Based on the documentation here: Contributor Onboarding · Azure/azure-functions-host Wiki
Visual Studio 2022 Download
Download a copy of the Dev branch or whichever branch you want to test locally and extract the contents to a safe location. Azure/azure-functions-host: The host/runtime that powers Azure Functions (github.com)
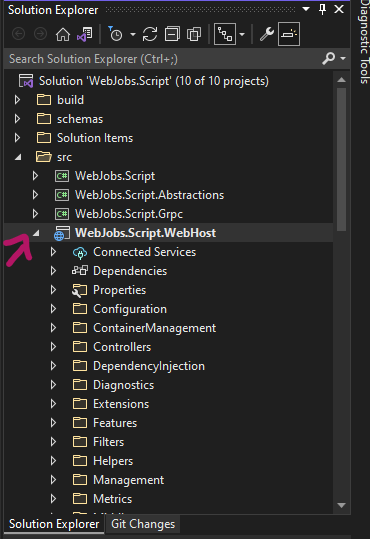
Open up the WebJob.Script.sln with Visual Studios 2022
Set the WebJobs.Script.WebHost to the startup project
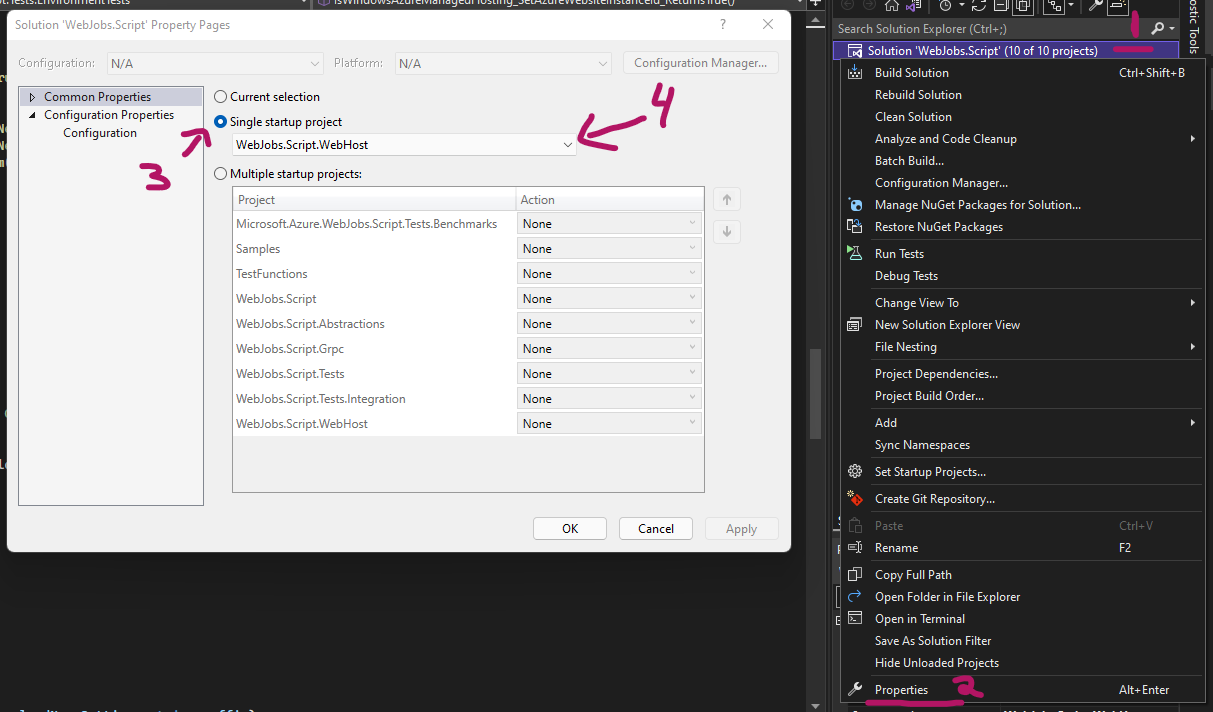
- Right click the solution in the solution explorer
- Click on Properties
- Select "Single startup project"
- select WebJobs.Script.WebHost
With the Properties opened up…
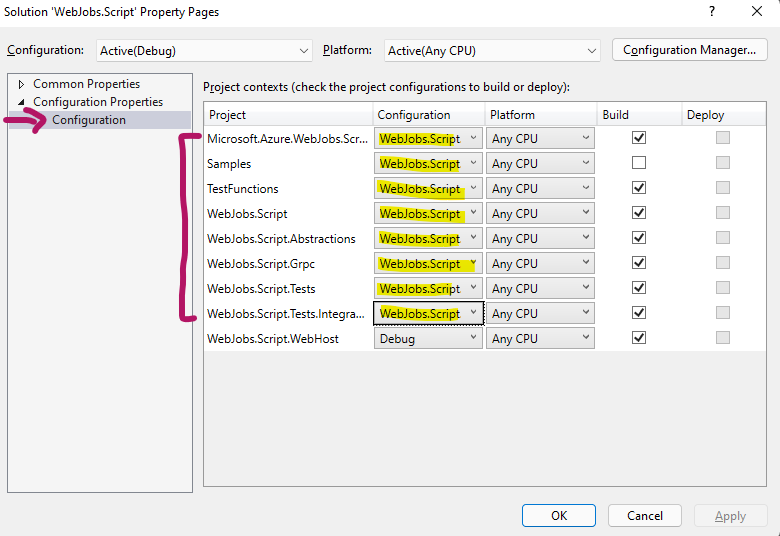
- Select Configuration under the Configuration Properties
- Set every project EXCEPT the WebJobs.Script.WebHost Configuration to "WebJobs.Script.WebHost.Core"
Now we need to add some Environment Variables.
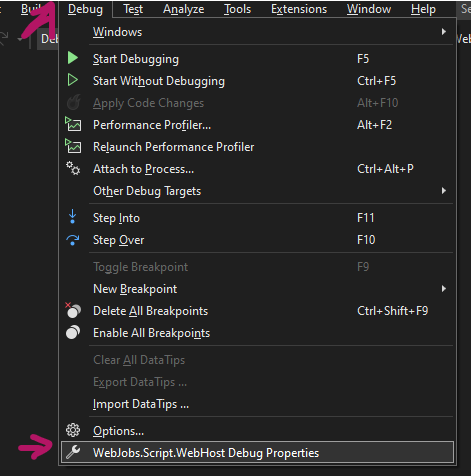
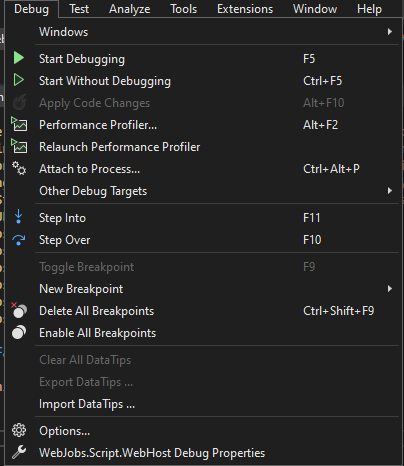
- Click Debug from the top menu and select WebJobs.Script.WebHost Debug Properties
Now Select WebJosbs.Script.WebHost as the launching program
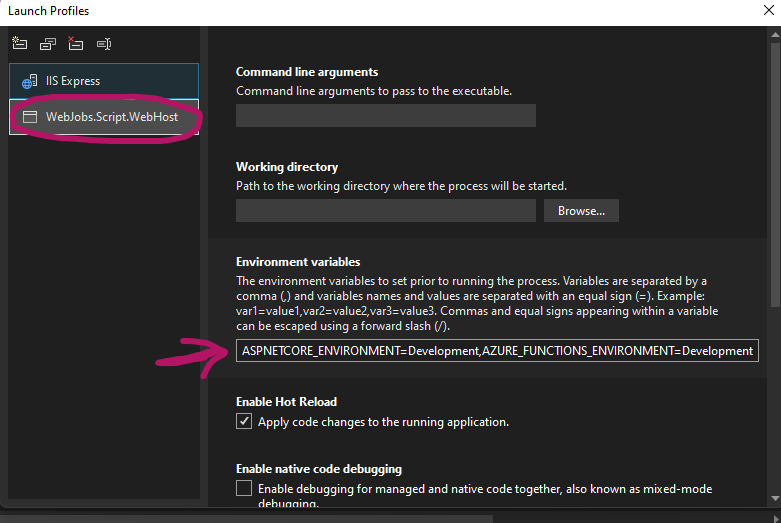
- Add in 2 variables, Note that they may already be there.
ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Development
AZURE_FUNCTIONS_ENVIRONMENT=Development
At this point, we want to verify that host will come up locally for us.
Ensure that WebJobs.Script.WebHost shows up in the top menu like below, and click on the debug button.

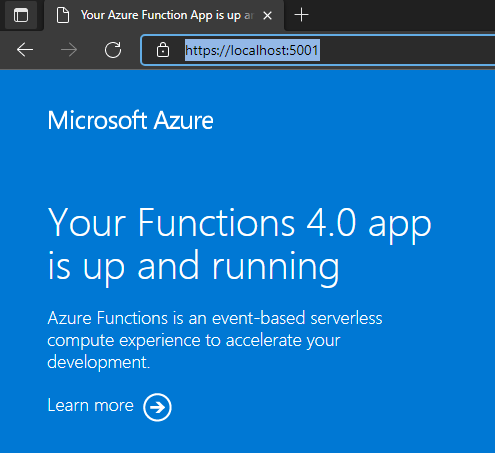
It may take a minute to come up. You can view the Console window that opens up, which will contain some logging info during the startup.
After it is running it should automatically open a browser window which will show that your functions x.0 app is up and running.
To get the Locally running function host to identify and trigger a locally stored and built function is pretty straight-forward.
First we just open Visual Studios 2022 and create a simple HttpTrigger (I will mention other trigger types later).
Note: That when creating an HttpTrigger to select the Authorization Level as Anonymous. This is because when running the function host locally, it does not create the function keys used to trigger the function.
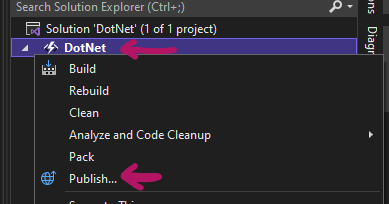
Once you are ready to publish the function, right click on the function in the solution explorer and click publish.
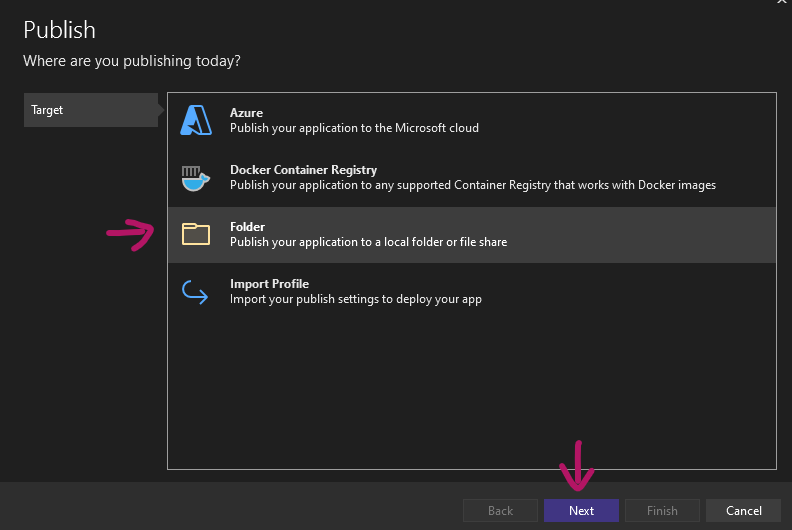
Rather then selecting the usual Azure, we will select Folder and click next.
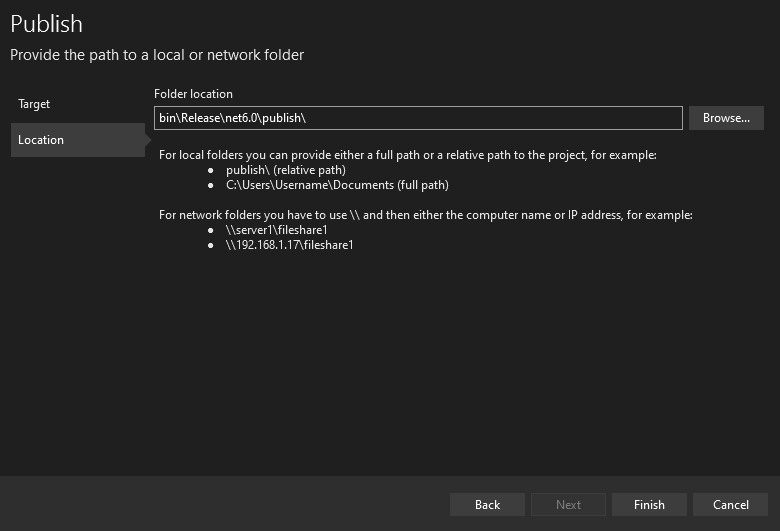
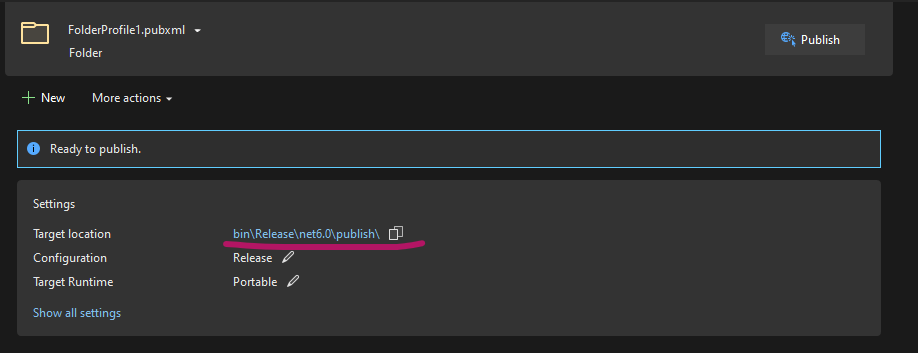
On the Publish page, select the folder path of the published content. Remember that it is relative to the project path.
Note: You will need the full path for the final section.
Once you are on this scree, you can click Publish.
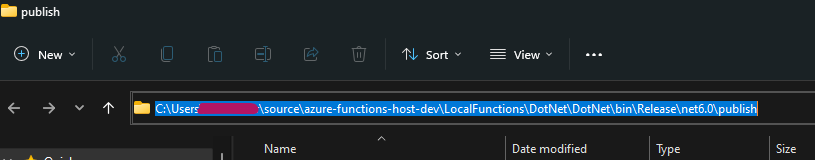
After it has successfully published you can click on the Target location link to open the location in a file explorer window.
Select the Url bar and highlight the full path and copy it to the clipboard
We now need to add the full path to the locally published function to the functions host.
Open back up the Function Host sln in Visual Studios 2022, if it isn't already still open.
Once it is open, select Debug from the top menu bar and select WebJobs.Script.WebHost Debug Properties
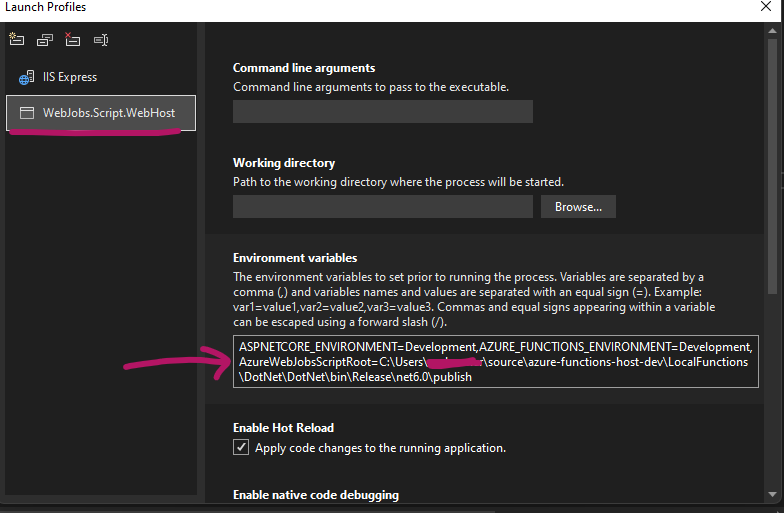
Now select the WebJobs.Script.WebHost and we are going to add a new Environment variable to the list.
Add the AzureWebJobsScriptRoot which will have the value of the full path to the published folder from earlier like below.
Note: Remember to separate the variables with a comma (,)
In order to use another Function Trigger type, we need to add in the AzureWebJobsStorage appSettings and any other needed appSetting.
Once you created and published to folder a function of another trigger type, such as a QueueTrigger, we need to add the needed dependency / settings and connection string.
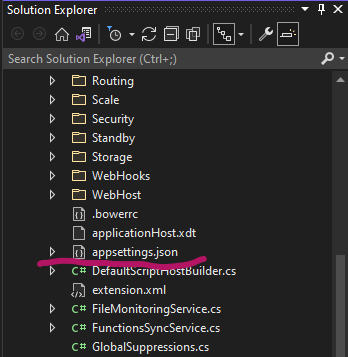
In the solution Explorer expand the WebJobs.Script.WebHost
Scroll down and you will see appsettings.json, double click to open it.
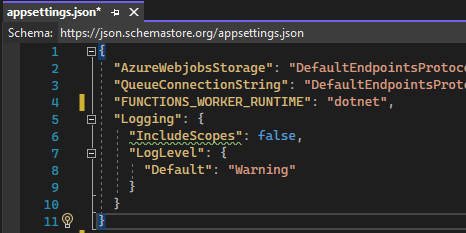
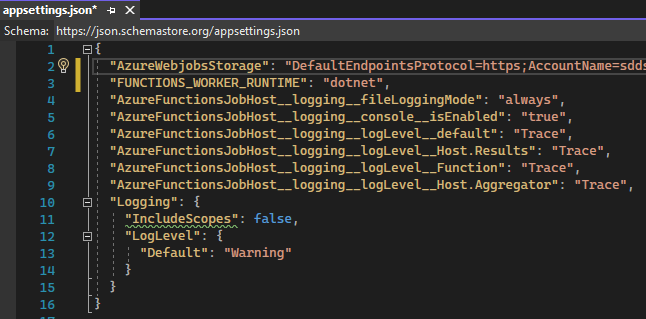
Now we will add in the AzureWebJobsStorage and QueueConnectionString to the appsettings.json
Note: Your appsettings.json may look a little different then mine.
The AzureWebJobsStorage is the connection string to a Azure blob storage account.
The QueueConnectionString is the connection string used by my Queue Trigger function to connect to the storage queue.
Note: Your appsetting name may be different then mine, depending on what you named it in your function
To add in additional logging output, we can override the Functions host logging levels.
Note: the below settings are recommended for Debug environment only and should not be used in a fully deployed function or functions host.
"AzureFunctionsJobHost__logging__fileLoggingMode": "always",
"AzureFunctionsJobHost__logging__console__isEnabled": "true",
"AzureFunctionsJobHost__logging__logLevel__default": "Trace",
"AzureFunctionsJobHost__logging__logLevel__Host.Results": "Trace",
"AzureFunctionsJobHost__logging__logLevel__Function": "Trace",
"AzureFunctionsJobHost__logging__logLevel__Host.Aggregator": "Trace",
"Logging": {
"IncludeScopes": false,
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Warning"
}
}