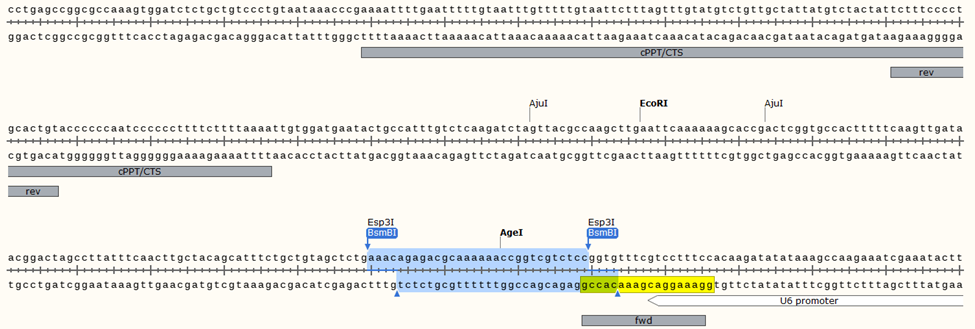
Most sgRNA libraries are housed in the LentiCRISPRv1 or v2 backbones.
i. Guides are inserted into typeIIS restriction sites (see below) downstream of U6
ii. Transduce with pool, proceed with positive or negative selection based on desired phenotype, and isolate gDNA from your filtered population. Pre-selection cells are used as a control.
iii. Libraries are made in a 1- or 2-step PCR reaction priming the guide-containing region from the lenti insert. See below for priming sites. Template + product ≈ 350bp
iv. Primers contain the whole illumina adapter needed for sequencing.
-
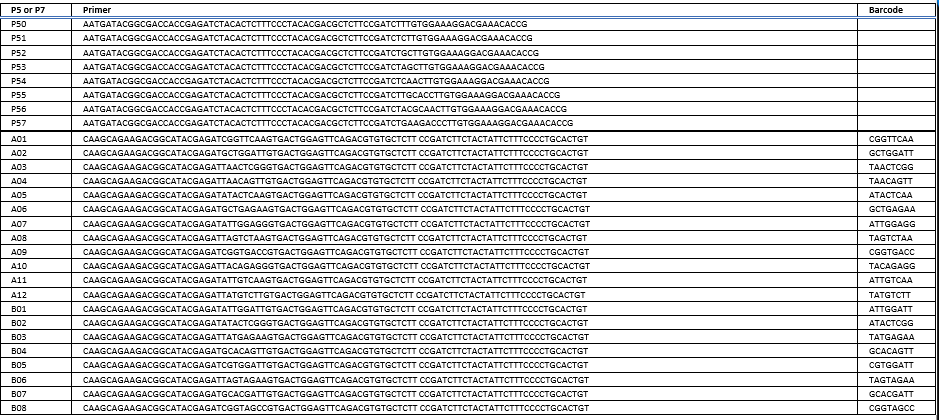
The P5 primer (fwd) is usually not barcoded. It’s also ordered as a pool, staggered by 1nt for library complexity. Read 1 uses this primer.
-
The P7 primer (rev) contains the barcode (index 1).
v. I recommend using a Nextseq 500/550 75-cycle high-output kit (or NextSeq 2000 P3 50 cycle kit) for sequencing multiple libraries. Minimum coverage should == #guides x 200. Allocate cycles as 75 | 8 | 0 | 0 (R1 | I1 |I2 |R2). You’re only sequencing from P5 on the U6 end.
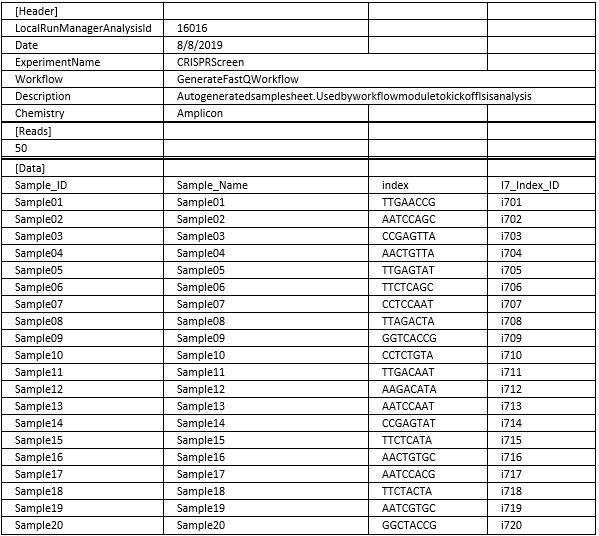
vi. Run sequencer in Manual mode, opting for monitoring AND storage on basespace. Upload a sample sheet saved as CSV (below is for Nextseq 500/550, Miniseq. Nextseq 2000 has different sample sheets). Sheet below corresponds to primers above. Experiment name should be unique—you’ll need this to download your FASTQs
Consult the relevant publicatioin before processing to see whether your libraries are compatible with MAGeCK. It should work with all the lenti backbones. It has a published protocol, but I don’t find it particularly helpful.
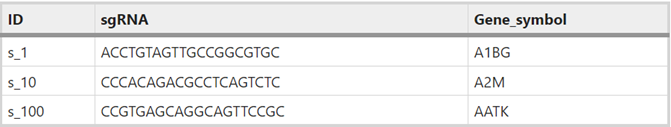
- You need a 3-column sgRNA library table. ID should be unique. Check the supplementary information of the article describing your library. They should have a table like this. Get these three columns, name the columns, save as “library.csv” and upload to the cluster.
- Log in to the cluster and start an interactive job:
#Here is a job with 15 cores, 30G RAM
bsub -n 15 -R "span[hosts=1]" -R "rusage[mem=2048]" -W 4:00 -q interactive -Is bash
- Get your sequencing data onto the cluster. I recommend the illumina commandline uitility. Follow setup instructions if first time. Find your project and download.
#Find your project and id. It’s the experiment name above
bin/bs list projects
# Download and name output folder
bin/bs download projects -i 378654281 -o CRISPRScreen_output
- Your files should be named something like “Sample01_R1_L001_001.fastq.gz”. If you used a Nextseq, you’ll need to combine files from all 4 lanes before proceeding. This isn’t an issue on 1-lane machines like the Miniseq, or FASTQs from outside vendors.
cd CRISPRScreen_output
#Schedule jobs to merge the lanes (all one line)
for i in *L001_*gz; do bsub -n 4 -R "span[hosts=1]" -R "rusage[mem=1024]" -o myjob.out -e myjob.err -oo myjob.out -eo myjob.err -W 3:59 -q short -J "$i" "zcat ${i%_L00*}*.gz > ${i%_S*}_R1.fq && gzip ${i%_S*}_R1.fq";done
#Remove input FASTQs
rm *L00*.gz
- MAGeCK isn’t on the cluster as a module, so I made a docker image compatible with singularity. Enter the image and start the software. First time will take a couple minutes to download the container from docker and convert to singularity image.
singularity shell docker://umasstr/mageckvispr:latest
source activate mageck-vispr
- Align and count sgRNAs for all samples. Make sure you have your library file from step 1.
# mageck count -l <library csv file> -n <name of analysis> --sample-label <comma separated sample names> --fastq <space separated FASTQs>
mageck count -l library.csv -n Screen --sample-label Sample1,Sample2,Sample3,Sample4,Sample5 --fastq Sample1_R1.fq.gz Sample2_R1.fq.gz Sample3_R1.fq.gz Sample4_R1.fq.gz Sample5_R1.fq.gz
#Your output is:
# Screen.count.txt
# Screen.count_normalized.txt
# Screen.count_report.Rmd
# Screen.countsummary.txt
# Screen.log
# Screen_countsummary.R
# Screen_countsummary.Rnw
- Now, run the comparisons between your experimental and control samples. Here, Sample01 is experimental and Sample02 is a control.
# mageck test -k <count table> -t <EXP> -c <CTRL> -n <name output>
mageck test -k Screen.count.txt -t Sample01 -c Sample02 -n 01vs02
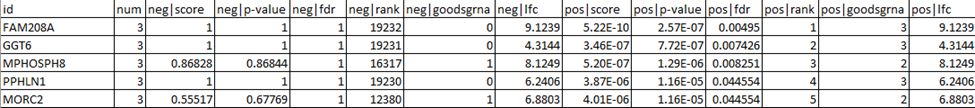
- The output file “01vs02.gene_summary.txt” contains enrichment information for your guides. They’re ranked by positive and negative selection: