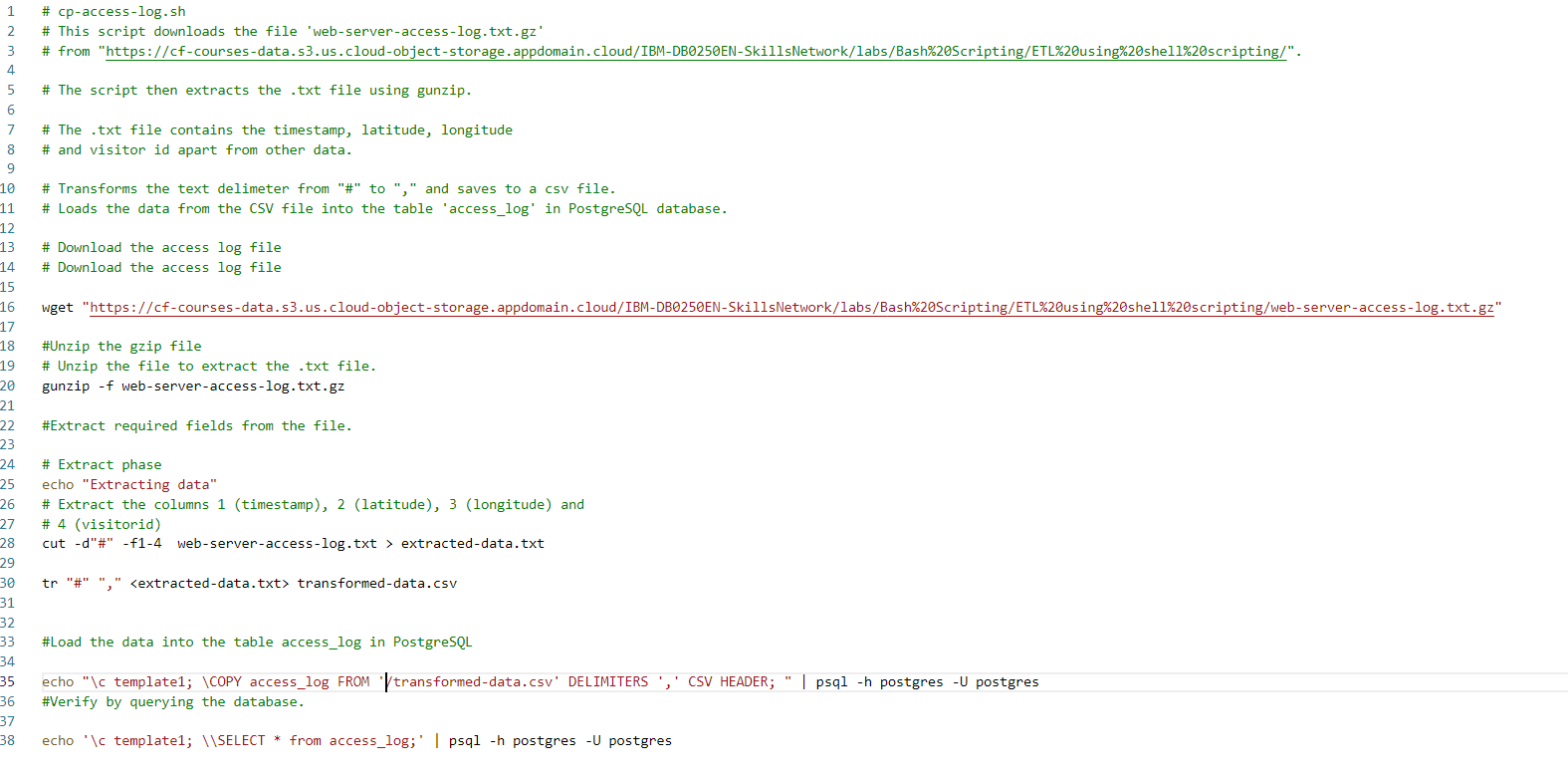
Using bash scripts to create data pipelines is incredibly useful as a data scientist
docker installation
we are going to work with docker containers
Launch a postgres container
"docker run --name some-postgres -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mysecretpassword -p 5432:5432 -d postgres"
This command starts a PostgreSQL container named "some-postgres", sets the password for the PostgreSQL user "postgres" to "mysecretpassword", and publishes the PostgreSQL port (5432) to the host.
docker run --name some-ubuntu --link some-postgres:postgres -it ubuntu bash
This command starts an Ubuntu container named "some-ubuntu", links it to the PostgreSQL container "some-postgres" and gives it the alias "postgres", and launches the bash shell.
apt-get update
apt-get install -y postgresql-client
apt-get install cron
docker exec some-postgres psql -U postgres
\c template1;
CREATE TABLE access_log(timestamp TIMESTAMP, latitude float, longitude float, visitor_id char(37));
bash script.sh