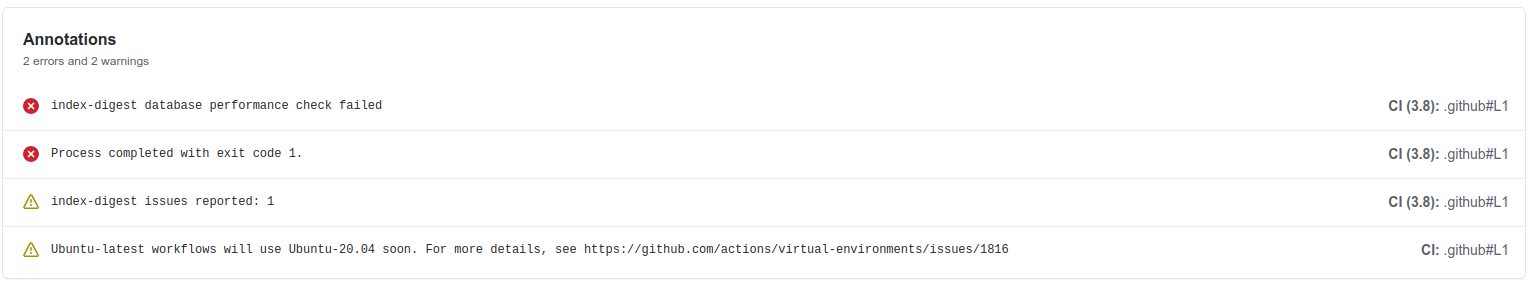
And GitHub Actions will log these warnings and errors:
---
meta:
version: index-digest v1.5.0
database_name: index_digest
database_host: eeae7273a00a
database_version: MySQL v8.0.22
reports:
- type: redundant_indices
table: 0001_redundant_indices
message: '"idx_foo" index can be removed as redundant (covered by "idx_foo_2")'
context:
redundant: UNIQUE KEY idx_foo (foo)
covered_by: UNIQUE KEY idx_foo_2 (foo)
schema: "CREATE TABLE `0001_redundant_indices` (\n `item_id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,\n\
\ `foo` varbinary(16) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',\n PRIMARY KEY (`item_id`),\n UNIQUE\
\ KEY `idx_foo` (`foo`),\n UNIQUE KEY `idx_foo_2` (`foo`)\n) ENGINE=InnoDB\
\ DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci"
table_data_size_mb: 0.015625
table_index_size_mb: 0.03125
...The problem of collecting SQL query logs from your application can be approached from several different perspectives.
- You can tell your application / framework to collect the logs for you.
- Your legacy software or your framework does not allow you to get the log? Then you can instruct your MySQL instance to collect SQL queries log for you.
In this example we assume that you use Docker Compose to set up your CI environment on GitHub Actions. And that you have mysql-ci service defined there. Simply set up the slow query log for it:
mysql-ci:
image: mysql:8.0.22
command: --default-authentication-plugin=mysql_native_password
# enable slow query log for performance regression checks
# https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/slow-query-log.html
command: >-
--default-authentication-plugin=mysql_native_password
--slow-query-log=1
--slow-query-log-file=/tmp/log/slow_query.log
--long-query-time=0
volumes:
# if not existing, Docker will create a directory
- "/tmp/log:/tmp/log"You will then have all queries (not only slow ones - see --long-query-time option value) logged in /tmp/log/slow_query.log file that will be exposed in you host filesystem on GitHub Actions.
Then, having a slow query log, all you need to do is parse it with pt-query-digest and get the list of unique SQL queries:
pt-query-digest /tmp/log/slow_query.log --limit=1000 --output json | jq .classes[].example.query | sed 's/\\n/ /g'| jq -r . > /tmp/log.sql
And then run the action:
- name: Install and run index-digest
uses: macbre/actions-index-digest@0.9.0
with:
index-digest-version: "1.5.0"
index-digest-dsn: "mysql://test_user:test_password@127.0.0.1:3306/test_db"
index-digest-sql-log: "/tmp/log.sql" # use an absolute path here!
index-digest-report-file: "./report.yml"Please note that
index-digest-sql-logneeds to be provided with an absolute path.