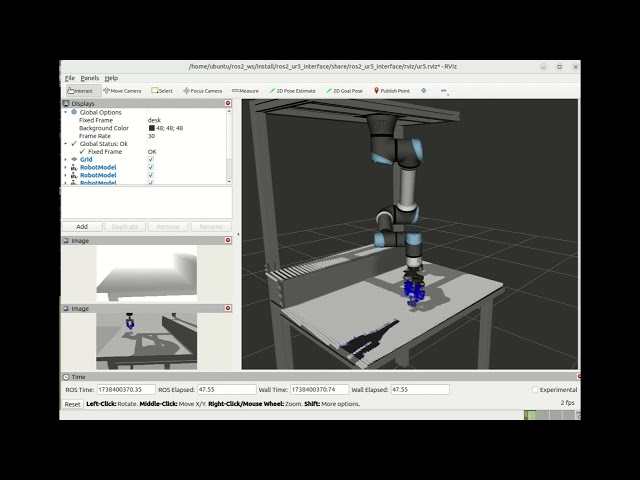
This is the official repository for the Robotics Project 2025. The project focuses on creating code for the movement of a robotic arm and allows us to identify and manipulate block of different types, placing them in designated locations regardless of their initial pose.
This project has been developed for the course Introduction to Robotics at the University of Trento, year 2024/2025.
- Block Recognition: Identify and classify 10 different types of blocks, even if flipped or placed on their sides.
- Task Execution: Picking up blocks from their starting positions and placing them in predefined final positions.
The motion_pkg is responsible for moving the robot in the simulation, it's written in C++ and it's responsible for computing the actual movement of the robot, while also checking the presence of singularities.
The planning_pkg handles a detection result, computes the sequence of poses for the robot to follow, and executes the planned poses while managing transformations and gripper operations.
The pose_estimator_package is responsible for detecting the blocks in the simulation, it's written in Python and its main purpose is to detect the blocks on the table and classify them, in order to understand where to put each one, and how to pick it up.
Before starting the simulation, make sure you have the repository downloaded to your workspace. To do this, clone the repository with the following command:
git clone https://github.com/KeithLeoni/ros2_ws.gitNavigate inside the directory
cd ros2_wsFollow the steps below to launch and control the robot simulation.
Before anything else, you need to launch the required nodes and services that bring up the robot's system. This will initialize all necessary components and services.
Run the following command to start the robot system:
ros2 launch arm_bringup bringup_launch.pyOnce the system is up and running, you can launch the planning node. This will allow the robot to perform the necessary planning operations.
ros2 run planning_pkg planning_node