Our dataset consists of 1.6 million tweets
source:
https://www.kaggle.com/code/tamoghna96saha/sentiment-analysis-using-transfer-learning-1
To get the sentiments of people's tweets as positive or negative, the parts of speech breakdown for each of the tweets, and to extract the subject from the tweet so that users can be suggested to one another for following based on the sentiment value and subject.
The dataset has 6 columns:
- target: the polarity of the tweet (0 = negative, 2 = neutral, 4 = positive)
- ids: The id of the tweet
- date: the date of the tweet
- flag: The query (lyx). If there is no query, then this value is NO_QUERY.
- user: the user that tweeted.
- text: the text of the tweet.
Extraction:
- Loaded dataset using pandas
Cleaning:
-
Removed stopwords
-
Removed @user_name
-
Focused on alphabets
-
Lemmatized words
After the cleaning process the files to be uplaoded to the database will be stored in the path group_2_final\Resources\final_clean_twitter.zip
Transformation(Word embeddings):
-
Represent each word as a vector of numbers
-
The closer related the words are the more similar the meaning
-
2B tweets, 27B tokens, 1.2M vocab
-
50 dimensions
https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/
Below is a picture of the word embeddings:
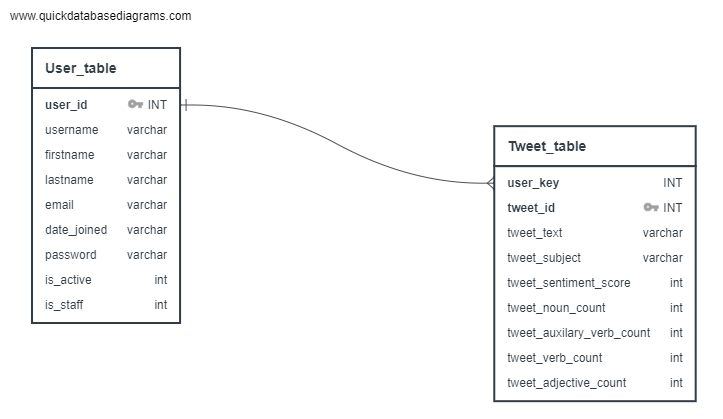
Below is the ERD that is used for our tweets database:
-
Model was trained on a 70/30 train/test split
-
The training set was further divided into training/validation set
-
Training set (~896,000 tweets)
-
Validation set (~224,000 tweets)
-
Testing set (~480,000 tweets)
-
Max length of words to consider per tweet was set to 500
Below is a picture showing the details of the model:
Final accuracy: 0.7494
Validation accuracy: 0.7403
Precision: 0.7357848
Recall: 0.754179497
The model predicted more false_positives than false_negatives
- Below is a picture of the confusion matrix:
Django was used to deploy the machine learning model. This application is comprised of PostgreSQL for the database, TensorFlow for the machine learning model, Spacy for the parts of speech breakdown, Wordnet for computational liguistics, the NewsAPI for the api and the pyttsx library for the AI chatbot.
The system works by taking a tweet, breaking the tweet down by parts of speech, getting the sentiment and subject from the tweet which is done by running through a series of functions and the ML model. This data is then called, via a get request, and returns the latest tweet and the revelant data assocaited with this tweet. Based on the subject, it then is sent to the NewsApi and returns topics relevant to the subject. This is synonmous to target marketing. To add, the data is then used to query the database for like users based on sentiment and subject so that other users are suggested to follow each other. This can be used to group like users. When there is no subject, the computational linguistics steps in to control the process. Based on the sentiment and the words in the tweet, the APi is then queried based on how the liguistics suggest based on the subject and sentiment.
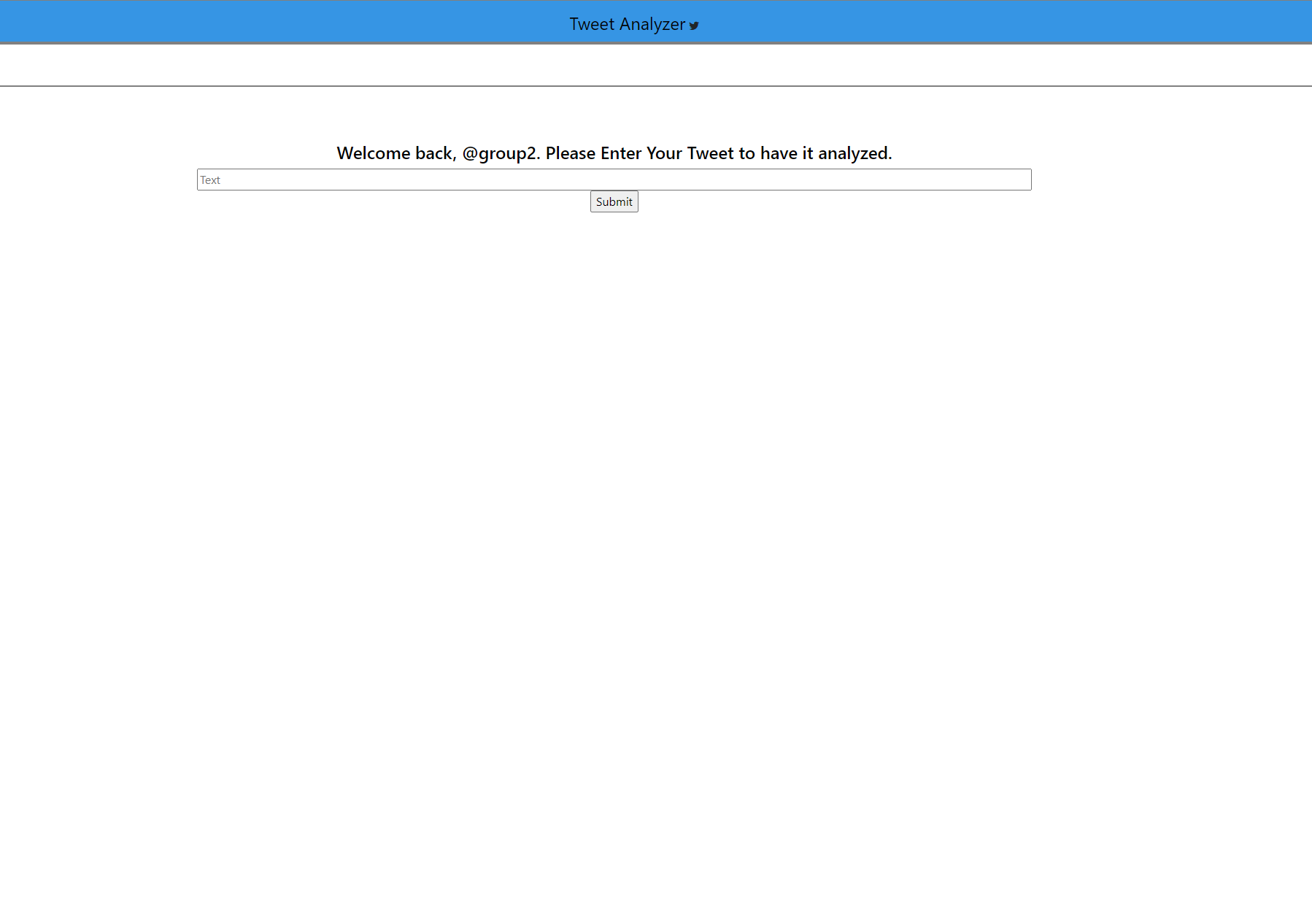
Figure 1-- The image below is the page to enter the tweet to be analyzed
Figure 2-- The image below is the page that analyzes the tweet
 Figure 3-- The image below is the page the API returns data based on subject of the tweet
Figure 3-- The image below is the page the API returns data based on subject of the tweet
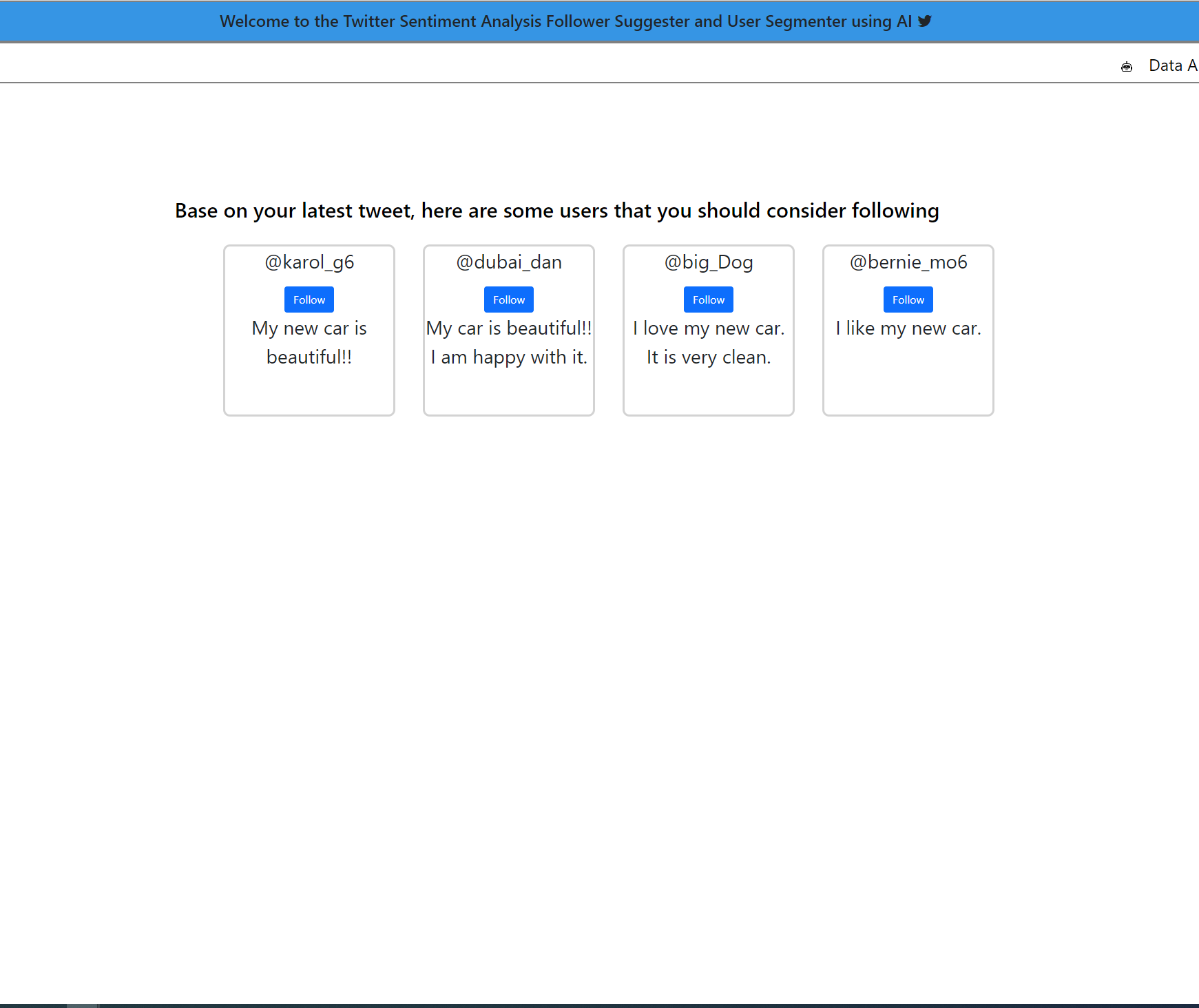
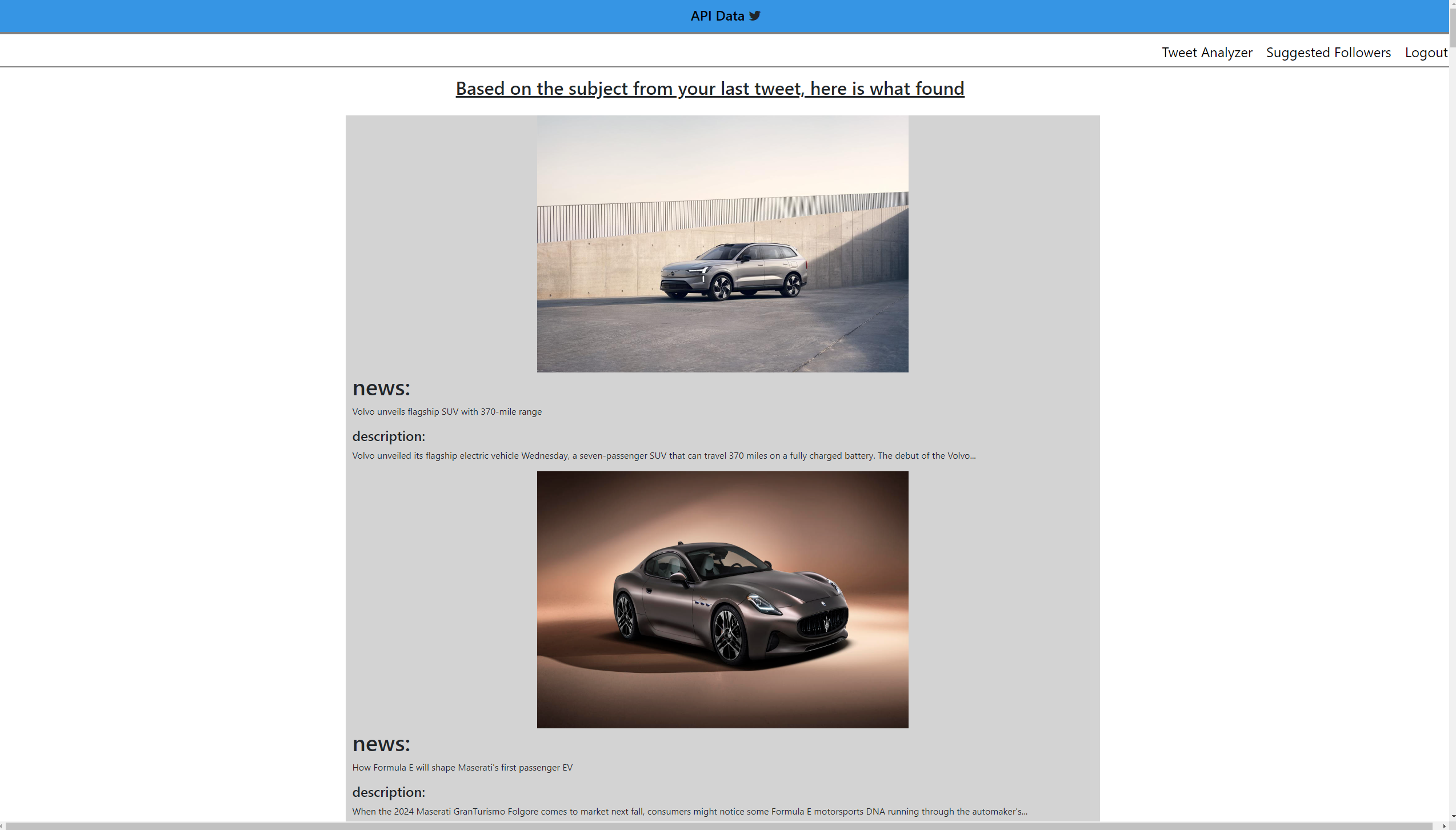 Figure 4-- The image below is the page that the followers are suggested
Figure 4-- The image below is the page that the followers are suggested