User-friendly setup for game of chess using various existing data structures and algorithms.
DATA STRUCTURES USED:
- 2D Array: To make the game board and store the positions of the chess pieces.
- Tuple: To keep track of player clicks to make valid moves
- Tree: Chess programs consider chess moves as a game tree. They examine all moves, then all counter-moves to those moves, then all moves countering them, and so on, where each individual move by one player is called a "ply". This evaluation continues until a certain maximum search depth or the program determines that a final "leaf" position has been reached (e.g. checkmate).
ALGORITHMS USED:
- NAÏVE ALGORITHM : Naïve Bayes classifiers are linear classifiers based on Bayes’ theorem. The model generated is probabilistic. It estimates conditional probability which is the probability that something will happen, given that something else has already occurred.
- GREEDY ALGORITHM : A Greedy algorithm is an algorithmic paradigm that follows the problem solving heuristic of making the locally optimal choice at each stage with the hope of finding a global optimum
- MIN-MAX ALGORITHM : Min-max is a kind of backtracking algorithm that is used in decision making and game theory to find the optimal move for a player, assuming that your opponent also plays optimally
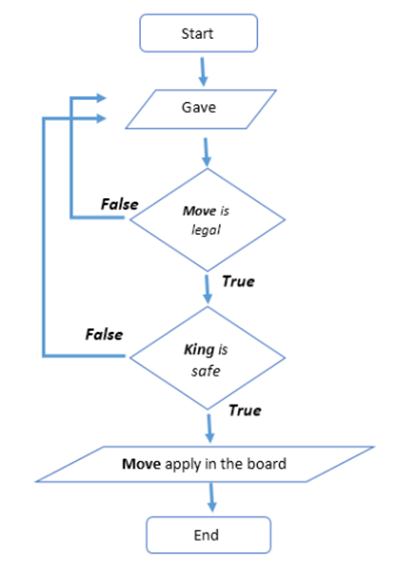
PLAYING STEPS (HUMAN):
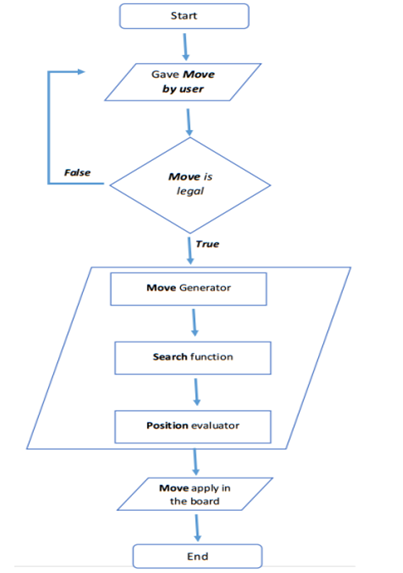
PLAYING STEPS (AI):
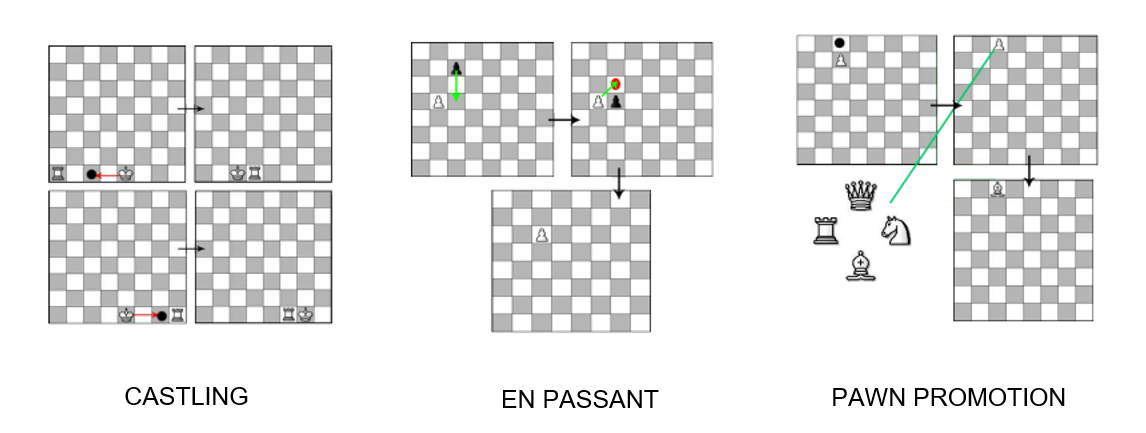
SPECIAL MOVES:
- CASTLING : It is a special rule that allows your king to move two spaces to its right or left, while the rook on that side moves to the opposite side of the king.
- EN PASSANT : En passant is a capture by a pawn of a horizontally adjacent enemy pawn that has just advanced two squares in one move.
- PAWN PROMOTION :Pawn Promotion is the replacement of a pawn with a new queen, rook, bishop, or knight of the same color . It occurs immediately when the pawn moves to its last rank .