Spring-Design-Patterns
Design Patterns and Implementation Source codes
Install terminal http
- Factory pattern in action
- The Builder pattern
- The Buillder pattern in action
- The Singleton pattern
- Singleton pattern in action
- The prototype pattern
- Prototype pattern in action
- The Adapter pattern
- Adapter pattern in action
- The Decorator pattern
- Decorator pattern in action
- The Proxy pattern
- The Repository pattern
- Repository pattern in action
- The Template pattern
- The Model-View-Controller (MVC)
- The Observer pattern
- The Command pattern
- The Mediator pattern
- The Interpreter pattern
Singleton Design Pattern is basically limiting our class so that whoever is using that class can only create 1 instance from that class.
I create a private constructor which limits access to the instance of the class. Than I create a getter method where we specify how to create&use the instance. - I am using JAVA Encapsulation OOP concept.
-
Factory pattern in action
a. Bean Factory b. Leveraged heavily in the framework. - Factory allows construction of similar classes of different types using a factory method. - Method call creates the object for you and serves it back - Constructed objects are from classes that share are interface or parent class.Why Use this pattern?
- Allows you to not worry about class construction in more that one place. - Allows you to leverage the interface for repetitive operations. - Lack of construction code cleans up code and also makes copy/paste errors less likely.
-
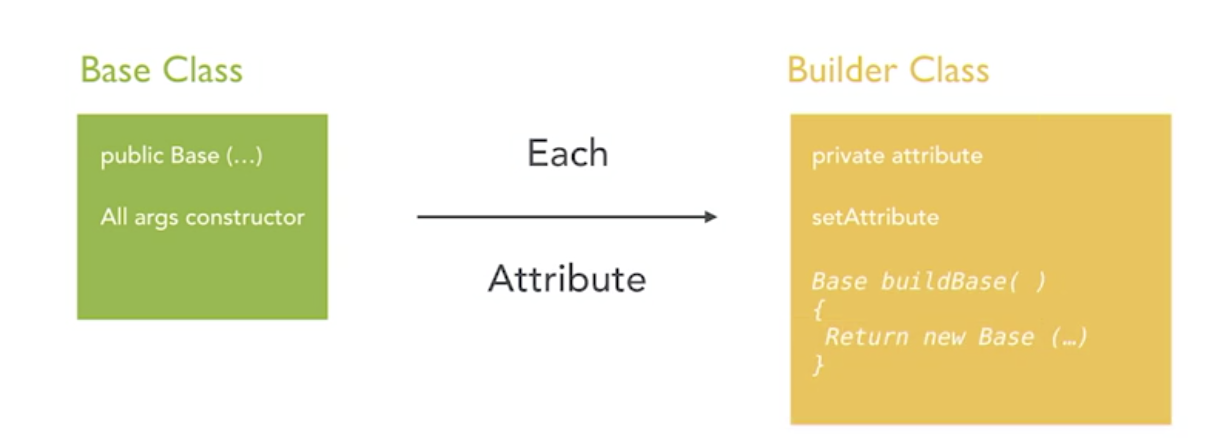
Building pattern
- Useful when object creation has many parameters. - Becomes increasingly more useful when some or all parameteres are optional. - Can make code easier to read because of reduced lines for construction when compared with setters. -
Singleton Pattern
- Every bean by default is a singleton. - NOT a classic singleton, but behaves the same. - Beans must be thread safe. - Class stores reference to instance of itself - Constructor is private - Static **getInstance()** method returns reference of self instance, or if not constructed it constructs in thread sage manner. - The **new** command is never called on the class outside of the **getInstance()** method. - Expensive object creation - Control concurrency associated shared resources - Storing static state for multiple parts of the application
-
Prototype pattern
- Beans marked as prototype are treated as such. - In Spring, the bean configuration is used as the prototype. - New instances are created, not cloned, when needed by runtime. - A class is created in a prototypical manner. - Instance is cloned at runtime to give new instances that are not the prototype, but act the same and have the same state. - In java, this is usually done with the Cloneable interface. - Prototypes are usually deep clones of objects to maintain safety. - Very useful when object creation is expensive, but the wrapper needs to be unique. - Useful with objects that must act thread safe, but need to store state. - Provide cost savings on object creation.
-
Adapter Pattern
- Used often in Spring integration when dealing with Channel Adapters for communication with different systems. - Used in internal operations of AspectJ and used during load. - Two different interfaces share a common operation. - Adapter is a wrapper class that is created that holds an instance of one interface and implements the others - The shared operation of the wrapper interface is implemented to call shared operation of the wrapped interface. - Legacy or third part code needs to fit into your code. - Shared functionality on disparate objects to reduce code. - Coding to interfaces in routine workflows and leveraging adapters reduces code while improving readablity.
-
Decorator Pattern
- The framework itself uses decorators.
- Injecting decorated objects is difficult in Spring because of how bean references work.
- To use of @Qualifier annotation becomes required.
- Adding responsibilities to an object dynamically at runtime.
- Composition instead of inheritance
- Inherited based classses compose new behavior and responsibility by becoming additive or decorated.
- Allows an object to be open for extension and closed for modification while still adding responsibilities.
- Composition over inheritance
- Add behavior without code modifications, support non breaking changes
- Can also remove behavior through encapsulation via decoration
-
Proxy Pattern - Every bean you create gets a proxy around it since Spring 4 - Additional proxies are added, usually through annotation - Creating proxies in Spring usually revolves around aspect-orient programming - Spring : Framework in Depth - Use a an intermediary object in place of a real object - Itermediary protects the real object - Intermediary controls the instantiation of the real object - Intermediary can add behavior to real object - Behavior needs to be added to a method when it is called in specific situations - Remote object access - Start with an interface - Create real object to extend the interface - Create proxy object to extend the interface and keep and handle the real object - Create the object add behavior, other protections - With Spring, should be leverage AOP - @Transactional, @Cacheable and others
-
Repository Pattern
- Most of Spring Data is based on the Repository Pattern
- Spring JDBC can be used to also create Repository actions
- Repository RestResource add a RESTful web service onto a raw repository
- Not a GoF pattern, but was introduced in Domain-Driven-Design by Eric Evans
- Simple operations of an entity or business object without knowledge of other entities (As a DAO)
-
Inversion of Control (IoC) - Reduces noise in your code - Reduces object coupling - Reduces the defects that arise form incorrect construction