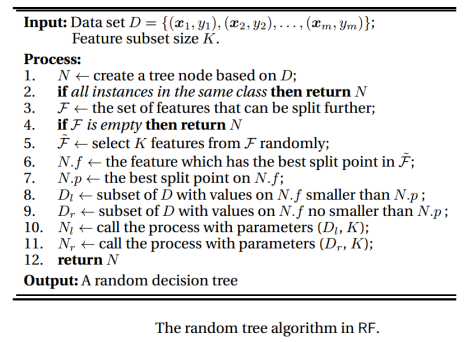
Random Forest (RF) is representative of the state-of-the-art ensemble methods. It is an extension of Bagging, where the major difference with Bagging is the incorporation of randomized feature selection. During the construction of a component decision tree, at each step of split selection, RF first randomly selects a subset of features and then carries out the conventional split selection procedure within the selected feature subset. This process is sometimes called "feature bagging". Notice that randomness is only introduced into the feature selection process, not into the choice of split points on the selected feature. The below algorithm indicates the pseudo-code for a random decision tree, which is considered the base classifier of the RF.
Note 1: The parameter K controls the incorporation of randomness. When K equals the total number of features, the constructed decision tree is identical to the traditional deterministic decision tree; when K = 1, a feature will be selected randomly. The suggested value of K is the logarithm of the number of features. (For a classification problem with 𝑝 features, 𝐾 = log 𝑝 (rounded down) features are used). Alternatively, The suggested value of K is the root of the number of features. (For a classification problem with 𝑝 features, 𝐾 = √𝑝 (rounded down) features are used.)
Note 2: Information Gain 𝐼𝐺 is used by the random tree to select the best split point (the best feature) at each step of growing the tree
-
Implementing a random decision tree as the base classifier of the random forest using both values for the parameter 𝐾.
-
Implementing the RF with random decision trees. The number of classifiers 𝐿 in RF has been obtained from set {11, 21, 31, 41, 51}. In other words, I have tested the performance of the algorithm with the given 𝐿 values for each data set and reported the best results over a fixed 𝐿 value.
-
The implemented algorithm has been compared with Bagging. ( the available codes for Bagging is used.)