DFA refers to deterministic finite automata. A DFA is a collection of 5-tuples:
Q: finite set of states
∑: finite set of the input symbol
q0: initial state
F: final state
δ: Transition function
-
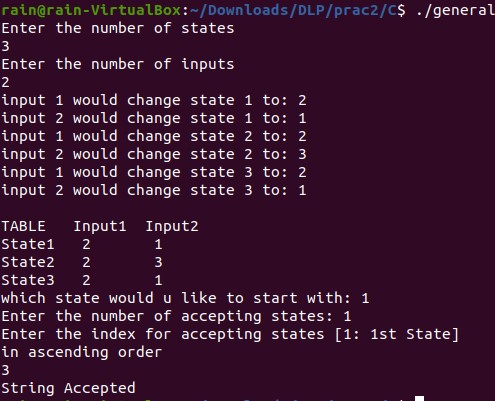
In the particular program, the user is can build a generic DFA by inputing the transition table for it.
-
Create a
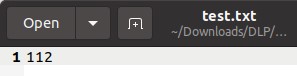
test.txtin the same directory where you will extract thegenericDFA.cprogram. -
Input any String in the .txt file.
Note: The Program accepts inputs from 1 to 9. So if you would want to try out a DFA with inputs as {a,b,c}, they will first have to be converted to {1,2,3}. Similarly a string as "aabccb" will have to be converted into "112332".
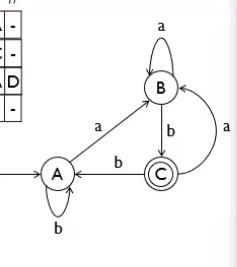
This DFA has
- Q: {A,B,C}
- ∑: {a,b,c}
- q0: {A}
- F: {C}
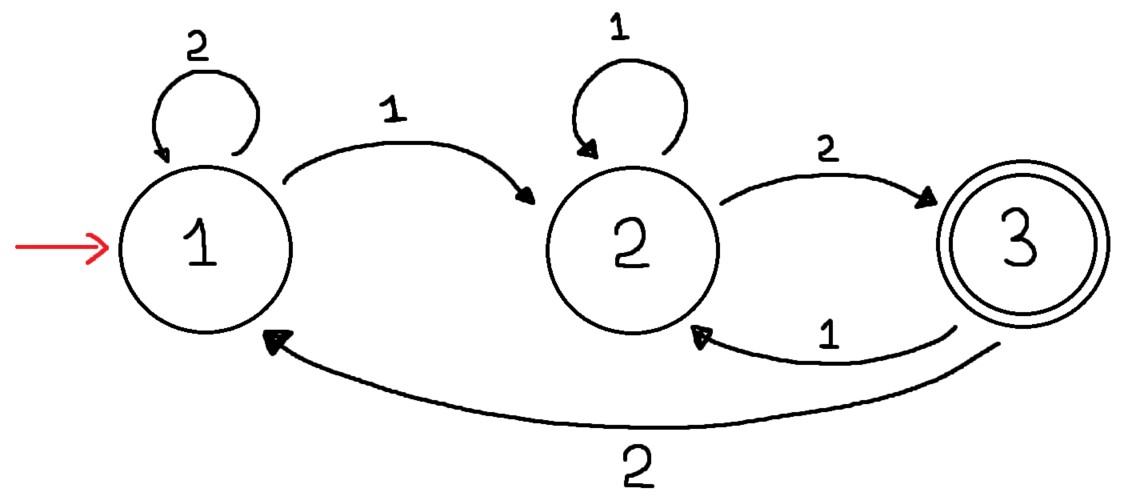
For the purposes of using this DFA on the code written above, Let’s convert the following:
A State will now become State 1.
B State will now become State 2.
C State will now become State 3.
a input will now become input 1.
b input will now become input 2.
c input will now become input 3.
Therefore the DFA will now look more like:
Let us take input as "aab" or "112".
Lexical analysis is the first phase of a compiler. It takes the modified source code from language preprocessors that are written in the form of sentences. The lexical analyser breaks these syntaxes into a series of tokens, by removing any whitespace or comments in the source code. If the lexical analyser finds a token invalid, it generates an error. The lexical analyzer works closely with the syntax analyser. It reads character streams from the source code, checks for legal tokens, and passes the data to the syntax analyser when it demands.
-
The following program takes in the name of a
.c programin the same directory as thelexicalAnalyzer.corlexicalAnalyzer.l -
The program will convert the c program into tokens and will output them along with their type.
-
There are 6 types of different tokens:
i. identifiers
ii. reserved keywords
iii. constants
iv. strings
v. operators
vi. special symbols -
The program will also ignore all comments.
-
Token errors genereted will also be displaced as "invalid symbols".
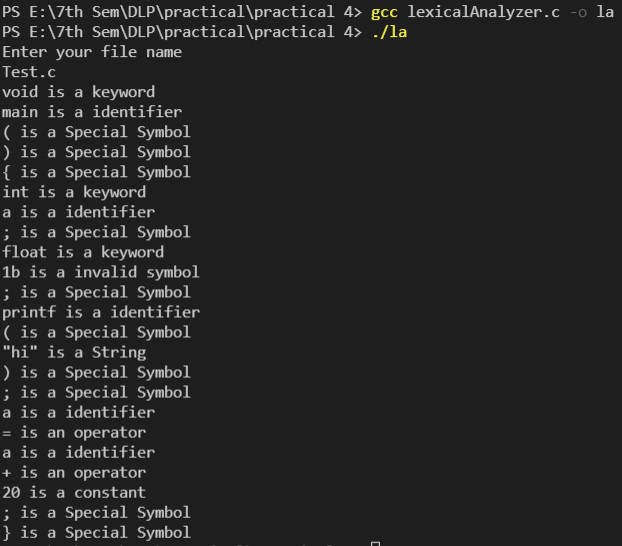
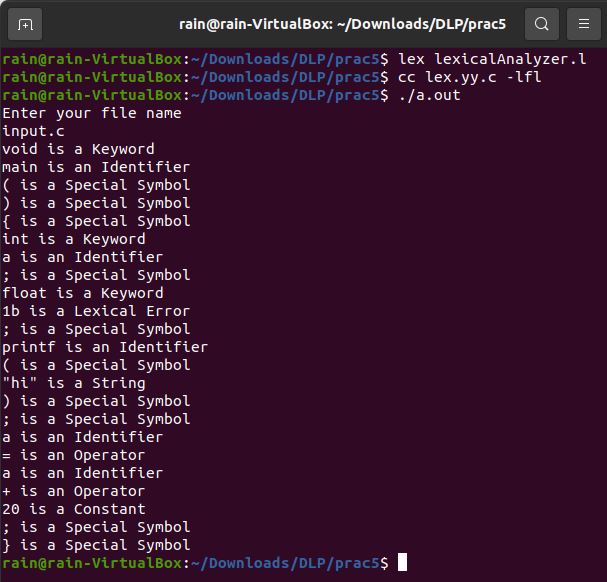
Lexical Analyzer/Test.c contains the following code.
/* compiler
Practical-4*/
void main()
{
int a; //variable declaration
float 1b;
printf ("hi");
a = a + 20;
}
There are two types of Parsers:
-
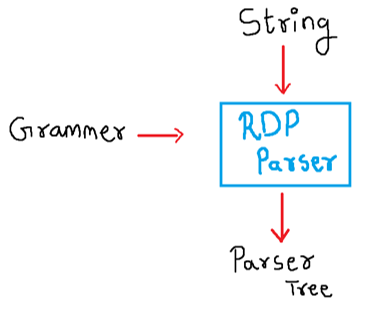
Top Down Parser : Parser where a start symbol is expanded into a whole program. Recursive Descent and LL Parser are Top-Down in nature.
-
Bottom Up Parser : Parser where the whole program is reduces to a start symbol. LR(0) is a Bottom Up Parser
RDP uses a set of recursive procedures to scan the input. Recursive Parsing method includes backtracking. Backtracking repeatedly scans its inputs. Grammer must first eliminate left recursion. The result can be passed to RDP Parser.
In this code, for every variable, we would be writing a function. The prime player in this code will be a global variable known as lookahead operator, which will be tasked with scanning the next character from the input.
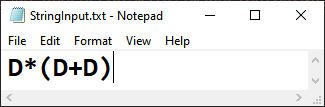
Recursive Descent Parser/RecursiveDescentParser.c takes in the name of a txt file as an input. You would write the grammer in this input file.