| title |
|---|
Web development |
For web development as for any other task, one can leverage Common
Lisp's advantages: the unmatched REPL and exception handling system,
performance, the ability to build a self-contained executable,
stability, good threads story, strong typing, etc. We can, say, define
a new route and try it right away, there is no need to restart any
running server. We can change and compile one function at a time
(the usual C-c C-c in Slime) and try it. The feedback is
immediate. We can choose the degree of interactivity: the web server
can catch exceptions and fire the interactive debugger, or print lisp
backtraces on the browser, or display a 404 error page and print logs
on standard output. The ability to build self-contained executables eases
deployment tremendously (compared to, for example, npm-based apps), in
that we just copy the executable to a server and run it.
We'll present here some established web frameworks and other common libraries to help you getting started in developing a web application. We do not aim to be exhaustive nor to replace the upstream documentation. Your feedback and contributions are appreciated.
Hunchentoot and Clack are two projects that you'll often hear about.
Hunchentoot is
a web server and at the same time a toolkit for building dynamic websites. As a stand-alone web server, Hunchentoot is capable of HTTP/1.1 chunking (both directions), persistent connections (keep-alive), and SSL. It provides facilities like automatic session handling (with and without cookies), logging, customizable error handling, and easy access to GET and POST parameters sent by the client.
It is a software written by Edi Weitz ("Common Lisp Recipes",
cl-ppcre and much more), it's used and
proven solid. One can achieve a lot with it, but sometimes with more
friction than with a traditional web framework. For example,
dispatching a route by the HTTP method is a bit convoluted, one must
write a function for the :uri parameter that does the check, when it
is a built-in keyword in other frameworks like Caveman.
Clack is
a web application environment for Common Lisp inspired by Python's WSGI and Ruby's Rack.
Also written by a prolific lisper (E. Fukamachi), it actually uses Hunchentoot by default as the server, but thanks to its pluggable architecture one can use another web server, like the asynchronous Woo, built on the libev event loop, maybe "the fastest web server written in any programming language".
We'll cite also Wookie, an asynchronous HTTP server, and its companion library cl-async, for general purpose, non-blocking programming in Common Lisp, built on libuv, the backend library in Node.js.
Clack being more recent and less documented, and Hunchentoot a de-facto standard, we'll concentrate on the latter for this recipe. Your contributions are of course welcome.
Web frameworks build upon web servers and can provide facilities for common activities in web development, like a templating system, access to a database, session management, or facilities to build a REST api.
Some web frameworks include:
- Caveman, by E. Fukamachi. It provides, out of the box, database management, a templating engine (Djula), a project skeleton generator, a routing system à la Flask or Sinatra, deployment options (mod_lisp or FastCGI), support for Roswell on the command line, etc.
- Radiance, by Shinmera (Qtools, Portacle, lquery, …), is a web application environment, more general than usual web frameworks. It lets us write and tie websites and applications together, easing their deployment as a whole. It has thorough documentation, a tutorial, modules, pre-written applications such as an image board or a blogging platform, and more. For example websites, see https://shinmera.com/, reader.tymoon.eu and events.tymoon.eu.
- Snooze, by João Távora (Sly, Emacs' Yasnippet, Eglot, …), is "an URL router designed around REST web services". It is different because in Snooze, routes are just functions and HTTP conditions are just Lisp conditions.
- cl-rest-server is a library for writing REST web APIs. It features validation with schemas, annotations for logging, caching, permissions or authentication, documentation via OpenAPI (Swagger), etc.
- last but not least, Weblocks is a venerable Common Lisp web framework that permits to write ajax-based dynamic web applications without writing any JavaScript, nor writing some lisp that would transpile to JavaScript. It is seeing an extensive rewrite and update since 2017. We present it in more details below.
For a full list of libraries for the web, please see the awesome-cl list #network-and-internet and Cliki. If you are looking for a featureful static site generator, see Coleslaw.
Let's install the libraries we'll use:
(ql:quickload '("hunchentoot" "caveman" "spinneret" "djula"))To try Weblocks, please see its documentation. The Weblocks in Quicklisp is not yet, as of writing, the one we are interested in.
We'll start by serving local files and we'll run more than one local server in the running image.
Create and start a webserver like this:
(defvar *acceptor* (make-instance 'hunchentoot:easy-acceptor :port 4242))
(hunchentoot:start *acceptor*)We create an instance of easy-acceptor on port 4242 and we start
it. We can now access http://127.0.0.1:4242/. You should get a welcome
screen with a link to the documentation and logs to the console.
By default, Hunchentoot serves the files from the www/ directory in
its source tree. Thus, if you go to the source of
easy-acceptor (M-. in Slime), which is probably
~/quicklisp/dists/quicklisp/software/hunchentoot-v1.2.38/, you'll
find the root/ directory. It contains:
- an
errors/directory, with the error templates404.htmland500.html, - an
img/directory, - an
index.htmlfile.
To serve another directory, we give the option document-root to
easy-acceptor. We can also set the slot with its accessor:
(setf (hunchentoot:acceptor-document-root *acceptor*) #p"path/to/www")Let's create our index.html first. Put this in a new
www/index.html at the current directory (of the lisp repl):
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello local server!</h1>
<p>
We just served our own files.
</p>
</body>
</html>Let's start a new acceptor on a new port:
(defvar *my-acceptor* (make-instance 'hunchentoot:easy-acceptor :port 4444
:document-root #p"www/"))
(hunchentoot:start *my-acceptor*)go to http://127.0.0.1:4444/ and see the difference.
Note that we just created another acceptor on a different port on the same lisp image. This is already pretty cool.
With Hunchentoot we have nothing to do, we can see the server from the internet right away.
If you evaluate this on your VPS:
(hunchentoot:start (make-instance 'hunchentoot:easy-acceptor :port 4242))
You can see it right away on your server's IP.
Stop it with (hunchentoot:stop *).
To bind an existing function to a route, we create a "prefix dispatch"
that we push onto the *dispatch-table* list:
(defun hello ()
(format nil "Hello, it works!"))
(push
(hunchentoot:create-prefix-dispatcher "/hello.html" #'hello)
hunchentoot:*dispatch-table*)To create a route with a regexp, we use create-regex-dispatcher, where
the url-as-regexp can be a string, an s-expression or a cl-ppcre scanner.
If you didn't yet, create an acceptor and start the server:
(defvar *server* (make-instance 'hunchentoot:easy-acceptor :port 4242))
(hunchentoot:start *server*)and access it on http://localhost:4242/hello.html.
We can see logs on the REPL:
127.0.0.1 - [2018-10-27 23:50:09] "get / http/1.1" 200 393 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:58.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/58.0"
127.0.0.1 - [2018-10-27 23:50:10] "get /img/made-with-lisp-logo.jpg http/1.1" 200 12583 "http://localhost:4242/" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:58.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/58.0"
127.0.0.1 - [2018-10-27 23:50:10] "get /favicon.ico http/1.1" 200 1406 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:58.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/58.0"
127.0.0.1 - [2018-10-27 23:50:19] "get /hello.html http/1.1" 200 20 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:58.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/58.0"
define-easy-handler allows to create a function and to bind it to an uri at once.
Its form follows
define-easy-handler (function-name :uri <uri> …) (lambda list parameters)
where <uri> can be a string or a function.
Example:
(hunchentoot:define-easy-handler (say-yo :uri "/yo") (name)
(setf (hunchentoot:content-type*) "text/plain")
(format nil "Hey~@[ ~A~]!" name))Visit it at p://localhost:4242/yo and add parameters on the url: http://localhost:4242/yo?name=Alice.
Just a thought… we didn't explicitely ask Hunchentoot to add this
route to our first acceptor of the port 4242. Let's try another acceptor (see
previous section), on port 4444: http://localhost:4444/yo?name=Bob It
works too ! In fact, define-easy-handler accepts an acceptor-names
parameter:
acceptor-names (which is evaluated) can be a list of symbols which means that the handler will only be returned by DISPATCH-EASY-HANDLERS in acceptors which have one of these names (see ACCEPTOR-NAME). acceptor-names can also be the symbol T which means that the handler will be returned by DISPATCH-EASY-HANDLERS in every acceptor.
So, define-easy-handler has the following signature:
define-easy-handler (function-name &key uri acceptor-names default-request-type) (lambda list parameters)
It also has a default-parameter-type which we'll use in a minute to get url parameters.
There are also keys to know for the lambda list. Please see the documentation.
easy-routes is a route handling extension on top of Hunchentoot. It provides:
- dispatch based on HTTP method (otherwise cumbersome in Hunchentoot)
- arguments extraction from the url path
- and decorators.
To use it, don't create a server with hunchentoot:easy-acceptor but
with easy-routes:routes-acceptor:
(setf *server* (make-instance 'easy-routes:routes-acceptor))Then define a route like this:
(easy-routes:defroute name ("/foo/:x" :method :get) (y &get z)
(format nil "x: ~a y: ~y z: ~a" x y z))Here, :x captures the path parameter and binds it to the x
variable into the route body. y and &get z define url parameters,
and we can have &post parameters to extract from the HTTP request
body.
These parameters can take an :init-form and :parameter-type
options as in define-easy-handler.
Decorators are functions that are executed before the route body. They
should call the next parameter function to continue executing the
decoration chain and the route body finally. Examples:
(defun @auth (next)
(let ((*user* (hunchentoot:session-value 'user)))
(if (not *user*)
(hunchentoot:redirect "/login")
(funcall next))))
(defun @html (next)
(setf (hunchentoot:content-type*) "text/html")
(funcall next))
(defun @json (next)
(setf (hunchentoot:content-type*) "application/json")
(funcall next))
(defun @db (next)
(postmodern:with-connection *db-spec*
(funcall next)))See easy-routes' readme for more.
Caveman provides two ways to
define a route: the defroute macro and the @route pythonic
annotation:
(defroute "/welcome" (&key (|name| "Guest"))
(format nil "Welcome, ~A" |name|))
@route GET "/welcome"
(lambda (&key (|name| "Guest"))
(format nil "Welcome, ~A" |name|))A route with an url parameter (note :name in the url):
(defroute "/hello/:name" (&key name)
(format nil "Hello, ~A" name))It is also possible to define "wildcards" parameters. It works with
the splat key:
(defroute "/say/*/to/*" (&key splat)
; matches /say/hello/to/world
(format nil "~A" splat))
;=> (hello world)We must enable regexps with :regexp t:
(defroute ("/hello/([\\w]+)" :regexp t) (&key captures)
(format nil "Hello, ~A!" (first captures)))First of all, note that we can access query parameters anytime with
(hunchentoot:parameter "my-param")It acts on the default *request* object which is passed to all handlers.
There is also get-paramater and post-parameter.
Earlier we saw some key parameters to define-easy-handler. We now
introduce default-parameter-type.
We defined the following handler:
(hunchentoot:define-easy-handler (say-yo :uri "/yo") (name)
(setf (hunchentoot:content-type*) "text/plain")
(format nil "Hey~@[ ~A~]!" name))The variable name is a string by default. Let's check it out:
(hunchentoot:define-easy-handler (say-yo :uri "/yo") (name)
(setf (hunchentoot:content-type*) "text/plain")
(format nil "Hey~@[ ~A~] you are of type ~a" name (type-of name)))Going to http://localhost:4242/yo?name=Alice returns
Hey Alice you are of type (SIMPLE-ARRAY CHARACTER (5))
To automatically bind it to another type, we use default-parameter-type. It can be
one of those simple types:
'string(default),'integer,'character(accepting strings of length 1 only, otherwise it is nil)- or
'boolean
or a compound list:
'(:list <type>)'(:array <type>)'(:hash-table <type>)
where <type> is a simple type.
In all frameworks, we can choose the level of interactivity. The web framework can return a 404 page and print output on the repl, it can catch errors and invoke the interactive lisp debugger, or it can show the lisp backtrace on the html page.
The global variables to set are *catch-errors-p*,
*show-lisp-errors-p* and *show-lisp-backtraces-p*.
Hunchentoot also defines condition classes.
See the documentation: https://edicl.github.io/hunchentoot/#conditions.
Clack users might make a good use of plugins, like the clack-errors middleware: https://github.com/CodyReichert/awesome-cl#clack-plugins.
Weblocks is a widgets-based and server-based framework with a built-in ajax update mechanism. It allows to write dynamic web applications without the need to write JavaScript or to write lisp code that would transpile to JavaScript.
Weblocks is an old framework developed by Slava Akhmechet, Stephen Compall and Leslie Polzer. After nine calm years, it is seeing a very active update, refactoring and rewrite effort by Alexander Artemenko.
It was initially based on continuations (they were removed to date) and thus a lispy cousin of Smalltalk's Seaside. We can also relate it to Haskell's Haste, OCaml's Eliom, Elixir's Phoenix LiveView and others.
The Ultralisp website is an example Weblocks website in production known in the CL community.
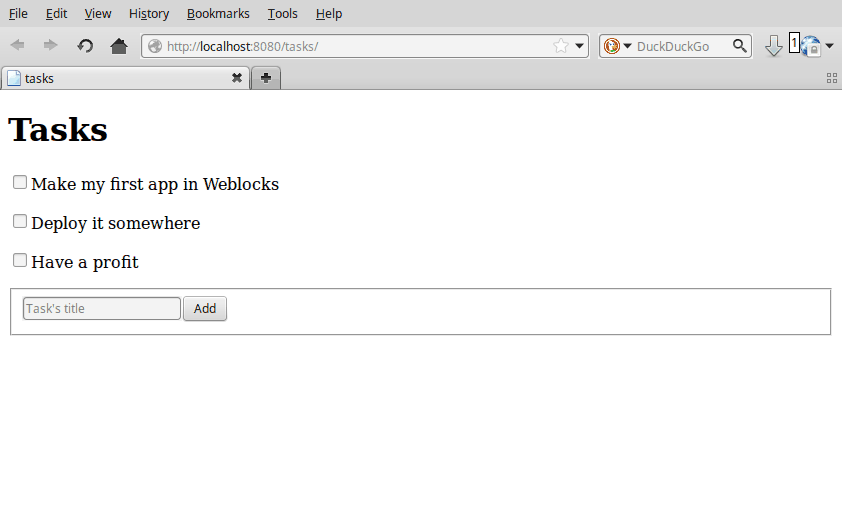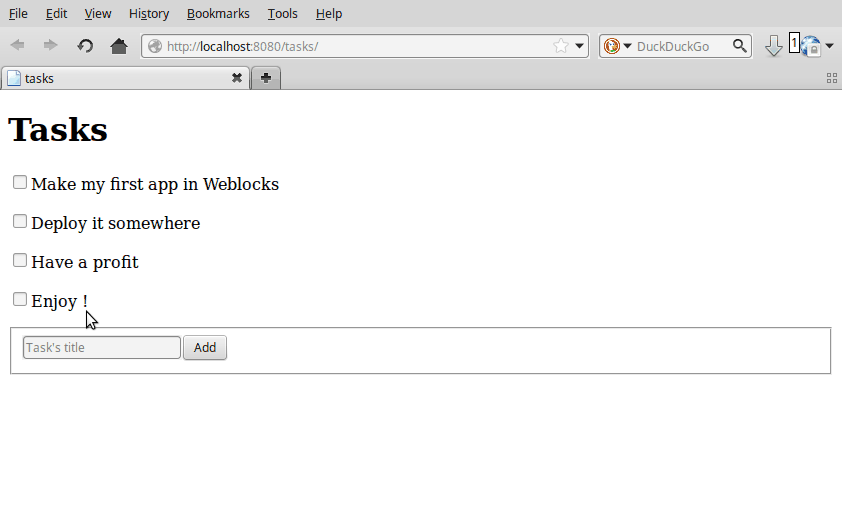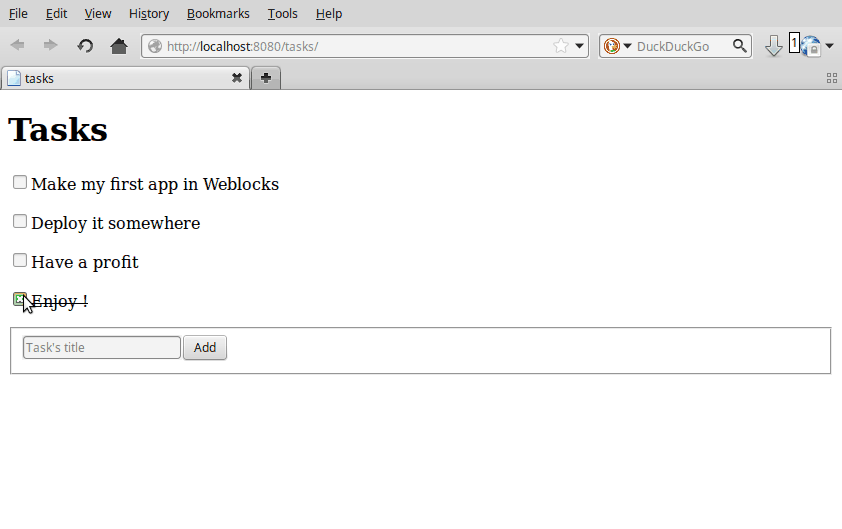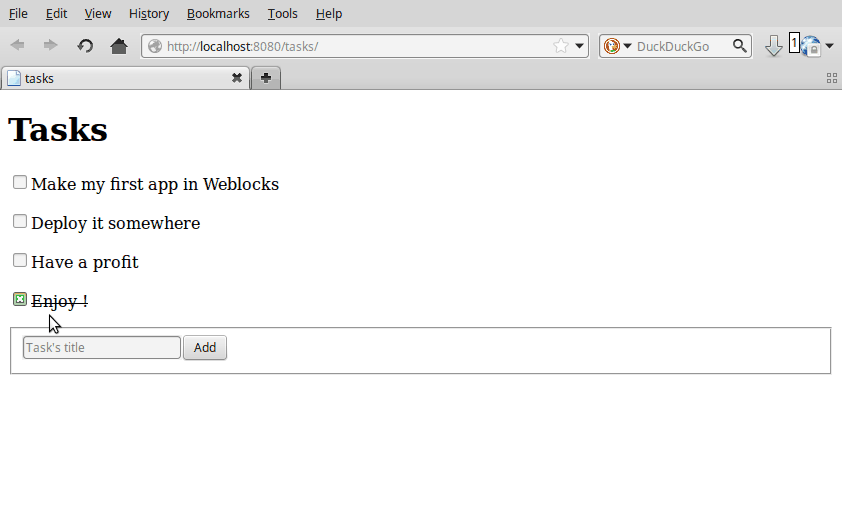
Weblock's unit of work is the widget. They look like a class definition:
(defwidget task ()
((title
:initarg :title
:accessor title)
(done
:initarg :done
:initform nil
:accessor done)))Then all we have to do is to define the render method for this widget:
(defmethod render ((task task))
"Render a task."
(with-html
(:span (if (done task)
(with-html
(:s (title task)))
(title task)))))It uses the Spinneret template engine by default, but we can bind any other one of our choice.
To trigger an ajax event, we write lambdas in full Common Lisp:
...
(with-html
(:p (:input :type "checkbox"
:checked (done task)
:onclick (make-js-action
(lambda (&key &allow-other-keys)
(toggle task))))
...The function make-js-action creates a simple javascript function
that calls the lisp one on the server, and automatically refreshes the
HTML of the widgets that need it. In our example, it re-renders one
task only.
Is it appealing ? Carry on this quickstart guide here: http://40ants.com/weblocks/quickstart.html.
Djula is a port of Python's Django template engine to Common Lisp. It has excellent documentation.
Caveman uses it by default, but otherwise it is not difficult to setup. We must declare where our templates are with something like
(djula:add-template-directory (asdf:system-relative-pathname "webapp" "templates/"))A Djula template looks like this, no surprises (forgive the antislash
in \%, this is a Jekyll limitation):
{\% extends "base.html" \%}
{\% block title %}Memberlist{\% endblock \%}
{\% block content \%}
<ul>
{\% for user in users \%}
<li><a href="{{ user.url }}">{{ user.username }}</a></li>
{\% endfor \%}
</ul>
{\% endblock \%}
Djula compiles the templates before rendering them.
It is, along with its companion access library, one of the most downloaded libraries of Quicklisp.
Spinneret is a "lispy" HTML5 generator. It looks like this:
(with-page (:title "Home page")
(:header
(:h1 "Home page"))
(:section
("~A, here is *your* shopping list: " *user-name*)
(:ol (dolist (item *shopping-list*)
(:li (1+ (random 10)) item))))
(:footer ("Last login: ~A" *last-login*)))The author finds it is easier to compose the HTML in separate functions and macros than with the more famous cl-who. But it has more features under it sleeves:
- it warns on invalid tags and attributes
- it can automatically number headers, given their depth
- it pretty prints html per default, with control over line breaks
- it understands embedded markdown
- it can tell where in the document a generator function is (see
get-html-tag)
Please see the databases section. The Mito ORM supports SQLite3, PostgreSQL, MySQL, it has migrations and db schema versioning, etc.
In Caveman, a database connection is alive during the Lisp session and is reused in each HTTP requests.
A framework will provide a way to work with sessions. We'll create a little macro to wrap our routes to check if the user is logged in.
In Caveman, *session* is a hash table that represents the session's
data. Here are our login and logout functions:
(defun login (user)
"Log the user into the session"
(setf (gethash :user *session*) user))
(defun logout ()
"Log the user out of the session."
(setf (gethash :user *session*) nil))We define a simple predicate:
(defun logged-in-p ()
(gethash :user cm:*session*))and we define our with-logged-in macro:
(defmacro with-logged-in (&body body)
`(if (logged-in-p)
(progn ,@body)
(render #p"login.html"
'(:message "Please log-in to access this page."))))If the user isn't logged in, there will nothing in the session store, and we render the login page. When all is well, we execute the macro's body. We use it like this:
(defroute "/account/logout" ()
"Show the log-out page, only if the user is logged in."
(with-logged-in
(logout)
(render #p"logout.html")))
(defroute ("/account/review" :method :get) ()
(with-logged-in
(render #p"review.html"
(list :review (get-review (gethash :user *session*))))))and so on.
In this recipe we use the de-facto standard Ironclad cryptographic toolkit and the Babel charset encoding/decoding library.
This snippet creates the password hash that should be stored in your database. Note that Ironclad expects a byte-vector, not a string.
(defun password-hash (password)
(ironclad:pbkdf2-hash-password-to-combined-string
(babel:string-to-octets password)))pbkdf2 is defined in RFC2898.
It uses a pseudorandom function to derive a secure encryption key
based on the password.
The following function checks if a user is active and verifies the entered password. It returns the user-id if active and verified and nil in all other cases even if an error occurs. Adapt it to your application.
(defun check-user-password (user password)
(handler-case
(let* ((data (my-get-user-data user))
(hash (my-get-user-hash data))
(active (my-get-user-active data)))
(when (and active (ironclad:pbkdf2-check-password (babel:string-to-octets password)
hash))
(my-get-user-id data)))
(condition () nil)))And the following is an example on how to set the password on the
database. Note that we use (password-hash password) to save the
password. The rest is specific to the web framework and to the DB
library.
(defun set-password (user password)
(with-connection (db)
(execute
(make-statement :update :web_user
(set= :hash (password-hash password))
(make-clause :where
(make-op := (if (integerp user)
:id_user
:email)
user))))))Credit: /u/arvid on /r/learnlisp.
As for all Common Lisp applications, we can bundle our web app in one single executable, including the assets. It makes deployment very easy: copy it to your server and run it.
$ ./my-web-app
Hunchentoot server is started.
Listening on localhost:9003.
See this recipe on scripting#for-web-apps.
Please see the section on testing#continuous-integration.
Ceramic makes all the work for us.
It is as simple as this:
;; Load Ceramic and our app
(ql:quickload '(:ceramic :our-app))
;; Ensure Ceramic is set up
(ceramic:setup)
(ceramic:interactive)
;; Start our app (here based on the Lucerne framework)
(lucerne:start our-app.views:app :port 8000)
;; Open a browser window to it
(defvar window (ceramic:make-window :url "http://localhost:8000/"))
;; start Ceramic
(ceramic:show-window window)and we can ship this on Linux, Mac and Windows.
There is more:
Ceramic applications are compiled down to native code, ensuring both performance and enabling you to deliver closed-source, commercial applications.
Thus, no need to minify our JS.
We can start our executable in a shell and send it to the bakcground (C-z bg), or run it inside a tmux session. These are not the best but hey, it works©.
This is actually a system-specific task. See how to do that on your system.
Most GNU/Linux distros now come with Systemd, so here's a little example.
Deploying an app with Systemd is as simple as writing a configuration file:
$ emacs -nw /etc/systemd/system/my-app.service
[Unit]
Description=stupid simple example
[Service]
WorkingDirectory=/path/to/your/app
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/sthg sthg
Type=simple
Restart=always
RestartSec=10
Then we have a command to start it:
sudo systemctl start my-app.service
a command to check its status:
systemctl status my-app.service
and Systemd can handle logging (we write to stdout or stderr, it writes logs):
journalctl -f -u my-app.service
and it handles crashes and restarts the app:
Restart=always
and it can start the app after a reboot:
[Install]
WantedBy=basic.target
to enable it:
sudo systemctl enable my-app.service
There are several Docker images for Common Lisp. For example:
- 40ants/base-lisp-image is based on Ubuntu LTS and includes SBCL, CCL, Quicklisp, Qlot and Roswell.
- container-lisp/s2i-lisp is CentOs based and contains the source for building a Quicklisp based Common Lisp application as a reproducible docker image using OpenShift's source-to-image.
GNU Guix is a transactional package manager, that can be installed on top of an existing OS, and a whole distro that supports declarative system configuration. It allows to ship self-contained tarballs, which also contain system dependencies. For an example, see the Next browser.
See heroku-buildpack-common-lisp and the Awesome CL#deploy section for interface libraries for Kubernetes, OpenShift, AWS, etc.
See Prometheus.cl for a Grafana dashboard for SBCL and Hunchentoot metrics (memory, threads, requests per second,…).
This this section: debugging#remote-debugging.
This is an example from Quickutil. It is actually an automated version of the precedent section.
It has a Makefile target:
hot_deploy:
$(call $(LISP), \
(ql:quickload :quickutil-server) (ql:quickload :swank-client), \
(swank-client:with-slime-connection (conn "localhost" $(SWANK_PORT)) \
(swank-client:slime-eval (quote (handler-bind ((error (function continue))) \
(ql:quickload :quickutil-utilities) (ql:quickload :quickutil-server) \
(funcall (symbol-function (intern "STOP" :quickutil-server))) \
(funcall (symbol-function (intern "START" :quickutil-server)) $(start_args)))) conn)) \
$($(LISP)-quit))It has to be run on the server (a simple fabfile command can call this
through ssh). Beforehand, a fab update has run git pull on the
server, so new code is present but not running. It connects to the
local swank server, loads the new code, stops and starts the app in a
row.