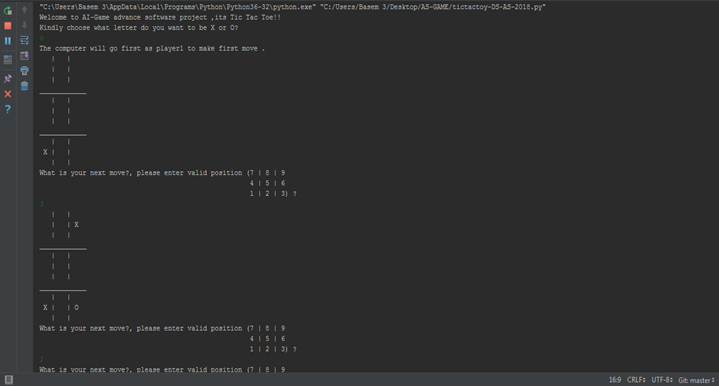
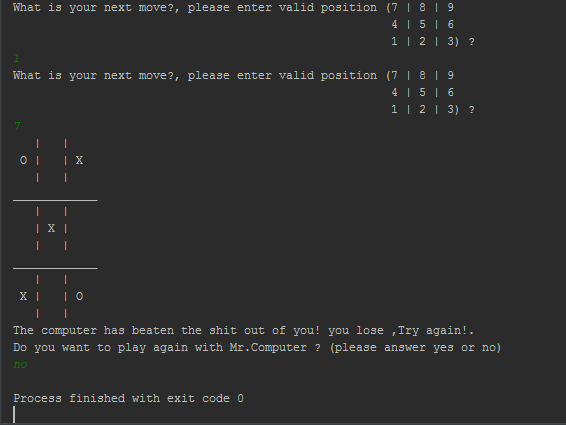
Tic Tac Toe is a game against a simple artificial intelligence. An artificial intelligence (or AI) is a computer program that can intelligently respond to the player’s moves. This game doesn’t introduce any complicated new concepts. The artificial intelligence that plays Tic Tac Toe is really just a few lines of code.. Back when we were a kids , two children’s used to play Tic Tac toy with paper and pencil when one of them is “X“ and the other is “O“ and if one of the players get three of the their marks on the board in row or column or one of the two diagonals , they WIN And when the board fills up with neither player winning the game break even.
-
Download Pycharm Professional from here
-
Install it on your local host
-
Open Pycharm after the installation
-
Create new project by clicking on File - > New Project, then in New Project panel choose (Pure Python) and location path of your project in the directory that you want
-
Click on Create and wait couple of minutes to create virtual environment
-
Right click on the project name that contain the path, it will look like this (test C:\Users...\test, which test is the name of the project
-
Choose New -> Python file
-
Copy and paste the code to Python file that you created
-
Click Run
-
Have Fun!
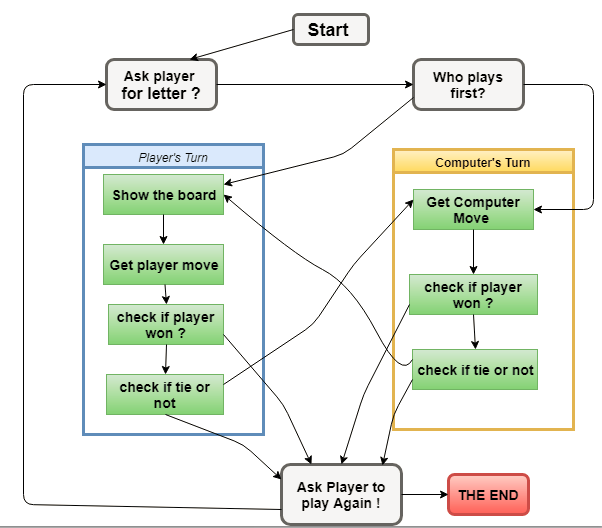
The below figure shows how the Flowchart for this Tic Tac Toe looks like, in this game the player (you) will choose between "X" and "O" and who take the first turn will be randomly chosen by using random module in python “ import random ”
Tic Tac Toe flowchart:
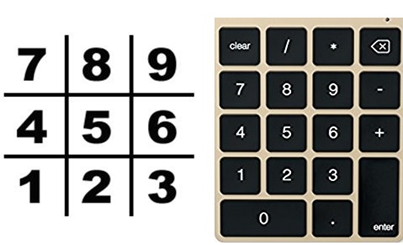
Note: the board is numbered as keyboard number pad as per the following sample
In this program, the Tic Tac Toe board is simply represented as a list of strings. Each string will represent one of the nine spaces on the board (either be 'X' for the X player, 'O' for the O player, or a single space ' ' for a blank space.). To make it easier to remember which index in the list is for which space, same as the numbers on a keyboard’s number keypad, as per the Figure 4 we can also agree that list of 10 strings stored in variable board will make board [5] in center, board [1] in bottom left and board [6] in the right side and so on so forth
Functions
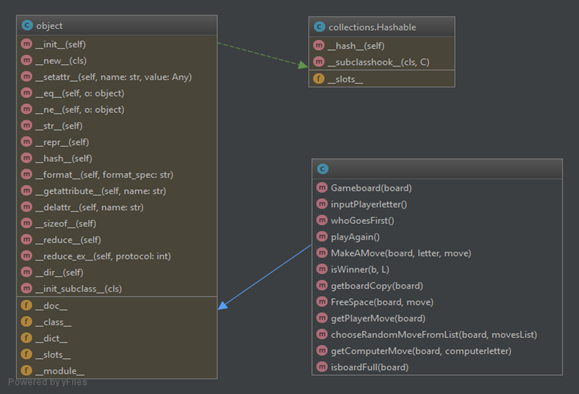
• GameBoard( ) function to draw the board of strings (1 till 9).
• inputPlayerletter( ) function so the player can choose which letter will start with “X” or “O” , and the computer will get the second letter.
• whoGoesFirst(): function to randomly choose the player who will go first in the game , in this case player or computer
• playAgain() Function to repeat the game again by using “random.randint(0, 1) == 0” , if (0) the computer will have the first move , (1) the player will have the first move.
• MakeAMove() Function to pass the parameter for the borad[ ] with chosen letter by player or computer.
• isWinner() Function with long return line to check if there is three spaces in board filled with same letter horizontally , vertically or diagonally.
• getboardCopy() Function to make copy of the board of TTT in the game , making append to the board with new copy of it without changing the original board and moves has been played before.
• FreeSpace() Function to check if the entire board filled with sting or not , make sure to choose the right empty slot to make a move, otherwise a message will pop up to ask for available move.
• getPlayerMove() Function to ask the player to enter the number of the space that wants to move on , the (while) loop here makes sure that the player is choosing the empty space each move and check if the space is already taken before or not by calling FreeSpace() , and finally return the move as integer from string.
• chooseRandomMoveFromList() Function will first check that the space is valid to make a move on , and returns a valid move from the passed list on the passed board and None in case of no valid/true move made.
• getComputerMove() The algorithm which has been used in TTT game is simple algorithm to compute the results , this algorithm is implemented and used in the getComputerMove() function.
• isboardFull() Function that returns True in case all moves(10 strings 1-9, index 0 not used) has already passed through with “X” or “O” , and False in case of any spaces found not filled yet , in other words , isbordFull() invert function of FreeSpace().
• Class Diagram
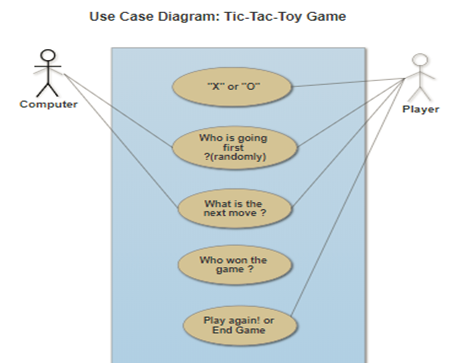
• Use Case Diagram
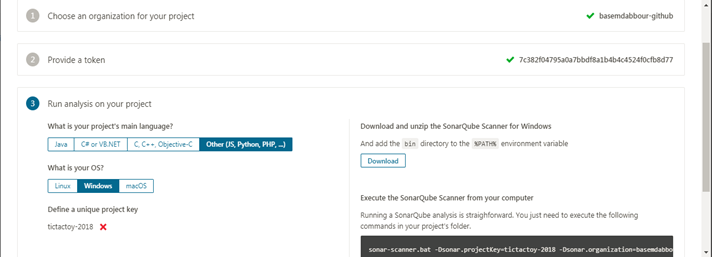
With SonarQube we can check how much the code is clean from bugs and vulnrability By creating new project with token name either existing one or generate new which is linked to new project for testing and analysing by applying one of the metrics (bugs test , line of cods ... e :
The following command will scan the code and do the test
sonar-scanner.bat -Dsonar.projectKey=AS-GAME -Dsonar.organization=basemdabbour-github -Dsonar.sources=. -Dsonar.host.url=https://sonarcloud.io -Dsonar.login=ca8628234e17b3cb7011afc999c047e0226ac2d7
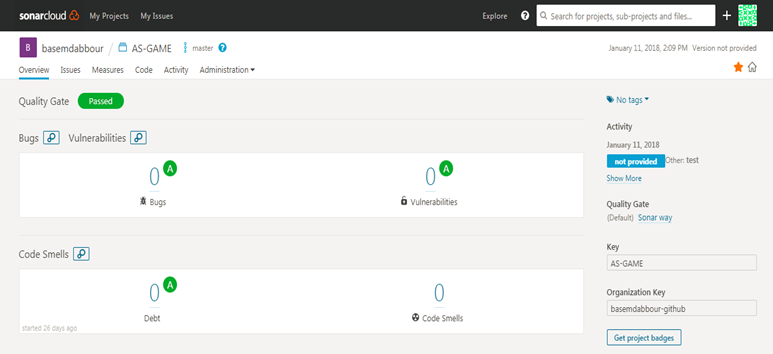
And the result will be like this
Writing any software is the most complicated endeavors for human, as Bidan Kernigan the co-author of the AWK PL who summed up the true nature of software development in his book, said "Controlling complexity is the essence of software development. The harsh reality of real world software development is that software is often created with intentional, or unintentional, complexity and a disregard for maintainability, testability, and quality. The end result of this unfortunate reality is software that can become increasingly difficult and expensive to maintain and that fails sporadically and even spectacularly.".
1. Always use Class-functions approach
Using function is a block of reusable line of codes that is used to perform a specific action and its one of the important steps when writing software code in any programing language. List of advantages
• Reducing duplication of code.
• Decomposing complex problems into simpler pieces.
• Improving clarity of the code.
• Reuse of code.
• Information hiding.
You can see all TicTacToy functions previouslly in section 5 - Game In Details.
2. Use modeul carefully
A module can contain executable statements as well as function definitions. These statements are intended to initialize the module. They are executed only the first time the module name is encountered in an import statement. Each module has its own private symbol table, which is used as the global symbol table by all functions defined in the module.
The Advantages
• No global namespace for objects
• Python Modules are very easy to import and use
In Tic Tac Toe game, a "random" module is imported not just to reduce the lines of code, but also contain useful commands as per the following
• random.randint(x,y) to return random integer from interverl
if random.randint(0, 1) == 0:
return 'computer'
else:
return 'player'
• random.choice(seq) to return random element from non empty sequance or list ,otherwise return None
if len(possibLMoves) != 0:
return random.choice(possibLMoves)
else:
return None
3. Organize your code
Don‘t make your code messy especially if you are writing thousands of lines of code, organize your python code by listing all functions first in the body and then the main
4. Use #Comments
Always use #comments in your project to describe what this lines of code do?, not just for your future reference, but also for other people who might end up reading your project and evaluating it.
5. A clean code hypothetical test
Always make hypnosis to check if there is any problem and solution for it: run tests on your code multiple times with different approach to insure and prove that your software can continuously works without breaking down so bad such as the following snippets code:
#Check if the player could win on their next move, and block them.
for i in range(1, 10):
copy = getboardCopy(board)
if FreeSpace(copy, i):
MakeAMove(copy, playerletter, i)
if isWinner(copy, playerletter):
return i
#Try to take one of the corners, if they are free.
move = chooseRandomMoveFromList(board, [ 1, 3, 7, 9 ])
if move != None:
return move
#Try to take the center, if it is free.
if FreeSpace(board, 5):
return 5
#Move on one of the sides.
return chooseRandomMoveFromList(board, [ 2, 4, 6, 8 ])
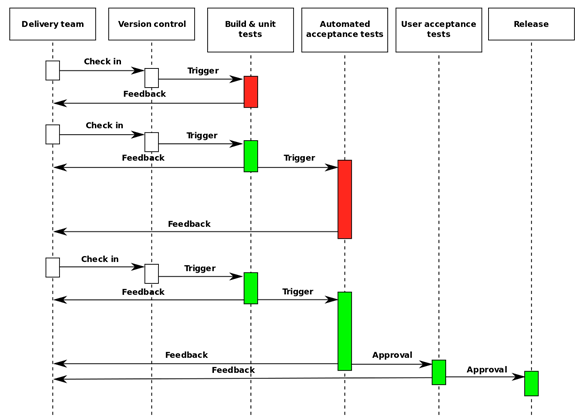
With the help of the Git plugin Jenkins can easily pull source code from any Git repository that the Jenkins build node can access.
AOP is very useful to avoid cross-cutting features that affect multiple components of the system. Some examples are logging, timing, security authorization, etc. In the case of Tic Tac Toe we can use AOP to add logging to the code, so instead of adding log.print to each function in the program we can define one logging Aspect and define a joint-point of all the main functions that we need to add log to.
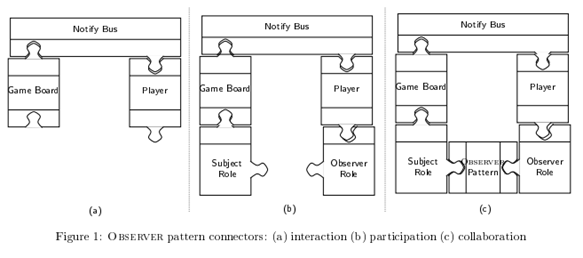
The below figure shows Separate deferent concerns of implementing the Observer pattern in the context of TicTacToe a board game of Two or more players each modify the board game and need to be notified whenever some of the other players has changed the board, this is one of the powerful illustration of the AOP technique.
The big picture was broken into smaller pieces of concern which improve the programming style.
In this figure, we can consider the component based approach for implementing an observer pattern. The board game and players are components, which means that in the board game, each player is an observer who needs to be notified whenever the board game is changed by another player. However it’s connecting the board and the player by a notification bus as shown in (a) which describe the connectors between the components.
The connector represents communication channels between board game and player, whenever a change happened, it will update the player about that change.
Domain Specific Languages can serve all sort of purposes. They can be used in different contexts and by different kinds of users. Some DSLs are intended to be used by programmers, and therefore are more technical, while others are intended to be used by someone who is not a programmer and therefore they use less geeky concepts and syntax.
There are several examples of public DSL which are used a lot as per the following
• DOT – A DSL to define graphs.
• Sed – A DSL to define text transformation.
• Gawk – A DSL to print and process text.
• Website-spec – A DSL for functional web testing.
• SQL – databases.
• HTML – web layout.
• UML – visual modeling.
• PlantUML – A DSL to draw UML diagrams: PlantUML Can be used to define UML diagrams of different kinds.
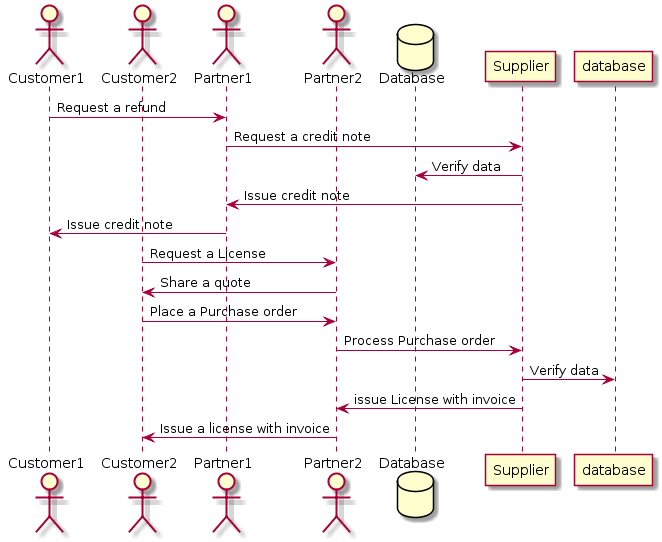
For example using PlantUML, we can define a Sequence Diagram as per the following DSL Demo example snippet:
@startuml
actor Customer1
actor Customer2
actor Partner1
actor Partner2
database Database
Customer1 -> Partner1: Request a refund
Partner1 -> Supplier: Request a credit note
Supplier -> Database: Verify data
Supplier -> Partner1: Issue credit note
Partner1 -> Customer1: Issue credit note
Customer2 -> Partner2: Request a License
Partner2 -> Customer2: Share a quote
Customer2 -> Partner2: Place a Purchase order
Partner2 -> Supplier: Process Purchase order
Supplier -> Database: Verify data
Supplier -> Partner2: issue License with invoice
Partner2-> Customer2: Issue a license with invoice
@enduml
Click Here and copy and past the above code in the PlantUML shell, you will get the following sequence diagram as output
We can define a DSL for Tic Tac Toe game definition and playing, let's say we want to extend Tic Tac Toe to support user defined game size and number of players:
GAME 5X5
PLAYERS 3
PLAYER_SIGN 1 *
PLAYER_SIGN 2 O
PLAYER_SIGN 2 &
START
PLAYER_CHOICE 1 (2,2)
PLAYER_CHOICE 2 (3,4)
.
.
.
.
EXIT
Note The methods addChoice and hasAWinner are just templates to explain the idea without implementation.
By using The MiniMax (MM) Algorithm, an unbeatable game can be built This algorithm designed for perfect information game (chess, checkers ...etc.) This Algorithm could calculate all the possible moves available for the computer player and use some metric to determine the best possible move. The following research which has been done In 2013, shows that the Minmax algorithm was the right for the job. In my code, I am focusing on two player games where Human-Player = +1, and Computer Player = -1
click here to check the full research article about MM algorithm
How it works?
a) We create a tree of all possible moves for all players to a certain depth.
b) Each position or node of the tree holds a heuristic value which basically it’s the state of the game in single value, so who is wining and who is losing? , so if there is a situation on tree in which player1 wins it would be represented by positive infinity ,and if there is a situation where player2/computer wins it will be represented as negative infinity , and if neither so its either 0 or somewhere in between [-1,+1].
c) Now after the tree has been created, then the algorithm goes to the bottom of the tree and works its way upwards deciding what is the best possible move for each player when it is their turn, which means listing out all the bad moves for that player and then take step upwards and repeat it for the opposite player, so its like removing/filtering all the bad moves for both.
d) From sys import maxsize : since computer cant assign value to infinity , instead we will import maxsize module in python , max size integer which is big number(positive) or small number(negative), and this value will be used to represent infinity or when the player wins or loses.
e) Create Node class , or you can name it anything other than “Node”, and this node will build the tree.
f) In this implementation , Human player is treated as maximizing player and the Computer is minimizing player and evaluating the board stats with minimizing player/computer.
g) In my code, function isWinner() checking if the player got the same letter 3 times in one of row/column/diagonal and returns true if the player won and false if player lost.
With Minmax (MM) algorithm, adding two functions to calculate the minimum and maximum score per the following sample and simple code to descripte the algorithm:
def MinScore(board):
if isWinner(board, 'x'):
return True
elif isWinner(board, 'o'):
return False
elif isboardFull(board):
return 0
else:
bestMoveValue = 100
move = 0
for i in range(1,10):
newBoard = MakeAMove(board, minPlayer, i)
if (newBoard==True):
predictedMoveValue = maxScore(newBoard)
if (predictedMoveValue < bestMoveValue):
bestMoveValue = predictedMoveValue
move = i
return bestMoveValue
def MaxScore(board):
if isWinner(board, 'x'):
return True
elif isWinner(board, 'o'):
return False
elif isboardFull(board):
return 0
else:
bestMoveValue = 100
move = 0
for i in range(1,10):
newBoard = MakeAMove(board, minPlayer, i)
if (newBoard==True):
predictedMoveValue = maxScore(newBoard)
if (predictedMoveValue > bestMoveValue):
bestMoveValue = predictedMoveValue
move = i
return bestMoveValue
The following is sample data structure of Tic Tac Toe game
case class Point(x:Int, y:Int)
case class Choice(p:Player, p:Point)
case class Player(name:String, sign:Char)
case class Board(width:Int, height:Int)
class Game(board:Board, p1: Player, p2:Player, choices: List[Choice]) {
addChoice(c:Choice):Game {
}
hasAWinner():Boolean {
}
}
Note The methods addChoice and hasAWinner are just templates to explain the idea without implementation.