tool2agent is a protocol that enables LLM agents to navigate complex business constraints via trial and error by communicating rich and structured feedback data from tools.
Real-world domain constraints are complex, dynamic, and non-publicly-known — in other words, can't be fed into a LLM context. tool2agent defines rules for producing structured errors and suggestions that give an agent enough context to iteratively improve on its request until the goal is achieved.
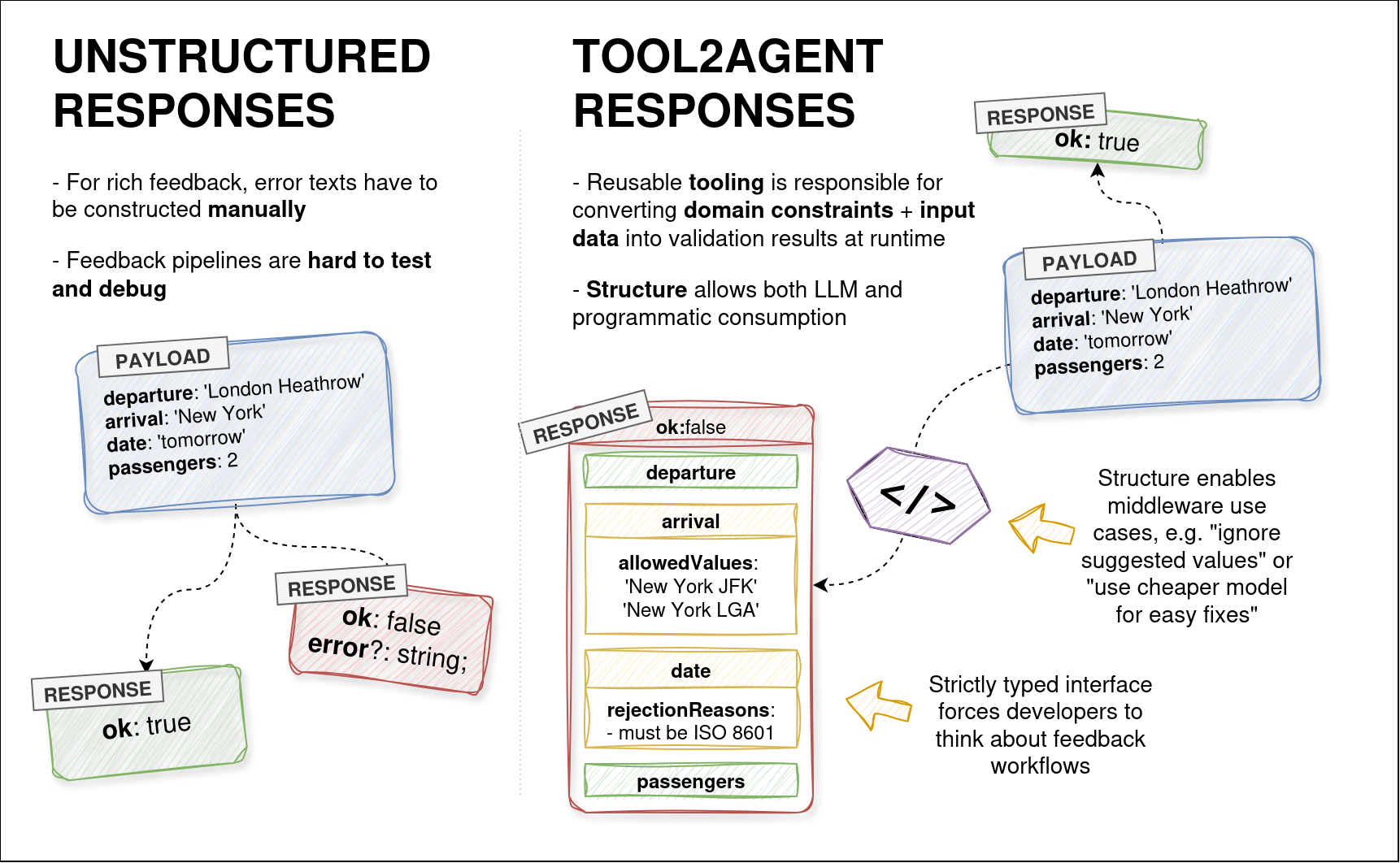
Technically speaking, tool2agent is a set of conventions that allow structuring tool call feedback flows in a predictable manner. These conventions enable novel tooling for agent builders.
Tool schemas alone are often not sufficient to convey enough information about expected inputs, so error-and-retry LLM workflows are needed.
A good feedback system combined with a very primitive schema may be better than a complex schema with precisely encoded variants, even though it requires more tool calls. This is especially true in contexts where there is no way to encode domain constraints in the schema or the system prompt.
tool2agent suggests schema discovery on the fly and encourages developers to build rich tool feedback systems.
Sometimes developers "leak" domain constraints into prompts to guide the model towards producing better tool call payloads, which bloats the context and erodes separation of concerns.
Domain constraints should be presented to the LLM context "on demand" because all LLMs have a limit to the number of rules they can follow before prompt amnesia kicks in.
With tool2agent, domain constraints can be applied on the fly, as opposed to being included in the prompt. This allows them to be kept private and dynamic (changing while inference is in progress).
Precise tool schemas occupy a lot of input tokens.
In the context of agentic workflows, most tools will not be called, so there is no reason for the LLM to be aware of their precise schemas.
tool2agent-enabled workflows consume much fewer tokens (but require more tool calls for trial and feedback).
Although there are common LLM tool response validation patterns (beyond schemas), in a real application they may not be turned into reusable code, because that would require additional engineering efforts.
Structuring the way information flows from tools to LLM allows for programmatic consumption of that data, e.g. in the form of reusable middleware.
@tool2agent/ai— Bindings for AI SDK.
@tool2agent/types— TypeScript type definitions for the protocol that act as a specification.@tool2agent/schemas— Zod schema generators that map user-defined domain type schemas to tool2agent schemas that use these domain types.