Download Link: https://greasyfork.org/en/scripts/535798-immediategui
ImmediateGUI is a lightweight, feature-rich JavaScript library for creating immediate-mode GUI interfaces in web applications. It provides a simple API for building customizable user interfaces with minimal setup.
- 🎨 Theming System: Built-in light and dark themes
- 📦 Immediate Mode Rendering: Build UIs with a simple, declarative API
- 🔧 Extensive Control Set: 20+ UI controls including buttons, inputs, sliders, and more
- 📑 Advanced Layouts: Support for sections, rows, tabs, and indentation
- 🎯 Draggable Interface: Optional draggable panels with auto-positioning
- 🔍 Control Registry: Query and manipulate controls by ID
- 📱 Responsive Design: Auto-scrolling with customizable max height
- 🎭 Modal Dialogs: Built-in modal and prompt systems
- ⚡ Performance: Efficient rendering with CSS variables and minimal DOM operations
- Getting Started
- Constructor
- Core Methods
- Layout Methods
- Control Methods
- Theme Methods
- Utility Methods
- Examples
// Create a new GUI instance
const gui = new ImmediateGUI({
title: 'My Application',
theme: 'dark',
position: 'right',
width: 300
});
// Add controls
gui.Label('Welcome to ImmediateGUI!');
gui.Button('Click Me', () => alert('Clicked!'));
gui.Textbox('Enter your name', '');
gui.Show();Creates a new ImmediateGUI instance.
Parameters:
options(Object, optional): Configuration object with the following properties:theme(String): Theme name -'light'or'dark'(default:'dark')position(String): Panel position -'left'or'right'(default:'right')width(Number|String): Panel width in pixels or CSS value (default:300)draggable(Boolean): Enable dragging (default:true)title(String): Panel title (default:'Immediate GUI')titleLeftAligned(Boolean): Align title to left (default:true)
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance
Example:
const gui = new ImmediateGUI({
title: 'Control Panel',
theme: 'dark',
position: 'right',
width: 350,
draggable: true,
titleLeftAligned: false
});Displays the GUI panel. If already visible, cleans up empty wrappers.
Parameters: None
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Example:
gui.Label('Hello World');
gui.Button('OK', () => console.log('OK'));
gui.Show();Hides the GUI panel without removing it from the DOM.
Parameters: None
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Example:
gui.Hide(); // Panel is hidden but can be shown againPermanently removes the GUI panel from the DOM.
Parameters: None
Returns: None
Example:
gui.Remove(); // Destroys the GUI completelyRetrieves a control element by its custom ID.
Parameters:
id(String): The custom ID assigned to the control
Returns: HTMLElement|null - The control element or null if not found
Example:
const button = gui.Button('Click', () => {}, '', 'myButton');
const retrieved = gui.GetControlById('myButton');
console.log(retrieved === button); // trueRetrieves the value of a control by its custom ID.
Parameters:
id(String): The custom ID assigned to the control
Returns: Any - The control's value (depends on control type) or null if not found
Example:
gui.Textbox('Name', '', '', 'nameInput');
gui.GetControlValueById('nameInput'); // Returns the input valueBegins a new section container for grouping controls.
Parameters:
title(String): Section header textcollapsible(Boolean, optional): Enable collapse/expand (default:false)collapsedByDefault(Boolean, optional): Start collapsed (default:false)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Example:
gui.BeginSection('Settings', true, false, 'Application settings');
gui.Label('Volume');
gui.Slider(0, 100, 50);
gui.EndSection();Ends the current section. Supports nested sections.
Parameters: None
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Example:
gui.BeginSection('Outer Section');
gui.BeginSection('Inner Section');
gui.Label('Nested content');
gui.EndSection();
gui.EndSection();Begins a horizontal row layout for placing controls side-by-side.
Parameters:
gap(Number, optional): Spacing between controls in pixels (default:2)
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Example:
gui.BeginRow(10);
gui.Button('Yes', () => {});
gui.Button('No', () => {});
gui.Button('Cancel', () => {});
gui.EndRow();Ends the current row layout.
Parameters: None
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Creates a tabbed interface with multiple panes.
Parameters:
tabs(Array): Array of tab namesdefaultTab(Number, optional): Index of initially active tab (default:0)
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Example:
gui.BeginTabs(['General', 'Advanced', 'About'], 0);
gui.SetActiveTab(0);
gui.Label('General settings');
gui.SetActiveTab(1);
gui.Label('Advanced settings');
gui.SetActiveTab(2);
gui.Label('Version 1.0');
gui.EndTabs();Switches to a specific tab for adding content.
Parameters:
tabIndexOrTabName(Number|String): Tab index (0-based) or tab name
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Example:
gui.BeginTabs(['Tab1', 'Tab2']);
gui.SetActiveTab('Tab2');
gui.Label('This goes in Tab2');
gui.SetActiveTab(0);
gui.Label('This goes in Tab1');
gui.EndTabs();Ends the tabbed interface.
Parameters: None
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Increases indentation level for subsequent controls.
Parameters:
level(Number, optional): Indentation level (default:-1for auto-increment)
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Example:
gui.Label('Level 0');
gui.BeginIndentation();
gui.Label('Level 1');
gui.BeginIndentation();
gui.Label('Level 2');
gui.EndIndentation();
gui.EndIndentation();Decreases indentation level.
Parameters: None
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Creates a text label.
Parameters:
text(String): Label textid(String, optional): Custom ID for querying (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The label element
Example:
const label = gui.Label('Status: Ready', 'statusLabel');
label.textContent = 'Status: Running';Creates a header element (h1-h6).
Parameters:
text(String): Header textlevel(Number, optional): Header level 1-6 (default:1)id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The header element
Example:
gui.Header('Main Title', 1);
gui.Header('Subtitle', 2);
gui.Header('Section', 3);Creates a clickable button.
Parameters:
text(String): Button textcallback(Function): Click event handlertooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The button element
Example:
const btn = gui.Button('Submit', () => {
console.log('Form submitted');
}, 'Click to submit', 'submitBtn');
btn.disabled = false;Creates a single-line text input.
Parameters:
placeholder(String): Placeholder textdefaultValue(String, optional): Initial value (default:'')tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The input element
Example:
const input = gui.Textbox('Enter username', 'admin', '', 'usernameInput');
console.log(input.value); // 'admin'Creates a multi-line text input area.
Parameters:
placeholder(String, optional): Placeholder text (default:'')defaultValue(String, optional): Initial value (default:'')rows(Number, optional): Number of visible rows (default:4)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The textarea element
Example:
const textarea = gui.TextArea('Enter description', '', 6, 'Describe your issue', 'descBox');
textarea.value = 'New text content';Creates a labeled number input field.
Parameters:
label(String): Label textdefaultValue(Number, optional): Initial value (default:0)min(Number, optional): Minimum value (default:null)max(Number, optional): Maximum value (default:null)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The input element
Example:
const ageInput = gui.NumberInput('Age', 25, 0, 120, 'Enter your age', 'ageField');
console.log(ageInput.value); // 25Creates a range slider with value display.
Parameters:
minValue(Number, optional): Minimum value (default:0)maxValue(Number, optional): Maximum value (default:100)defaultValue(Number, optional): Initial value (default:50)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The slider input element (has .label property for value display)
Example:
const slider = gui.Slider(0, 100, 75, 'Adjust volume', 'volumeSlider');
slider.addEventListener('input', () => {
console.log('Volume:', slider.value);
});Creates a checkbox with label.
Parameters:
label(String): Label textchecked(Boolean, optional): Initial checked state (default:false)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')onChangeCallback(Function, optional): Change event handler (default:null)id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The checkbox input element (has .label property)
Example:
const checkbox = gui.Checkbox('Accept Terms', false, '', (checked) => {
console.log('Accepted:', checked);
}, 'termsCheckbox');
checkbox.checked = true;Creates an iOS-style toggle switch.
Parameters:
label(String): Label textchecked(Boolean, optional): Initial checked state (default:false)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')onChangeCallback(Function, optional): Change event handler (default:null)id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The hidden input element with helper methods:
.toggle()- Toggle the state.setChecked(value)- Set checked state.label- Reference to label element.track- Reference to track element.thumb- Reference to thumb element
Example:
const toggle = gui.ToggleSwitch('Dark Mode', true, '', (checked) => {
console.log('Dark mode:', checked);
}, 'darkModeToggle');
toggle.toggle(); // Toggles state
toggle.setChecked(false); // Sets to uncheckedCreates a group of radio buttons.
Parameters:
options(Array, optional): Array of option labels (default:[])defaultValue(String, optional): Initially selected value (default:null)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: Object - Radio group object with helper methods:
.getChecked()- Returns the currently selected value.setChecked(value, checked)- Sets the checked state for a value[optionValue]- Direct access to individual radio elements
Example:
const radioGroup = gui.RadioButtons(['Option A', 'Option B', 'Option C'], 'Option A', '', 'optionsRadio');
console.log(radioGroup.getChecked()); // 'Option A'
radioGroup.setChecked('Option B', true);Creates a dropdown select element.
Parameters:
options(Array<String|Object>, optional): Array of options (strings or{text, value}objects) (default:[])defaultValue(String, optional): Initially selected value (default:null)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The select element
Example:
// Simple string options
const dropdown1 = gui.Dropdown(['Red', 'Green', 'Blue'], 'Red', '', 'colorSelect');
// Object options with custom values
const dropdown2 = gui.Dropdown([
{text: 'Small', value: 's'},
{text: 'Medium', value: 'm'},
{text: 'Large', value: 'l'}
], 'm', 'Select size', 'sizeSelect');
console.log(dropdown2.value); // 'm'Creates a progress bar with optional text display.
Parameters:
value(Number, optional): Initial value (default:0)min(Number, optional): Minimum value (default:0)max(Number, optional): Maximum value (default:100)showText(Boolean, optional): Show percentage text (default:true)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The progress bar element with methods:
.setValue(newValue)- Update the progress value.getValue()- Get current value.increment()- Increase by step amount.decrement()- Decrease by step amount.value- Current value.min- Minimum value.max- Maximum value.step- Step increment (default: 1)
Example:
const progress = gui.ProgressBar(30, 0, 100, true, 'Download progress', 'downloadProgress');
progress.setValue(50);
progress.increment(); // Now 51
progress.step = 10;
progress.increment(); // Now 61Creates a color picker input.
Parameters:
defaultValue(String, optional): Initial color in hex format (default:'#000000')tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The color input element
Example:
const colorPicker = gui.ColorPicker('#ff5733', 'Choose a color', 'bgColorPicker');
colorPicker.addEventListener('input', () => {
console.log('Selected color:', colorPicker.value);
});Creates a date picker input.
Parameters:
defaultValue(String, optional): Initial date in YYYY-MM-DD format (default: current date)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The date input element
Example:
const datePicker = gui.DatePicker('2025-12-31', 'Select a date', 'deadlinePicker');
console.log(datePicker.value); // '2025-12-31'Displays an image.
Parameters:
src(String): Image URL or data URIalt(String, optional): Alternative text (default:'')width(String, optional): Width in CSS units (default:'auto')height(String, optional): Height in CSS units (default:'auto')tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The img element
Example:
const img = gui.Image('https://example.com/logo.png', 'Company Logo', '200px', 'auto', '', 'logoImage');
img.src = 'https://example.com/new-logo.png'; // Update imageCreates a scrollable list of selectable items.
Parameters:
items(Array<String|Object>, optional): Array of items (default:[])defaultSelected(String|Number, optional): Initially selected item (default:null)tooltip(String, optional): Tooltip text (default:'')onChange(Function, optional): Selection change handler (default:null)itemType(String, optional): Item type -'text'or'html'(default:'text')id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The listbox (ul) element with methods:
.getSelected()- Returns selected item index or -1.setSelected(idxOrItem)- Selects item by index or value
Example:
const listBox = gui.ListBox(
['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry', 'Date'],
0,
'Select a fruit',
(item, idx) => console.log('Selected:', item, 'at index', idx),
'text',
'fruitList'
);
listBox.setSelected(2); // Selects 'Cherry'
console.log(listBox.getSelected()); // 2Creates a horizontal separator line.
Parameters:
plain(Boolean, optional): Create invisible spacer (default:false)id(String, optional): Custom ID (default:null)
Returns: HTMLElement - The separator (hr) element
Example:
gui.Label('Section 1');
gui.Separator(); // Stylized spacer
gui.Label('Section 2');
gui.Separator(true); // Invisible spacer
gui.Label('Section 3');Changes the GUI theme.
Parameters:
themeName(String): Theme name -'light'or'dark'
Returns: ImmediateGUI instance (chainable)
Example:
gui.SetTheme('dark');
// Switches to dark theme
gui.SetTheme('light');
// Switches to light themeDisplays a modal dialog box.
Parameters:
message(String|HTMLElement): Message contenttitle(String, optional): Modal title (default:'')options(Object, optional): Configuration object:title(String): Override titletype(String): Modal type -'info','warning','error','success'(default:'info')buttons(Array<String|Object>): Button configurations (default:['OK'])closeOnBackdropClick(Boolean): Close when clicking outside (default:true)width(Number): Modal width in pixels (default:400)
Returns: Object with methods:
.close()- Close the modal.element- Reference to modal element.backdrop- Reference to backdrop element
Example:
// Simple alert
const modal1 = gui.ShowModal('Operation completed successfully!', 'Success', {
type: 'success'
});
// Confirmation dialog
const modal2 = gui.ShowModal('Are you sure you want to delete this?', 'Confirm', {
type: 'warning',
buttons: [
{
text: 'Delete',
onClick: () => {
console.log('Deleted');
modal2.close();
}
},
{
text: 'Cancel',
onClick: () => modal2.close()
}
]
});Displays a prompt dialog (currently falls back to native prompt).
Parameters:
message(String): Prompt messagetitle(String): Prompt titledefaultValue(String, optional): Default input value (default:'')options(Object, optional): Configuration options (currently unused)
Returns: String|null - User input or null if cancelled
Example:
const name = gui.ShowPrompt('Enter your name', 'User Input', 'John Doe');
console.log('Name entered:', name);const gui = new ImmediateGUI({
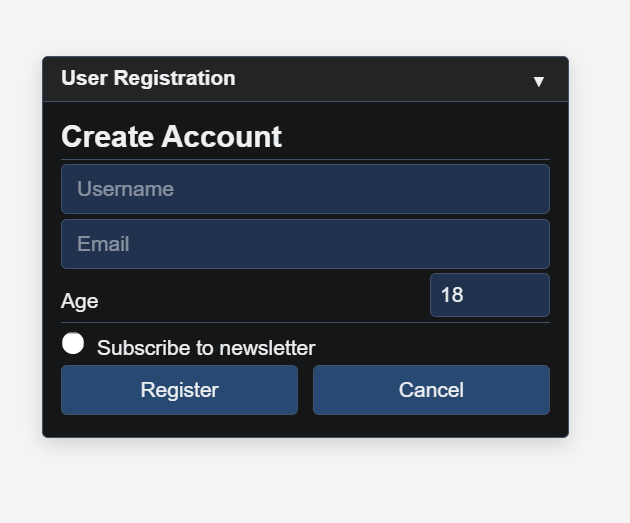
title: 'User Registration',
theme: 'dark',
width: 350
});
gui.Header('Create Account', 2);
gui.Separator();
gui.Textbox('Username', '', 'Enter your username', 'username');
gui.Textbox('Email', '', 'Enter your email', 'email');
gui.NumberInput('Age', 18, 13, 120, 'Your age', 'age');
gui.Separator();
gui.Checkbox('Subscribe to newsletter', false, '', null, 'subscribe');
gui.BeginRow(10);
gui.Button('Register', () => {
const data = {
username: gui.GetControlValueById('username'),
email: gui.GetControlValueById('email'),
age: gui.GetControlValueById('age'),
subscribe: gui.GetControlValueById('subscribe')
};
console.log('Registration data:', data);
});
gui.Button('Cancel', () => gui.Hide());
gui.EndRow();
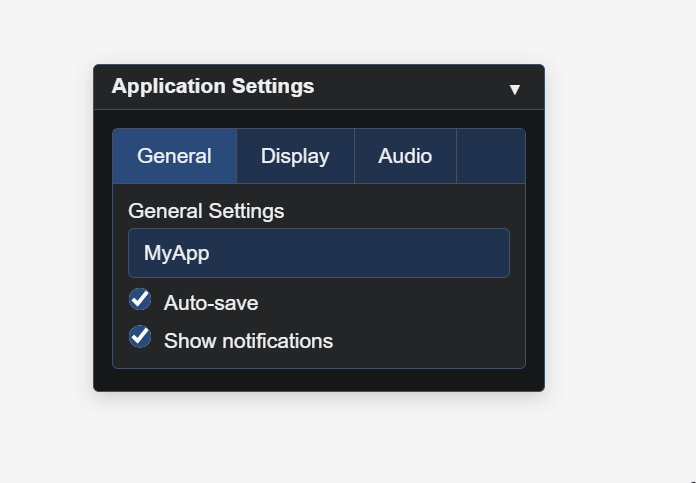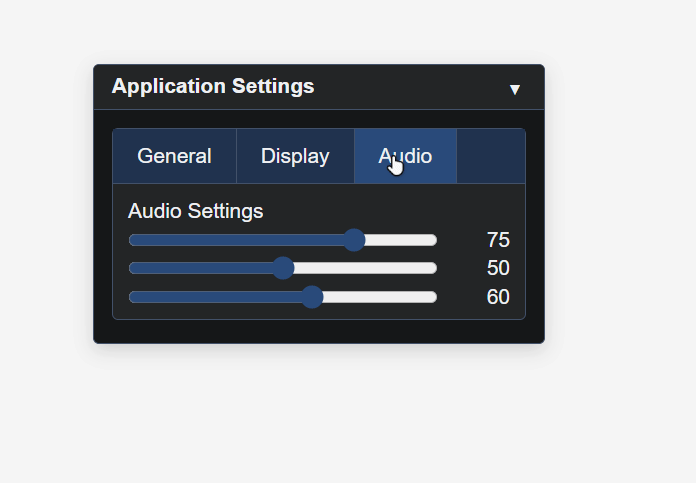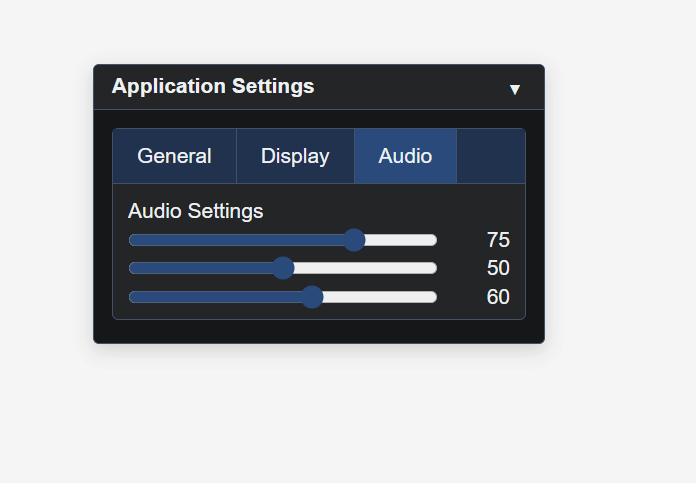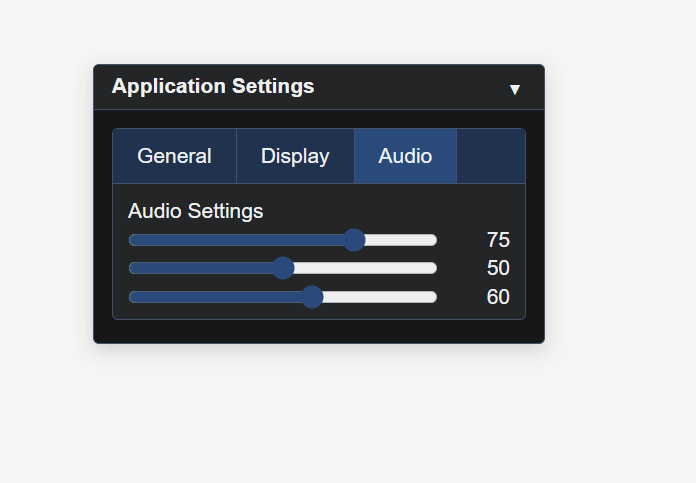
gui.Show();const gui = new ImmediateGUI({
title: 'Application Settings',
theme: 'dark'
});
gui.BeginTabs(['General', 'Display', 'Audio'], 0);
// General Tab
gui.SetActiveTab(0);
gui.Label('General Settings');
gui.Textbox('Application Name', 'MyApp');
gui.Checkbox('Auto-save', true);
gui.Checkbox('Show notifications', true);
// Display Tab
gui.SetActiveTab(1);
gui.Label('Display Settings');
gui.ToggleSwitch('Dark Mode', true);
gui.Dropdown(['Small', 'Medium', 'Large'], 'Medium');
gui.ColorPicker('#3498db', 'Theme color');
// Audio Tab
gui.SetActiveTab(2);
gui.Label('Audio Settings');
gui.Slider(0, 100, 75, 'Master volume');
gui.Slider(0, 100, 50, 'Music volume');
gui.Slider(0, 100, 60, 'Effects volume');
gui.EndTabs();
gui.Show();const gui = new ImmediateGUI({
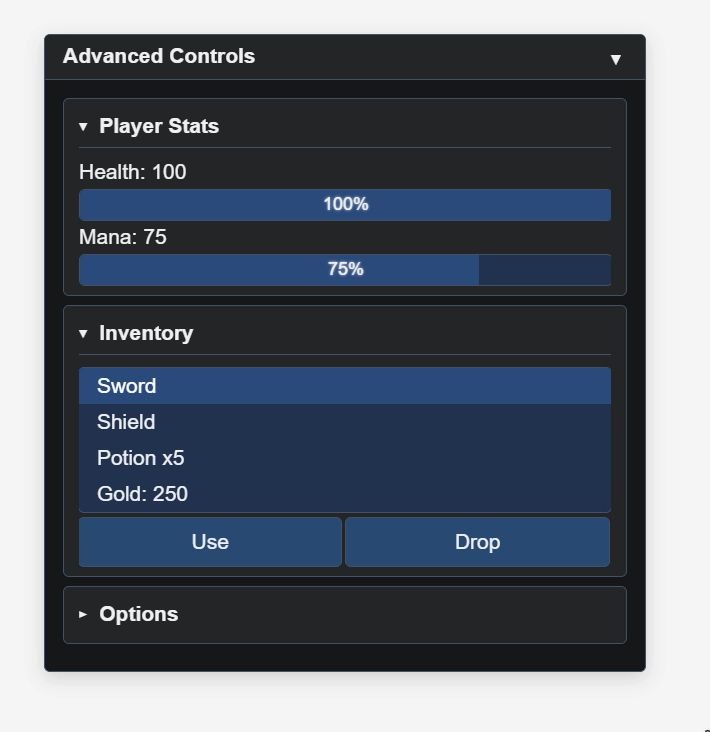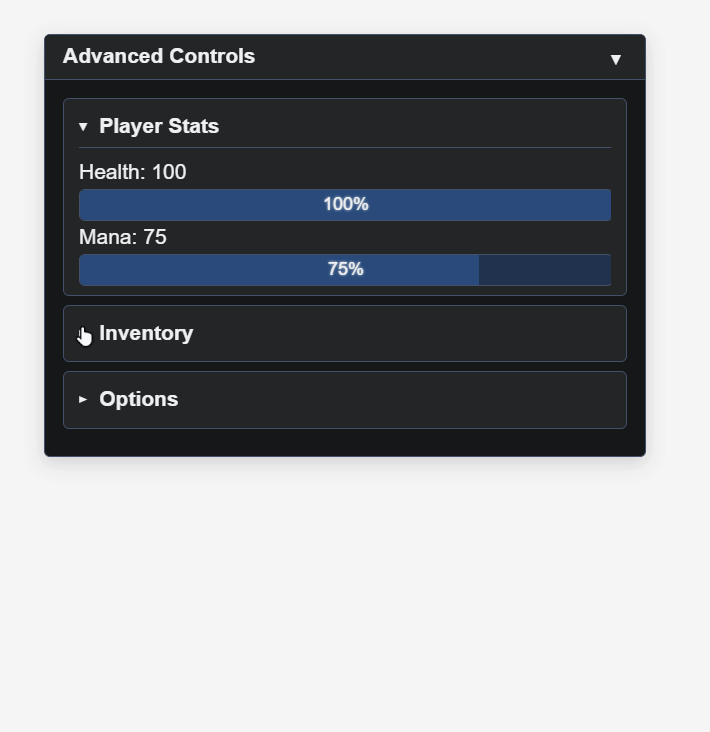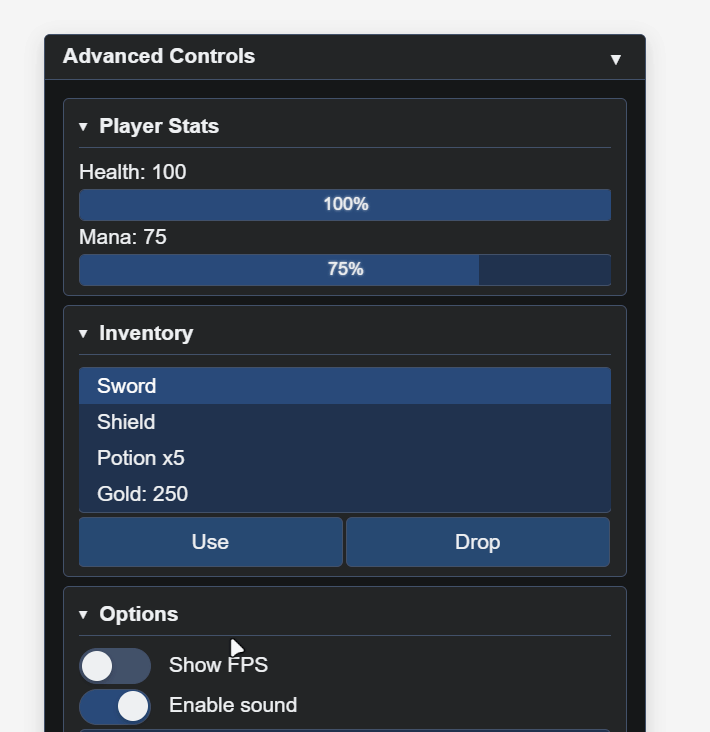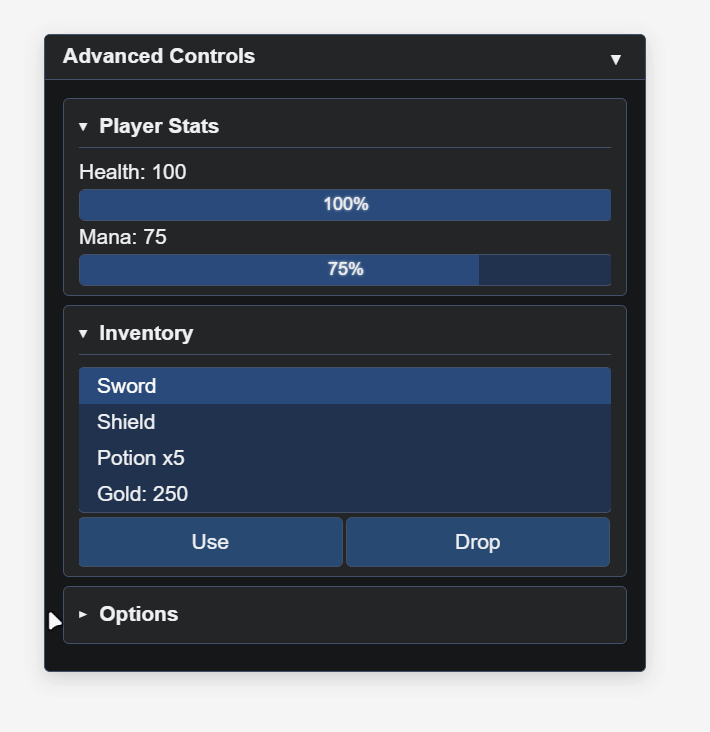
title: 'Advanced Controls',
width: 400
});
gui.BeginSection('Player Stats', true, false);
gui.Label('Health: 100');
gui.ProgressBar(100, 0, 100, true);
gui.Label('Mana: 75');
gui.ProgressBar(75, 0, 100, true);
gui.EndSection();
gui.BeginSection('Inventory', true, false);
gui.ListBox(['Sword', 'Shield', 'Potion x5', 'Gold: 250'], 0);
gui.BeginRow();
gui.Button('Use', () => {});
gui.Button('Drop', () => {});
gui.EndRow();
gui.EndSection();
gui.BeginSection('Options', true, true); // Collapsed by default
gui.ToggleSwitch('Show FPS', false);
gui.ToggleSwitch('Enable sound', true);
gui.Dropdown(['Low', 'Medium', 'High', 'Ultra'], 'High');
gui.EndSection();
gui.Show();const gui = new ImmediateGUI({
title: 'Download Manager'
});
gui.Header('Downloading Files...', 3);
gui.ProgressBar(0, 0, 100, true, '', 'downloadProgress');
gui.Label('Status: Initializing...', 'statusLabel');
gui.Show();
// Simulate download
let current = 0;
const interval = setInterval(() => {
current += 5;
const progressBar = gui.GetControlById('downloadProgress');
const statusLabel = gui.GetControlById('statusLabel');
progressBar.setValue(current);
statusLabel.textContent = `Status: ${current}% complete`;
if (current >= 100) {
clearInterval(interval);
statusLabel.textContent = 'Status: Complete!';
}
}, 200);const gui = new ImmediateGUI({
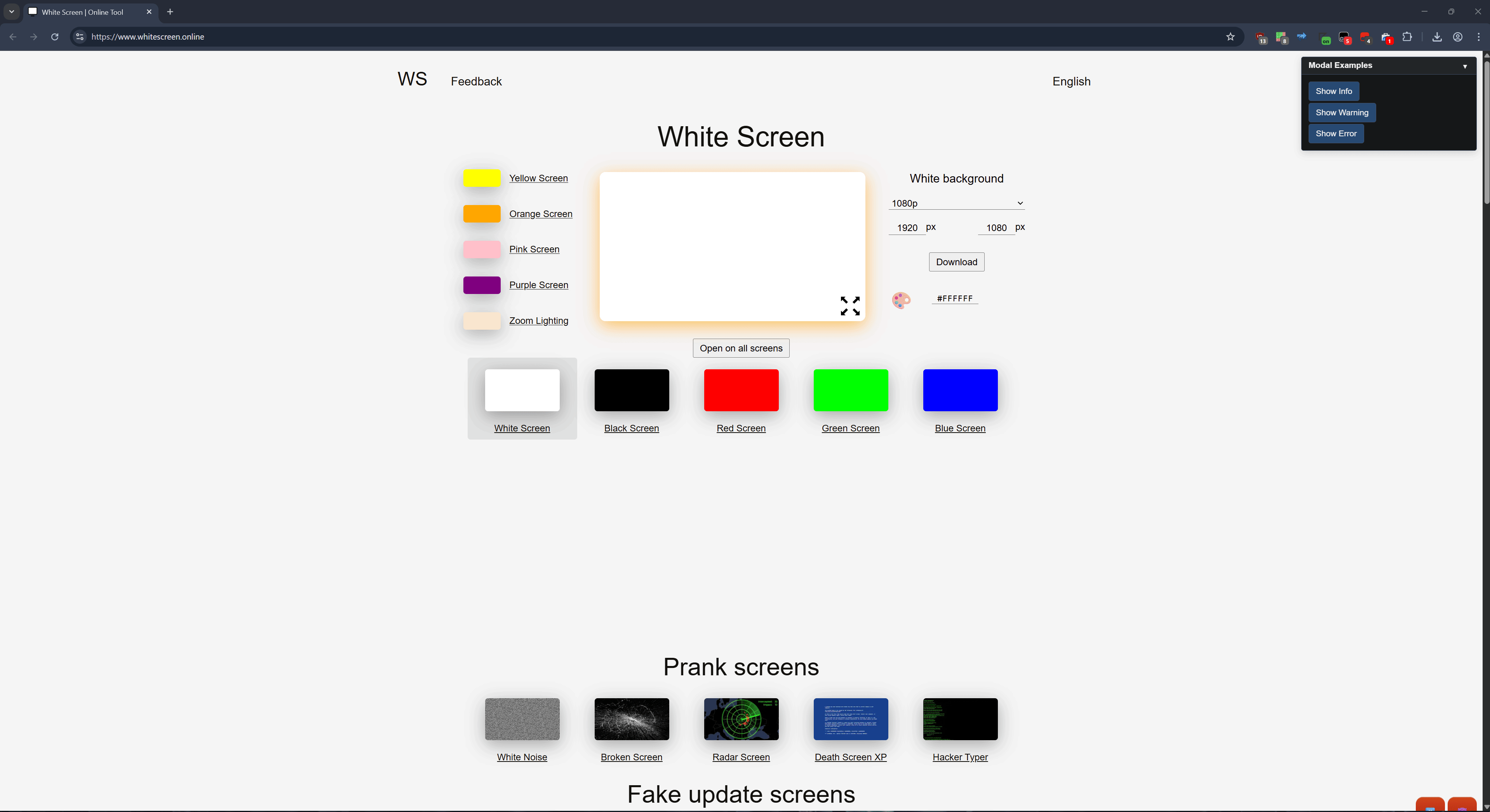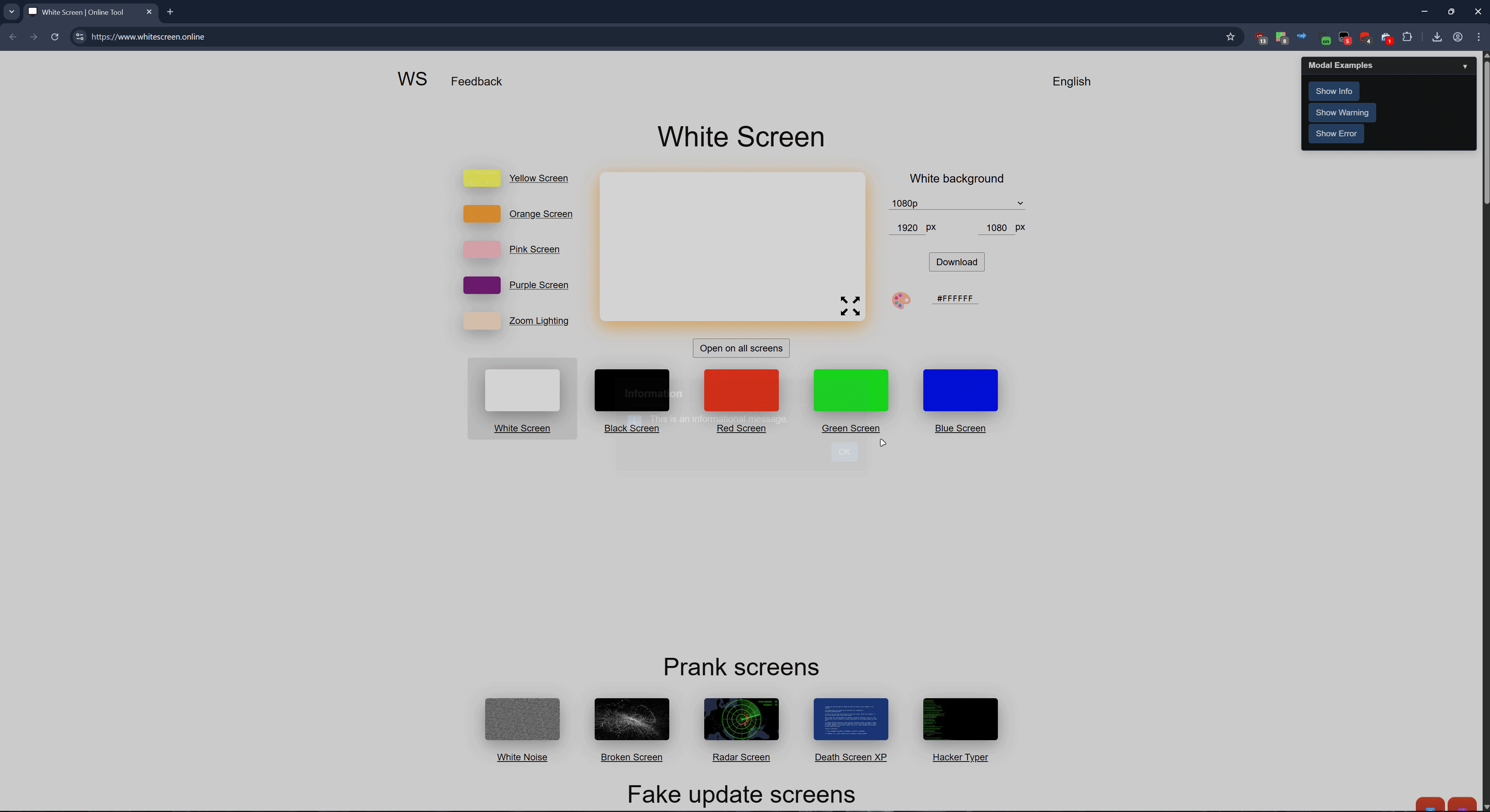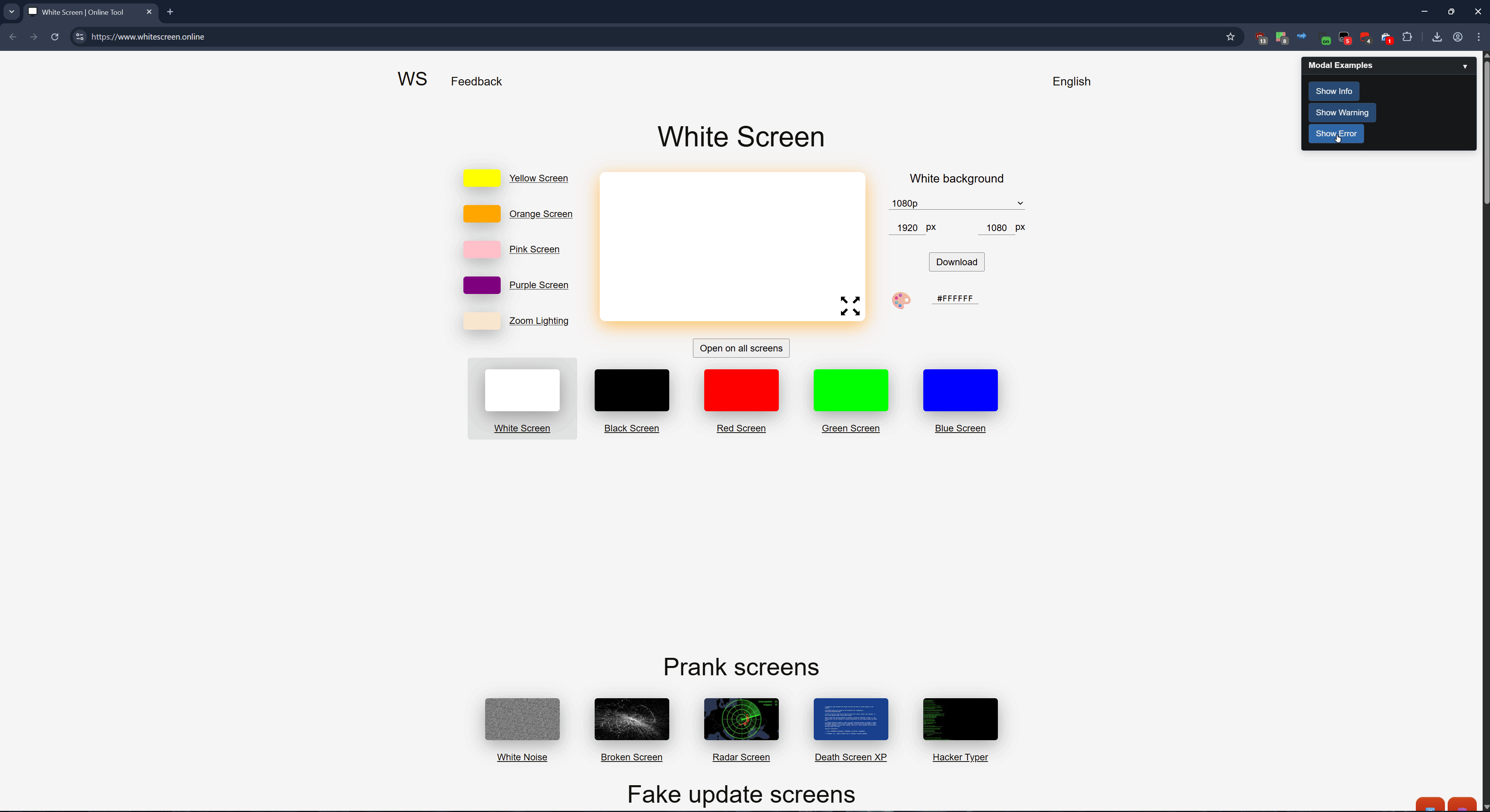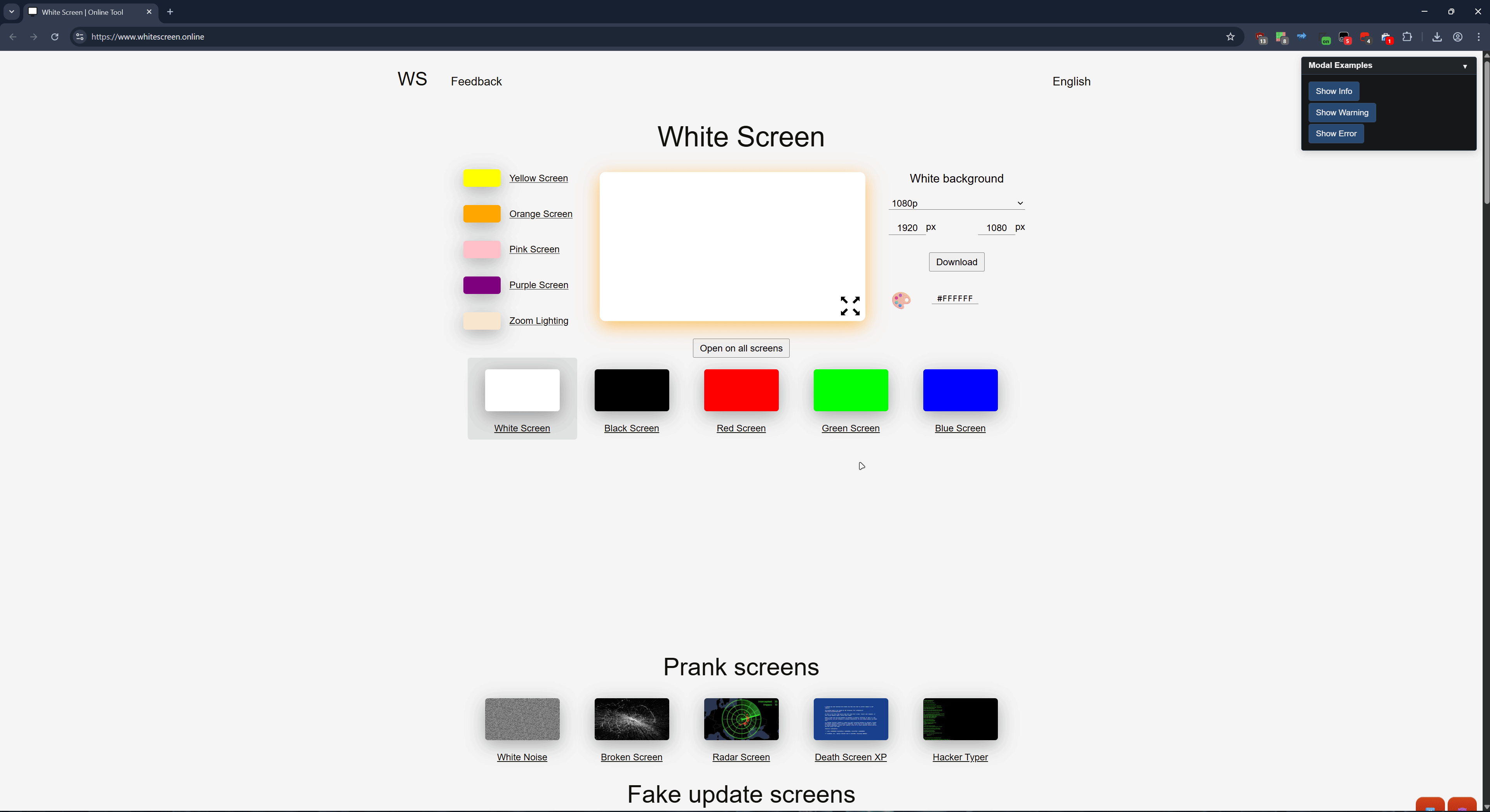
title: 'Modal Examples'
});
gui.Button('Show Info', () => {
gui.ShowModal('This is an informational message.', 'Information', {
type: 'info'
});
});
gui.Button('Show Warning', () => {
gui.ShowModal('This action cannot be undone!', 'Warning', {
type: 'warning',
buttons: [
{
text: 'Proceed',
onClick: (modal) => {
console.log('User proceeded');
modal.close();
}
},
{
text: 'Cancel',
onClick: (modal) => modal.close()
}
]
});
});
gui.Button('Show Error', () => {
gui.ShowModal('An error occurred while processing your request.', 'Error', {
type: 'error'
});
});
gui.Show();const gui = new ImmediateGUI({
title: 'Task Manager'
});
let tasks = [];
gui.Header('Add New Task', 4);
gui.Textbox('Task description', '', '', 'taskInput');
gui.Button('Add Task', () => {
const input = gui.GetControlById('taskInput');
if (input.value.trim()) {
tasks.push(input.value);
input.value = '';
updateTaskList();
}
});
gui.Separator();
gui.Label('Tasks:', 'taskListLabel');
gui.Show();
function updateTaskList() {
const label = gui.GetControlById('taskListLabel');
label.textContent = 'Tasks: ' + (tasks.length > 0 ? tasks.join(', ') : 'None');
}const gui = new ImmediateGUI({
title: 'Complex Layout',
width: 450
});
gui.BeginSection('User Profile');
gui.BeginRow();
gui.Image('https://via.placeholder.com/80', 'Avatar', '80px', '80px');
gui.Label('John Doe');
gui.EndRow();
gui.BeginIndentation();
gui.Label('Email: john@example.com');
gui.Label('Member since: 2025');
gui.EndIndentation();
gui.BeginSection('Preferences', true);
gui.RadioButtons(['Email', 'SMS', 'Push'], 'Email');
gui.EndSection();
gui.EndSection();
gui.Separator();
gui.BeginRow(15);
gui.Button('Save', () => console.log('Saved'));
gui.Button('Cancel', () => gui.Hide());
gui.EndRow();
gui.Show();ImmediateGUI uses modern JavaScript and CSS features. It is compatible with:
- Chrome/Edge 90+
- Firefox 88+
- Safari 14+
- Always call
gui.Show()to display your GUI after adding controls - Use custom IDs when you need to query or update controls later
- Layout methods are chainable -
BeginSection(),EndSection(),BeginRow(), etc. return the GUI instance - Control methods return the control element - Use
GetControlById()to access controls later - Use sections and tabs to organize complex interfaces
- Leverage the control registry with
GetControlById()for dynamic updates - Remember to call
EndSection(),EndRow(), andEndTabs()to properly close layouts - Use tooltips to provide additional context without cluttering the interface
Q: Controls aren't appearing
- A: Make sure you called
.Show()at the end of your chain
Q: Layout looks broken
- A: Check that all
Begin*methods have correspondingEnd*methods
Q: Can't access control after creation
- A: Control methods return the control element itself. Store the return value or assign a custom ID and use
GetControlById()
Q: Theme not updating
- A: Call
SetTheme()after creating controls, or recreate the GUI with the new theme
Q: Modal not showing
- A: Ensure the GUI container is in the DOM (call
.Show()first)