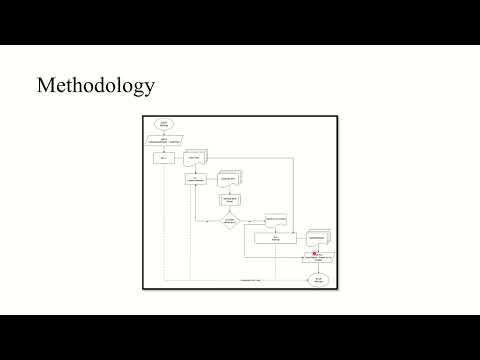
ReForge is an end-to-end research framework that fuses AFL++ fuzzing, cloud-grade LLM exploit generation, and a local analyst model under a single orchestrator. At its core, ReForge pushes every crash- or hang-inducing input through an AI "forge":
AI-1 · Exploit Generator – turns raw crash data into a runnable Python PoC.
MCP Orchestrator – coordinates validation loops and state-sharing between the AIs.
AI-2 · Analyzer – produces a human-readable report that explains the exploit in plain English.
Because ReForge's pipeline is model-agnostic, you can swap the cloud model, the local model, or even the decision logic in MCP without touching the fuzzing harness. The result is a repeatable cycle that discovers, weaponises, and explains software weaknesses with minimal human intervention.
-
AFL++ finds interesting inputs (crashes, hangs, anomalous paths).
-
MCP streams each artifact—plus binary metadata—into AI-1.
-
AI-1 returns a candidate exploit. MCP executes it against the un-instrumented binary.
-
If the exploit fails to execute, MCP feeds the error context back to AI-1 until it passes or loop termination conditions, whichever comes first.
-
A validated exploit and its provenance are handed to AI-2, which writes a beginner-friendly analysis report.
-
All the files (exploit, explanation, report, validation log) will include in
/results.
-
Fully Autonomous Pipeline: - From fuzzing to exploit generation to human-readable reporting — all triggered via a single script, minimal manual intervention required.
-
Exploit Generation via LLMs
ReForge integrates directly with cloud-based LLMs to convert crash artifacts into working Python exploits. It does this intelligently, validating and refining output until execution succeeds. -
On-Device Vulnerability Analysis
A local custom-model translates technical exploits into plain-English explanations, ideal for reporting, documentation, or onboarding junior analysts. -
Model Coordination Protocol (MCP)
The modular design includes a lightweight orchestration layer that tracks state between models, handles decision logic, and supports pluggable backend upgrades. -
AFL++ Integration (In & Out of the Loop)
ReForge leverages AFL++ for crash discovery, with instrumentation for fuzzing and clean binaries for validation — making your toolchain both surgical and repeatable. -
Robust Validation Loop
Every AI-generated exploit is executed and tested against the original binary. If it fails, contextual output is looped back to the generator to improve the payload via Model Context Protocol (MCP). -
Clean Output for Further Automation
All artifacts — validated exploits, original crashes, logs, and AI reports — are saved in a predictable folder structure suitable for CI/CD pipelines or security audits.
- Operating System: Linux (Ubuntu/Debian recommended)
- Python: 3.8+
- Memory: 8GB+ RAM recommended
- Storage: 8GB+ free space
- AFL++ fuzzer
- GCC/Clang compiler toolchain
- Python development headers
The above tools will be automatically installed during Docker deployment.
The easiest way to get started is using our pre-configured Docker container:
#Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/danindu/reforge.git
cd reforge
# Build the Docker image
docker build -t reforge .
# Run the container interactively
docker run -it reforge
# Inside the container, set up your API keys (for Proof of Concept (PoC))
echo "AI_API_KEY=your_key_here" > .env
# Make the main script executable
chmod +x run_reforge.sh
# Run the complete automation pipeline
./run_reforge.shFor AFL++ fuzzing, you need TWO versions of your target binary:
- Instrumented Binary: Compiled with AFL++ instrumentation
# Example compilation
afl-clang-fast++ -o target_instrumented target.c- Uninstrumented Binary: Standard compilation for exploit testing
# Example compilation
gcc -o target_uninstrumented target.c# Create seed directory
mkdir -p corpus/seeds
# Add sample input files
echo "sample input" > corpus/seeds/seed1.txt
echo "another sample" > corpus/seeds/seed2.txtReForge/
├── run_reforge.sh
├── run_fuzzing.sh
├── setup/
│ └── install_afl.sh
├── api_handlers/
│ ├── ai1_handler.py
│ └── ai2_handler.py
├── utils/
│ ├── exploit_validator.py
│ └── mcp_terminal.py
├── models/
│ └── llama/
├── corpus/
│ └── seeds/
├── results/
│ ├── crashes/
│ ├── exploits/
│ └── reports/
├── requirements.txt
└── .env
| Artifact | Path | What You Get |
|---|---|---|
| Validated exploits | results/exploits/ |
Self-contained Python Proof of Concept (PoC)s ready for red-team use or bug-bounty submission. |
| Raw inputs | results/crashes/ / results/hangs/ |
Original AFL++ files that triggered abnormal behaviour—kept for triage or alt-analysis. |
| Validator logs | results/validation/ |
Exact console output, return codes, and timing data for every exploit attempt—perfect for CI regression checks. |
| Human-readable reports | results/reports/ |
Markdown files from AI-2 that cover vulnerability mechanism, exploit path, impact, and defensive guidance. |
| ReForge’s directory layout makes it trivial to feed artifacts into downstream pipelines—static analysis, SBOM attestation, or continuous red-team testing—without additional parsing. |
Contributions are always welcome!
We welcome contributions from the community. Here's a detailed guide on how to get involved:
Click the Fork button on the GitHub repository to create your own copy.
Create a new branch for your feature
git checkout -b feature/your-feature-namegit commit -m "Add detailed feature description"git request-pull main origin/my-feature-branchWe sincerely thank all open-source developers and contributors for their invaluable contributions.