The outline of reuasble solution to a general problem encounter in a particular context.
- Behavioral patterns: Deal with responsibles and communication between objects (Ex: Strategy)
- Creational patterns: Deal with instantialation of objects (Ex: Singleton)
- Structural patterns: Deal with composition and relations (Ex: Adapter)
- Define a family of algorithms, encapsulate each one and make them interchangable
- Let the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it.
- The stratergy pattern useful for situations where it is necessary to dynamically swap the algorithms used in application.
- Use composition instead of inheritance
- Singleton pattern is a convention for ensuring one and only one object is instantiated for a given class.
- The Singleton pattern ensures a class has only be instance and provides a point to access to it.
- Use private constructor to guarantee that no morethan one instance will be created.
- The single instance must also be accessible to all classes that require it.
- 2 types of initializations:
- Eager initialization: initiating the class at the time of class loading. Drawbacks: always initialized whether it is being used or not.
- Lazy initatialization: initiated only when it is required, save you form instanting the class when you don't need it.
- Thread safe solutions:
- Synchroized GetInstance(): expensive
- Eager initialization: always initialized whether it is being used or not.
- Double checked locking: best practice
- The Observer design pattern defines a one-to-many dependency between objects, so that when one object changes states, all of its dependents are notified and updated automatically.
- A newspaper subscription service with its publisher and subscribers is a good way to visualize observer pattern.
- The Observer pattern provides an object design where subjects and observers are loosely coupled.
- You should use this pattern in your application where multiple objects are dependent on the state of one object.
- Applications: Event Listener, Email subscription, Youtube Notification.
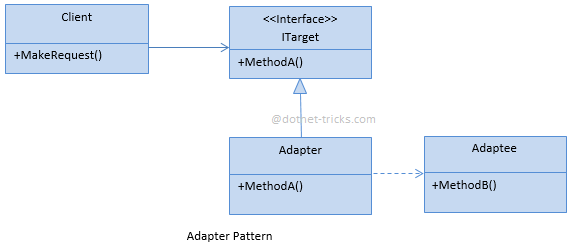
- A wrapper allows 2 incompatible interfaces to work together.
- The Adapter pattern onverts the interface of a class into another interface the client expect.
- How clients use adapter
- The client makes a request to the adapter by calling a method on it using the target interface.
- The adapter translates the request into one or more calls on the adaptees ising adaptee interface.
- The client recieves the results of the call and never knows there is an adpter doing the translation.
- There are two types of adapters
- Object adapter: Use composition, Adapter has an Adaptee.
- Class adapter: Use inheritance, Adapter is subclass of both Target and Adaptee.
- Remember that adapter pattern doesn't create new responsibilities.
(source: https://www.amazon.com/Head-First-Design-Patterns-Brain-Friendly/dp/0596007124)
(source: https://vngeeks.com/adapter-design-pattern/)
(source: https://www.dotnettricks.com/learn/designpatterns/adapter-design-pattern-dotnet)
- The Decorator pattern provides a flexible alternative to subclassing for extending functionality
- Decorators attached additional responsibilities to an object dynamically
- Decorator pattern involves a set of decorator classes that are used to wrap around concrete components
- Decorator classes mirror the type of the components (Have the same type, through inheritance or interface implementation)
- Decorators change the behavior of their components by adding new functionality before / after method class to the component.
- Drawback: Decorators can results in many small objects in design and overuse can be complex.
- Application: File reader
(source: https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/learning-javascript-design/9781449334840/ch09s14.html)