Basic Digital Signal Processing codes in Matlab. In this repo, several DSP projects can be found in different folders, each one including the executable file (main.m) and every extra file needed (audio files .WAV or data container files .mat) The structure and content of this repo is the following:
Basic concepts of sampling and quantification of continuous signals. For this purpose, the following data are provided in a .mat file:
- The amplitude of a signal x(t) (vector x) sampled as a function of time (vector t)
- The amplitude of a signal k(t) (vector k) sampled as a function of time (vector t_k)
Work with two types of quantization (uniform and non-uniform) and analyze the results obtained by applying each of them to the same signal, so differences among types can be noted. For this purpose, an audio file is provided.
Work with different techniques (decimation, interpolation by an integer factor, or frequency changing by a rational factor) to change the frequency of sampling of a signal, in the discrete domain, without changing to the analog domain. For this purpose, an audio file .WAV and a low pass filter (.mat file) are provided.
Different techniques will be used (superposition, filter order) to apply FIR filters to a signal, and different concepts of this type of filter will be analyzed. For this purpose, the following data are provided in a .mat file:
- The amplitude of the signal x(t) (vector x) sampled as a function of the time (vector t)
- The coefficients bk(vector b) of an FIR filter already design by the professor
Moreover, a FIR filter will be designed using a Matlab graphic tool (Filter Design & Analysis Tool)
Various IIR filters (different low and high pass) will be designed using a Matlab graphic tool (Filter Design & Analysis Tool). For that purpose, values of the needed parameters are provided.
Moreover, the characteristics from their frequency responses and their pole-zero plots will be analyzed (module and phase, estability).
Study the effects that occur due to the fact that the numbers used in the implementation of digital IIR filters (coefficients and samples) are quantified when working with them with a finite precision microprocessor. For this purpose, the values of the parameters of the IIR filter are provided.
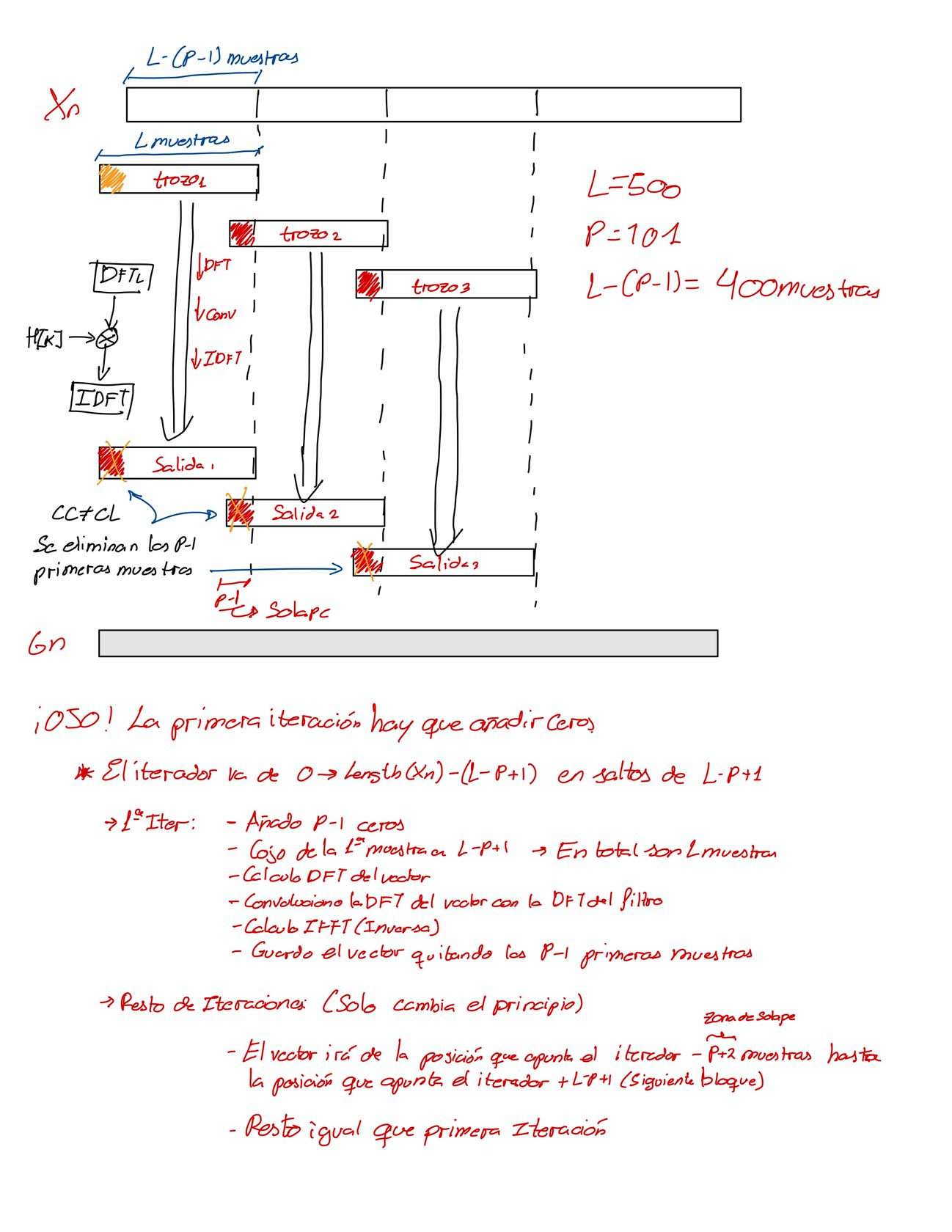
A provided audio signal is going to be filtered using the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) by the overlap-store method. This method is explained in the following figure (in Spanish):
For this purpose, a FIR filter (Constrained Equiripple) is designed using the values of the parameters provided.
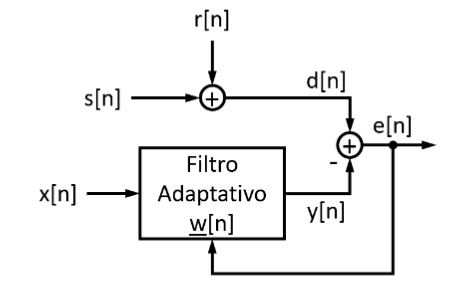
An adaptive filter is built using the Least Mean Squares (LMS) algorithm, which is based on the approximation of the gradient of the error surface, and will allow the ambient noise of an audio signal to be canceled. For this purpose, an audio file is povided.
The blocks diagram of an adaptative system is the following: